The HPLMIXED Procedure
RANDOM Statement
-
RANDOM random-effects </ options>;
The RANDOM statement defines the random effects that constitute the 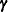 vector in the mixed model. You can use this statement to specify traditional variance component models and to specify random
coefficients. The random effects can be classification or continuous, and multiple RANDOM statements are possible.
vector in the mixed model. You can use this statement to specify traditional variance component models and to specify random
coefficients. The random effects can be classification or continuous, and multiple RANDOM statements are possible.
Using notation from the section Linear Mixed Models Theory, the purpose of the RANDOM statement is to define the 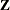 matrix of the mixed model, the random effects in the
matrix of the mixed model, the random effects in the 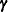 vector, and the structure of
vector, and the structure of 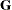 . The
. The 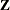 matrix is constructed exactly as the
matrix is constructed exactly as the 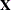 matrix for the fixed effects is constructed, and the
matrix for the fixed effects is constructed, and the 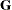 matrix is constructed to correspond with the effects that constitute
matrix is constructed to correspond with the effects that constitute 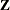 . The structure of
. The structure of 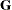 is defined by using the TYPE=
option.
is defined by using the TYPE=
option.
You can specify INTERCEPT (or INT) as a random effect to indicate the intercept. PROC HPLMIXED does not include the intercept in the RANDOM statement by default as it does in the MODEL statement.
Table 53.5 summarizes important options in the RANDOM statement. All options are subsequently discussed in alphabetical order.
Table 53.5: Summary of Important RANDOM Statement Options
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Construction of Covariance Structure |
|
|
Identifies the subjects in the model |
|
|
Specifies the covariance structure |
|
|
Statistical Output |
|
|
Determines the confidence level ( |
|
|
Requests confidence limits for predictors of random effects |
|
|
Displays solutions |
|
You can specify the following options in the RANDOM statement after a slash (/).
- ALPHA=number
-
sets the confidence level to be
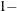 number for each confidence interval of the random-effects estimates. The value of number must be between 0 and 1; the default is 0.05.
number for each confidence interval of the random-effects estimates. The value of number must be between 0 and 1; the default is 0.05.
- CL
-
requests that t-type confidence limits be constructed for each of the random-effect estimates. The confidence level is 0.95 by default; this can be changed with the ALPHA= option.
-
SOLUTION
S -
requests that the solution for the random-effects parameters be produced. Using notation from the section Linear Mixed Models Theory, these estimates are the empirical best linear unbiased predictors (EBLUPs),
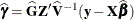 . They can be useful for comparing the random effects from different experimental units and can also be treated as residuals
in performing diagnostics for your mixed model.
. They can be useful for comparing the random effects from different experimental units and can also be treated as residuals
in performing diagnostics for your mixed model.
The numbers displayed in the SE Pred column of the "Solution for Random Effects" table are not the standard errors of the
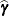 displayed in the Estimate column; rather, they are the standard errors of predictions
displayed in the Estimate column; rather, they are the standard errors of predictions 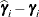 , where
, where 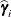 is the ith EBLUP and
is the ith EBLUP and 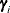 is the ith random-effect parameter.
is the ith random-effect parameter.
-
SUBJECT=effect
SUB=effect -
identifies the subjects in your mixed model. Complete independence is assumed across subjects; thus, for the RANDOM statement, the SUBJECT= option produces a block-diagonal structure in
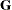 with identical blocks. In fact, specifying a subject effect is equivalent to nesting all other effects in the RANDOM statement
within the subject effect.
with identical blocks. In fact, specifying a subject effect is equivalent to nesting all other effects in the RANDOM statement
within the subject effect.
When you specify the SUBJECT= option and a classification random effect, computations are usually much quicker if the levels of the random effect are duplicated within each level of the SUBJECT= effect.
- TYPE=covariance-structure
-
specifies the covariance structure of
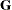 . Valid values for covariance-structure and their descriptions are listed in Table 53.6. Although a variety of structures are available, most applications call for either TYPE=VC
or TYPE=UN
. The TYPE=VC
(variance components) option is the default structure, and it models a different variance component for each random effect.
. Valid values for covariance-structure and their descriptions are listed in Table 53.6. Although a variety of structures are available, most applications call for either TYPE=VC
or TYPE=UN
. The TYPE=VC
(variance components) option is the default structure, and it models a different variance component for each random effect.
