Introduction to Regression Procedures
Testing Linear Hypotheses
Testing of linear hypotheses based on estimable functions is discussed in the section Test of Hypotheses in Chapter 3: Introduction to Statistical Modeling with SAS/STAT Software, and the construction of special sets of estimable functions corresponding to Type I–Type IV hypotheses is discussed in Chapter 15: The Four Types of Estimable Functions. In linear regression models, testing of general linear hypotheses follows along the same lines. Test statistics are usually
formed based on sums of squares that are associated with the hypothesis in question. Furthermore, when 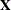 is of full rank—as is the case in many regression models—the consistency of the linear hypothesis is guaranteed.
is of full rank—as is the case in many regression models—the consistency of the linear hypothesis is guaranteed.
Recall from Chapter 3: Introduction to Statistical Modeling with SAS/STAT Software, that the general form of a linear hypothesis for the parameters is 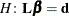 , where
, where  is
is  ,
, 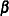 is
is  , and
, and 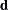 is
is  . To test this hypothesis, you take the linear function with respect to the parameter estimates:
. To test this hypothesis, you take the linear function with respect to the parameter estimates: 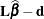 . This linear function in
. This linear function in 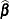 has variance
has variance
![\[ \mr{Var}\left[\bL \widehat{\bbeta }\right] = \bL \mr{Var}[\widehat{\bbeta }]\bL ’ = \sigma ^2\bL \left(\bX ’\bW \bX \right)^{-} \bL ’ \]](images/statug_introreg0106.png)
The sum of squares due to the hypothesis is a simple quadratic form:
![\[ \mr{SS}(H) = \mr{SS}(\bL \widehat{\bbeta } - \mb{d}) = \left(\bL \widehat{\bbeta } - \mb{d}\right)^{\prime } \left(\bL \left(\mb{X}’\bW \mb{X}\right)^{-} \bL ’\right)^{-1} \left(\bL \widehat{\bbeta } - \mb{d}\right) \]](images/statug_introreg0107.png)
If this hypothesis is testable, then  can be used in the numerator of an F statistic:
can be used in the numerator of an F statistic:
![\[ F = \frac{\mbox{SS}(H) / q}{s^2} = \frac{\mbox{SS}(\mb{Lb} - \mb{d}) / q}{s^2} \]](images/statug_introreg0109.png)
If 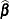 is normally distributed, which follows as a consequence of normally distributed model errors, then this statistic follows
an F distribution with q numerator degrees of freedom and
is normally distributed, which follows as a consequence of normally distributed model errors, then this statistic follows
an F distribution with q numerator degrees of freedom and  denominator degrees of freedom. Note that it was assumed in this derivation that
denominator degrees of freedom. Note that it was assumed in this derivation that  is of full row rank q.
is of full row rank q.