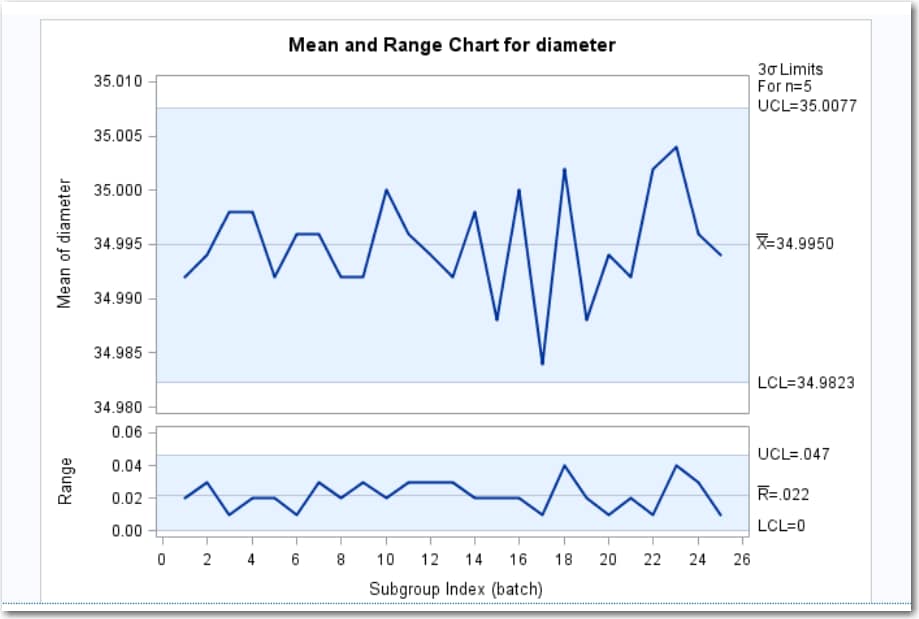
Example: Determine the Mean and Range for the Diameters of Wafers
To create this example:
-
Copy and paste this code into the Program tab.
data wafers; input batch @; do i=1 to 5; input diameter @; output; end; drop i; datalines; 1 35.00 34.99 34.99 34.98 35.00 2 35.01 34.99 34.99 34.98 35.00 3 34.99 35.00 35.00 35.00 35.00 4 35.01 35.00 34.99 34.99 35.00 5 35.00 34.99 34.98 34.99 35.00 6 34.99 34.99 35.00 35.00 35.00 7 35.01 34.98 35.00 35.00 34.99 8 35.00 35.00 34.99 34.98 34.99 9 34.99 34.98 34.98 35.01 35.00 10 34.99 35.00 35.01 34.99 35.01 11 35.01 35.00 35.00 34.98 34.99 12 34.99 34.99 35.00 34.98 35.01 13 35.01 34.99 34.98 34.99 34.99 14 35.00 35.00 34.99 35.01 34.99 15 34.98 34.99 34.99 34.98 35.00 16 34.99 35.00 35.00 35.01 35.00 17 34.98 34.98 34.99 34.99 34.98 18 35.01 35.02 35.00 34.98 35.00 19 34.99 34.98 35.00 34.99 34.98 20 34.99 35.00 35.00 34.99 34.99 21 35.00 34.99 34.99 34.98 35.00 22 35.00 35.00 35.01 35.00 35.00 23 35.02 35.00 34.98 35.02 35.00 24 35.00 35.00 34.99 35.01 34.98 25 34.99 34.99 34.99 35.00 35.00 run;Click to create the Work.Wafers data set.
to create the Work.Wafers data set.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.