The TYPE=UN (unstructured) option is useful for correlated random coefficient models. For example, the following statement specifies a random intercept-slope model that has different variances for the intercept and slope and a covariance between them:
random intercept age / type=un subject=person;
You can also use TYPE=FA0(2) here to request a
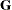 estimate that is constrained to be nonnegative definite.
estimate that is constrained to be nonnegative definite.
If you are constructing your own columns of
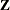 with continuous variables, you can use the TYPE=TOEP
(1) structure to group them together to have a common variance component. If you want to have different covariance structures
in different parts of
with continuous variables, you can use the TYPE=TOEP
(1) structure to group them together to have a common variance component. If you want to have different covariance structures
in different parts of 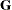 , you must use multiple RANDOM statements with different TYPE= options.
, you must use multiple RANDOM statements with different TYPE= options.
Table 53.6: Covariance Structures
Structure
Description
Parms
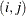 element
element
ANTE(1)
Antedependence
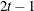
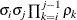
AR(1)
Autoregressive(1)
2
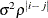
ARH(1)
Heterogeneous AR(1)
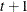
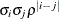
ARMA(1,1)
Autoregressive moving average(1,1)
3
![$\sigma ^2[\gamma \rho ^{|i-j|-1} 1(i\neq j) + 1(i=j)]$](images/statug_hplmixed0073.png)
CS
Compound symmetry
2
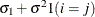
CSH
Heterogeneous compound symmetry
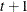
![$\sigma _{i}\sigma _{j}[\rho 1(i \neq j)+ 1(i=j)]$](images/statug_hplmixed0075.png)
FA(q)
Factor analytic
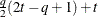
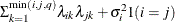
FA0(q)
No diagonal FA
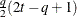
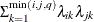
FA1(q)
Equal diagonal FA
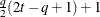
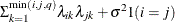
HF
Huynh-Feldt
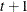
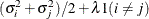
SIMPLE
An alias for VC
q
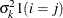 for the kth effect
for the kth effect
TOEP
Toeplitz
t
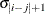
TOEP(q)
Banded Toeplitz
q
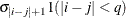
TOEPH
Heterogeneous TOEP
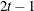
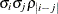
TOEPH(q)
Banded heterogeneous TOEP
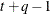
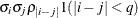
UN
Unstructured
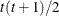
UN(q)
Banded
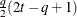
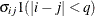
UNR
Unstructured correlation
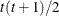
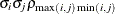
UNR(q)
Banded correlations
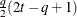
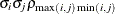
VC
Variance components
q
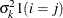 for the kth effect
for the kth effect
In Table 53.6, the Parms column represents the number of covariance parameters in the structure, t is the overall dimension of the covariance matrix, and
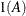 equals 1 when A is true and 0 otherwise. For example, 1
equals 1 when A is true and 0 otherwise. For example, 1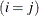 equals 1 when
equals 1 when 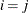 and 0 otherwise, and 1
and 0 otherwise, and 1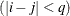 equals 1 when
equals 1 when 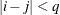 and 0 otherwise. For the TYPE=TOEPH
structures,
and 0 otherwise. For the TYPE=TOEPH
structures, 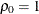 ; for the TYPE=UNR
structures,
; for the TYPE=UNR
structures, 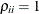 for all i.
for all i.
Table 53.7 lists some examples of the structures in Table 53.6.
Table 53.7: Covariance Structure Examples
Description
Structure
Example
Variance
componentsVC (default)
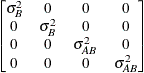
Compound
symmetryCS
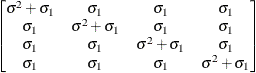
Unstructured
UN
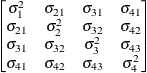
Banded main
diagonalUN(1)
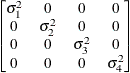
First-order
autoregressiveAR(1)
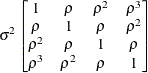
Toeplitz
TOEP
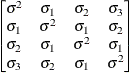
Toeplitz with
two bandsTOEP(2)
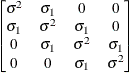
Heterogeneous
autoregressive(1)ARH(1)
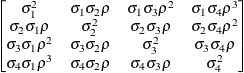
First-order
autoregressive
moving averageARMA(1,1)
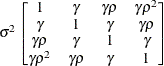
Heterogeneous
compound symmetryCSH
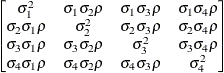
First-order
factor
analyticFA(1)
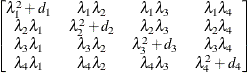
Huynh-Feldt
HF
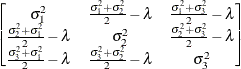
First-order
antedependenceANTE(1)
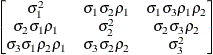
Heterogeneous
ToeplitzTOEPH
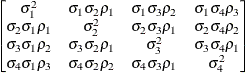
Unstructured
correlationsUNR
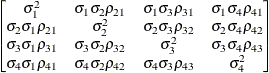
The following list provides some further information about these covariance structures:
- TYPE=ANTE(1)
-
specifies the first-order antedependence structure (Kenward 1987; Patel 1991; Macchiavelli and Arnold 1994). In Table 53.6,
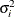 is the i variance parameter, and
is the i variance parameter, and 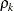 is the k autocorrelation parameter that satisfies
is the k autocorrelation parameter that satisfies 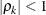 .
