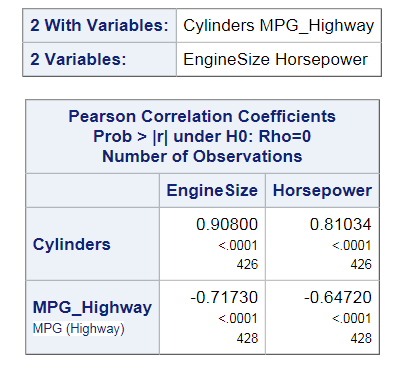
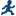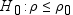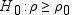Correlation Analysis Task
About the Correlation Analysis Task
Correlation is a statistical
procedure for describing the relationship between numeric variables.
The relationship is described by calculating correlation coefficients
for the variables. The correlations range from –1 to 1. The
Correlation Analysis task provides graphs and statistics for investigating
associations among variables.
Assigning Data to Roles
To run the Correlation
Analysis task, you must assign at least two columns to the Analysis
variables role, or you must assign at least one column
to the Analysis variables role and one column
to the Correlate with role.
|
Roles
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Roles
|
|
|
Analysis
variables
|
lists the variables
for which to compute correlation coefficients.
|
|
Correlate
with
|
lists the variables
with which the correlations of the analysis variables are to be computed.
|
|
Partial
variables
|
removes the correlation
of these variables from the analysis and correlates with variables
before calculating the correlation.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Frequency
count
|
lists a numeric variable
whose value represents the frequency of the observation. If you assign
a variable to this role, the task assumes that each observation represents n observations,
where n is the value of the frequency variable.
If n is not an integer, SAS truncates it. If n is
less than 1 or is missing, the observation is excluded from the analysis.
The sum of the frequency variable represents the total number of observations.
|
|
Weight
|
lists the weights to
use in the calculation of Pearson weighted product-moment correlation.
|
|
Group analysis
by
|
enables you to obtain
separate analyses of observations in groups that are defined by the
BY variables.
|
Setting Options
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Methods
|
|
|
Missing
values
|
specifies how to treat
observations with missing values. If you select the Use
nonmissing values for all selected variables option,
all observations with missing values are excluded from the analysis.
If you select the Use nonmissing values for pairs of variables option,
the correlation statistics are computed using the nonmissing pairs
of variables.
|
|
Statistics
|
|
|
By default, the results
contain a table with the correlations and p-values.
You can also include these statistics:
Correlations
Selecting this option
includes the correlations in the results. You can also specify probabilities
that are associated with each correlation coefficient and whether
to order the correlations from highest to lowest in absolute value.
Covariances
Selecting this option
includes the variance and covariance matrix in the results. Also,
the Pearson correlations are displayed. If you assign a column to
the Partial variables role, the task computes
a partial covariance matrix.
Sum of squares and cross-products
Selecting this option
displays a table of the sums of squares and cross products in the
results. The Pearson correlations are also included in the results.
If you assign a column to the Partial variables role,
the unpartial sums of squares and cross-products matrix is displayed.
Corrected
sum of squares and cross-products
Selecting this option
displays a table of the corrected sums of squares and cross products.
The Pearson correlations are also included in the results. If you
assign a column to the Partial variables role,
the task computes both an unpartial and a partial corrected sum of
squares and cross-products matrix.
Descriptive statistics
Selecting this option
includes the simple descriptive statistics for each variable. Even
if you do not select this option and you choose to create an output
data set, the data set contains the descriptive statistics for the
variables.
|
|
|
Fisher’s z transformation
For a Pearson correlation,
you can use the Fisher transformation options to request confidence
limits and p-values under a specified alternative
(null) hypothesis,
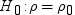 , for correlation coefficients that use Fisher’s z transformation.
If you select the Fisher’s z transformation check
box, you must specify a value in the Null hypothesis box. , for correlation coefficients that use Fisher’s z transformation.
If you select the Fisher’s z transformation check
box, you must specify a value in the Null hypothesis box.
You can choose from
these types of confidence limits:
By default, the level
of the confidence limits for the correlation is 95%.
|
|
|
Nonparametric Correlations
|
|
|
Spearman’s
rank-order correlation
|
calculates Spearman
rank-order correlation. This is a nonparametric measure of association
that is based on the rank of the data values. The correlations range
from –1 to 1.
|
|
Kendall’s
tau-b
|
calculates Kendall tau-b.
This is a nonparametric measure of association that is based on the
number of concordances and discordances in paired observations. Concordance
occurs when paired observations vary together, and discordance occurs
when paired observations vary differently. Kendall's tau-b ranges
from –1 to 1.
|
|
Hoeffding’s
measure of dependence
|
calculates Hoeffding's
measure of dependence, D. This is a nonparametric measure of association
that detects more general departures from independence. This D statistic
is 30 times larger than the usual definition and scales the range
between –0.5 and 1 so that only large positive values indicate
dependence.
|
|
Plots
|
|
|
You can include either
of these plots in your results:
You can also specify
the number of variables to plot and the maximum number of points to
plot.
|
|
Setting the Output Options
You can specify whether
to create an output data set that contains the Pearson correlation
statistics. This data set also includes means, standard deviations,
and the number of observations.
You can also choose
to include these statistics in the output data set:
-
Correlations – By default, the output data set contains the correlation coefficients with the corresponding _TYPE_ variable value of ‘CORR’.
-
Covariances – When you select this option, the output data set contains the covariance matrix with the corresponding _TYPE_ variable value of ‘COV’.
-
Sum of squares and cross-products – If you assign a column to the Partial variables role, the output data set does not contain a sum of squares and cross-products matrix.
-
Corrected sum of squares and cross-products — If you assign a column to the Partial variables role, the output data set contains a partial corrected sum of squares and cross-products matrix.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.