The GLM Procedure
-
Overview

-
Getting Started

-
Syntax

-
Details
 Statistical Assumptions for Using PROC GLMSpecification of EffectsUsing PROC GLM InteractivelyParameterization of PROC GLM ModelsHypothesis Testing in PROC GLMEffect Size Measures for F Tests in GLMAbsorptionSpecification of ESTIMATE ExpressionsComparing GroupsMultivariate Analysis of VarianceRepeated Measures Analysis of VarianceRandom-Effects AnalysisMissing ValuesComputational ResourcesComputational MethodOutput Data SetsDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Statistical Assumptions for Using PROC GLMSpecification of EffectsUsing PROC GLM InteractivelyParameterization of PROC GLM ModelsHypothesis Testing in PROC GLMEffect Size Measures for F Tests in GLMAbsorptionSpecification of ESTIMATE ExpressionsComparing GroupsMultivariate Analysis of VarianceRepeated Measures Analysis of VarianceRandom-Effects AnalysisMissing ValuesComputational ResourcesComputational MethodOutput Data SetsDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples
 Randomized Complete Blocks with Means Comparisons and ContrastsRegression with Mileage DataUnbalanced ANOVA for Two-Way Design with InteractionAnalysis of CovarianceThree-Way Analysis of Variance with ContrastsMultivariate Analysis of VarianceRepeated Measures Analysis of VarianceMixed Model Analysis of Variance with the RANDOM StatementAnalyzing a Doubly Multivariate Repeated Measures DesignTesting for Equal Group VariancesAnalysis of a Screening Design
Randomized Complete Blocks with Means Comparisons and ContrastsRegression with Mileage DataUnbalanced ANOVA for Two-Way Design with InteractionAnalysis of CovarianceThree-Way Analysis of Variance with ContrastsMultivariate Analysis of VarianceRepeated Measures Analysis of VarianceMixed Model Analysis of Variance with the RANDOM StatementAnalyzing a Doubly Multivariate Repeated Measures DesignTesting for Equal Group VariancesAnalysis of a Screening Design - References
See Chapter 15: The Four Types of Estimable Functions, for a complete discussion of the four standard types of hypothesis tests.
To illustrate the four types of tests and the principles upon which they are based, consider a two-way design with interaction based on the following data:
|
B |
||||||||
|
1 |
2 |
|||||||
|
1 |
23.5 |
28.7 |
||||||
|
23.7 |
||||||||
|
A |
2 |
8.9 |
5.6 |
|||||
|
8.9 |
||||||||
|
3 |
10.3 |
13.6 |
||||||
|
12.5 |
14.6 |
|||||||
Invoke PROC GLM and specify all the estimable functions options to examine what the GLM procedure can test. The following statements produce the summary ANOVA table displayed in Figure 45.10.
data example; input a b y @@; datalines; 1 1 23.5 1 1 23.7 1 2 28.7 2 1 8.9 2 2 5.6 2 2 8.9 3 1 10.3 3 1 12.5 3 2 13.6 3 2 14.6 ;
proc glm; class a b; model y=a b a*b / e e1 e2 e3 e4; run;
The following sections show the general form of estimable functions and discuss the four standard tests, their properties, and abbreviated output for the two-way crossed example.
Figure 45.11 is the general form of estimable functions for the example. In order to be testable, a hypothesis must be able to fit within the framework displayed here.
If a hypothesis is estimable, the ![]() s in the preceding scheme can be set to values that match the hypothesis. All the standard tests in PROC GLM can be shown
in the preceding format, with some of the
s in the preceding scheme can be set to values that match the hypothesis. All the standard tests in PROC GLM can be shown
in the preceding format, with some of the ![]() s zeroed and some set to functions of other
s zeroed and some set to functions of other ![]() s.
s.
The following sections show how many of the hypotheses can be tested by comparing the model sum-of-squares regression from one model to a submodel. The notation used is
where SS(A effects) denotes the regression model sum of squares for the model consisting of A effects. This notation is equivalent to the reduction notation defined by Searle (1971) and summarized in Chapter 15: The Four Types of Estimable Functions.