.
- TYPE=AR(1)
-
specifies a first-order autoregressive structure. PROC HPLMIXED imposes the constraint
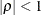 for stationarity.
for stationarity.
- TYPE=ARH(1)
-
specifies a heterogeneous first-order autoregressive structure. As with TYPE=AR(1), PROC HPLMIXED imposes the constraint
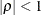 for stationarity.
for stationarity.
- TYPE=ARMA(1,1)
-
specifies the first-order autoregressive moving average structure. In Table 53.6,
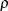 is the autoregressive parameter,
is the autoregressive parameter, 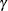 models a moving average component, and
models a moving average component, and 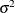 is the residual variance. In the notation of Fuller (1976, p. 68),
is the residual variance. In the notation of Fuller (1976, p. 68), 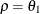 and
and
![\[ \gamma = \frac{(1 + b_1\theta _1)(\theta _1 + b_1)}{1 + b^2_1 + 2 b_1 \theta _1} \]](images/statug_hplmixed0123.png)
The example in Table 53.7 and
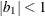 imply that
imply that
![\[ b_1 = \frac{\beta - \sqrt {\beta ^2 - 4\alpha ^2}}{2\alpha } \]](images/statug_hplmixed0125.png)
where
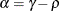 and
and 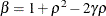 . PROC HPLMIXED imposes the constraints
. PROC HPLMIXED imposes the constraints 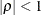 and
and 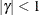 for stationarity, although the resulting covariance matrix is not positive definite for some values of
for stationarity, although the resulting covariance matrix is not positive definite for some values of 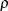 and
and 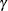 in this region. When the estimated value of
in this region. When the estimated value of 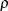 becomes negative, the computed covariance is multiplied by
becomes negative, the computed covariance is multiplied by 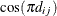 to account for the negativity.
to account for the negativity.
- TYPE=CS
-
specifies the compound-symmetry structure, which has constant variance and constant covariance.
- TYPE=CSH
-
specifies the heterogeneous compound-symmetry structure. This structure has a different variance parameter for each diagonal element, and it uses the square roots of these parameters in the off-diagonal entries. In Table 53.6,
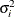 is the i variance parameter, and
is the i variance parameter, and 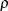 is the correlation parameter that satisfies
is the correlation parameter that satisfies 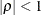 .
.
- TYPE=FA(q)
-
specifies the factor-analytic structure with q factors (Jennrich and Schluchter 1986). This structure is of the form
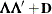 , where
, where 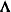 is a
is a 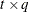 rectangular matrix and
rectangular matrix and 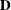 is a
is a 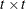 diagonal matrix with t different parameters. When
diagonal matrix with t different parameters. When 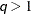 , the elements of
, the elements of 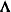 in its upper right corner (that is, the elements in the i row and j column for
in its upper right corner (that is, the elements in the i row and j column for 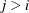 ) are set to zero to fix the rotation of the structure.
) are set to zero to fix the rotation of the structure.
- TYPE=FA0(q)
-
is similar to the FA(q) structure except that no diagonal matrix
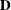 is included. When
is included. When 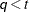 (that is, when the number of factors is less than the dimension of the matrix), this structure is nonnegative definite but
not of full rank. In this situation, you can use this structure for approximating an unstructured
(that is, when the number of factors is less than the dimension of the matrix), this structure is nonnegative definite but
not of full rank. In this situation, you can use this structure for approximating an unstructured 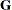 matrix in the RANDOM
statement. When
matrix in the RANDOM
statement. When 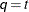 , you can use this structure to constrain
, you can use this structure to constrain 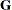 to be nonnegative definite in the RANDOM
statement.
to be nonnegative definite in the RANDOM
statement.
