Step 5: Add the Apache Velocity Code
About the Apache Velocity Code
The
CodeTemplate element
contains the Apache Velocity code, which is used to generate the SAS
code for the task. Apache Velocity code is a template engine based
on Java. In the code, keywords that are identified with a dollar sign
($) are Velocity variables. Keywords with a number sign (#) are directives.
For more information about this code, see Apache Velocity
User’s Guide.
Until this point, you
have focused on creating the user interface for the task. In your
example task, the following code is in the
CodeTemplate element
by default:<CodeTemplate> <![CDATA[ proc print=sashelp.cars; run; ]]> </CodeTemplate>
If you ran the task
(in other words, selected a variable to convert and clicked  ), you might have noticed that the contents of the
Sashelp.Cars data set appeared on the RESULTS tab.
The task ran successfully because the content in the
), you might have noticed that the contents of the
Sashelp.Cars data set appeared on the RESULTS tab.
The task ran successfully because the content in the
CodeTemplate element
is valid SAS code.
In this step, you replace
the default Velocity code with the Velocity code for the Convert Character
to Numeric task.
Add the Velocity Code for the Convert Character to Numeric Task
In the task definition,
find the
CodeTemplate element and remove
the highlighted code:<CodeTemplate>
<![CDATA[
proc print=sashelp.cars;
run;
]]>
</CodeTemplate>Now, add the highlighted
code to the
CodeTemplate element:
<CodeTemplate>
<![CDATA[
#set($charvar=$invarname.get(0))
#set($informat = "${informatType}${informatWidth}.")
data $outputDSName;
#if ($samename=='1')
#set($newCol = "${charvar}_old")
set $inlibname(rename=$charvar=$newCol);
$charvar = input($newCol,$informat);
drop $newCol;
#else
#set($newCol = "${charvar}_new")
set $inlibname;
$newCol = input($charvar,$informat);
#end
run;
]]>
</CodeTemplate>
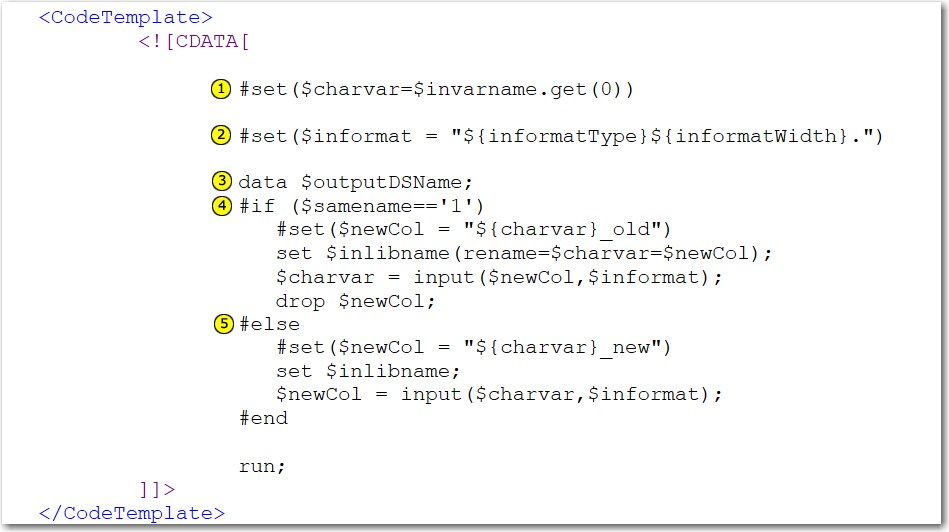
| 1 | $invarname is the Velocity variable for the role control. In this code, $charvar is set to the value of the invarname array. Because only one role is allowed, there can be only one item in the array, and you always fetch the role from the first location in the array. |
| 2 | $informatType
is the Velocity variable that holds the return value for the option
that you selected in the Category of informat option.
$informatWidth is the contents of the Informat width option.
In this line of code,
you set a new Velocity variable
$informat to
be the concatenation of the $informatType variable,
the $informatWidth variable, and a ‘.’
character. The period is required because all SAS informats end with
a period.
|
| 3 | This
line is the beginning of the SAS code and is the first line in the
DATA step. In this code, the $outputDSName Velocity variable represents
the name of the output data set. The name of the output data set is
determined by the value of the outputDSName option,
which you defined in this code in the metadata:<Option name="outputDSName" inputType="outputdata" defaultValue="Test"
required="true">Name of output data set:</Option>In the user interface,
this text box is labeled Name of output data set.
|
| 4 | If
you want the name of the variable that you are converting to remain
the same, you select the Same name? check
box in the user interface. Selecting this check box sets the $samename
Velocity variable to 1. When $samename == 1,
these steps occur:
|
| 5 | If
you want to create a new variable, do not select the Same
name? check box in the user interface. When the $samename
Velocity variable is not equal to 1, these steps occur:
|
Click  to save your CTM code.
to save your CTM code.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.