- TYPE=FA1(q)
-
is similar to the TYPE=FA(q) structure except that all of the elements in
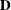 are constrained to be equal. This offers a useful and more parsimonious alternative to the full factor-analytic structure.
are constrained to be equal. This offers a useful and more parsimonious alternative to the full factor-analytic structure.
- TYPE=HF
-
specifies the Huynh-Feldt covariance structure (Huynh and Feldt 1970). This structure is similar to the TYPE=CSH structure in that it has the same number of parameters and heterogeneity along the main diagonal. However, it constructs the off-diagonal elements by taking arithmetic means rather than geometric means.
You can perform a likelihood ratio test of the Huynh-Feldt conditions by running PROC HPLMIXED twice, once with TYPE=HF and once with TYPE=UN , and then subtracting their respective values of
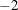 times the maximized likelihood.
times the maximized likelihood.
If PROC HPLMIXED does not converge under your Huynh-Feldt model, you can specify your own starting values with the PARMS statement. The default MIVQUE(0) starting values can sometimes be poor for this structure. A good choice for starting values is often the parameter estimates that correspond to an initial fit that uses TYPE=CS .
- TYPE=SIMPLE
-
is an alias for TYPE=VC .
- TYPE=TOEP<(q)>
-
specifies a banded Toeplitz structure. This can be viewed as a moving average structure with order equal to
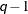 . The TYPE=TOEP option is a full Toeplitz matrix, which can be viewed as an autoregressive structure with order equal to the
dimension of the matrix. The specification TYPE=TOEP(1) is the same as
. The TYPE=TOEP option is a full Toeplitz matrix, which can be viewed as an autoregressive structure with order equal to the
dimension of the matrix. The specification TYPE=TOEP(1) is the same as 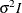 , where I is an identity matrix, and it can be useful for specifying the same variance component for several effects.
, where I is an identity matrix, and it can be useful for specifying the same variance component for several effects.
- TYPE=TOEPH<(q)>
-
specifies a heterogeneous banded Toeplitz structure. In Table 53.6,
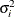 is the i variance parameter and
is the i variance parameter and 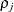 is the j correlation parameter that satisfies
is the j correlation parameter that satisfies 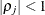 . If you specify the order parameter q, then PROC HPLMIXED estimates only the first q bands of the matrix, setting all higher bands equal to 0. The option TOEPH(1) is equivalent to both the TYPE=UN
(1) and TYPE=UNR
(1) options.
. If you specify the order parameter q, then PROC HPLMIXED estimates only the first q bands of the matrix, setting all higher bands equal to 0. The option TOEPH(1) is equivalent to both the TYPE=UN
(1) and TYPE=UNR
(1) options.
- TYPE=UN<(q)>
-
specifies a completely general (unstructured) covariance matrix that is parameterized directly in terms of variances and covariances. The variances are constrained to be nonnegative, and the covariances are unconstrained. This structure is not constrained to be nonnegative definite in order to avoid nonlinear constraints. However, you can use the TYPE=FA0 structure if you want this constraint to be imposed by a Cholesky factorization. If you specify the order parameter q, then PROC HPLMIXED estimates only the first q bands of the matrix, setting all higher bands equal to 0.
- TYPE=UNR<(q)>
-
specifies a completely general (unstructured) covariance matrix that is parameterized in terms of variances and correlations. This structure fits the same model as the TYPE=UN (q) option but with a different parameterization. The i variance parameter is
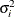 . The parameter
. The parameter 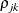 is the correlation between the j and k measurements; it satisfies
is the correlation between the j and k measurements; it satisfies 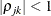 . If you specify the order parameter r, then PROC HPLMIXED estimates only the first q bands of the matrix, setting all higher bands equal to zero.
. If you specify the order parameter r, then PROC HPLMIXED estimates only the first q bands of the matrix, setting all higher bands equal to zero.
- TYPE=VC
-
specifies standard variance components. This is the default structure for both the RANDOM and REPEATED statements. In the RANDOM statement, a distinct variance component is assigned to each effect.
Jennrich and Schluchter (1986) provide general information about the use of covariance structures, and Wolfinger (1996) presents details about many of the heterogeneous structures.