Type I sums of squares (SS), also called sequential sums of squares, are the incremental improvement in error sums of squares as each effect is added to the model. They can be computed by fitting the model in steps and recording the difference in error sum of squares at each step.
|
Source |
Type I SS |
|
|---|---|---|
|
A |
SS |
|
|
B |
SS |
|
|
|
SS |
Type I sums of squares are displayed by default because they are easy to obtain and can be used in various hand calculations to produce sum of squares values for a series of different models. Nelder (1994) and others have argued that Type I and II sums are essentially the only appropriate ones for testing ANOVA effects; however, see also the discussion of Nelder’s article, especially Rodriguez, Tobias, and Wolfinger (1995) and Searle (1995).
The Type I hypotheses have these properties:
-
Type I sum of squares for all effects add up to the model sum of squares. None of the other sum of squares types have this property, except in special cases.
-
Type I hypotheses can be derived from rows of the Forward-Dolittle transformation of
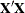 (a transformation that reduces
(a transformation that reduces 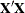 to an upper triangular matrix by row operations).
to an upper triangular matrix by row operations). -
Type I sum of squares are statistically independent of each other under the usual assumption that the true residual errors are independent and identically normally distributed.
-
Type I hypotheses depend on the order in which effects are specified in the MODEL statement.
-
Type I hypotheses are uncontaminated by parameters corresponding to effects that precede the effect being tested; however, the hypotheses usually involve parameters for effects following the tested effect in the model. For example, in the model
Y=A B;the Type I hypothesis for
Bdoes not involveAparameters, but the Type I hypothesis forAdoes involveBparameters. -
Type I hypotheses are functions of the cell counts for unbalanced data; the hypotheses are not usually the same hypotheses that are tested if the data are balanced.
-
Type I sums of squares are useful for polynomial models where you want to know the contribution of a term as though it had been made orthogonal to preceding effects. Thus, in polynomial models, Type I sums of squares correspond to tests of the orthogonal polynomial effects.
The Type I estimable functions and associated tests for the example are shown in Figure 45.12.
Figure 45.12: Type I Estimable Functions and Tests
| Type I Estimable Functions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Coefficients | ||
| a | b | a*b | |
| Intercept | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| a 1 | L2 | 0 | 0 |
| a 2 | L3 | 0 | 0 |
| a 3 | -L2-L3 | 0 | 0 |
| b 1 | 0.1667*L2-0.1667*L3 | L5 | 0 |
| b 2 | -0.1667*L2+0.1667*L3 | -L5 | 0 |
| a*b 1 1 | 0.6667*L2 | 0.2857*L5 | L7 |
| a*b 1 2 | 0.3333*L2 | -0.2857*L5 | -L7 |
| a*b 2 1 | 0.3333*L3 | 0.2857*L5 | L9 |
| a*b 2 2 | 0.6667*L3 | -0.2857*L5 | -L9 |
| a*b 3 1 | -0.5*L2-0.5*L3 | 0.4286*L5 | -L7-L9 |
| a*b 3 2 | -0.5*L2-0.5*L3 | -0.4286*L5 | L7+L9 |
The Type II tests can also be calculated by comparing the error sums of squares (SS) for subset models. The Type II SS are
the reduction in error SS due to adding the term after all other terms have been added to the model except terms that contain
the effect being tested. An effect is contained in another effect if it can be derived by deleting variables from the latter
effect. For example, A and B are both contained in A*B. For this model, the Type II SS are given by the reduced sums of squares as shown in the following table.
|
Source |
Type II SS |
|
|---|---|---|
|
A |
SS |
|
|
B |
SS |
|
|
|
SS |
Type II SS have these properties:
-
Type II SS do not necessarily sum to the model SS.
-
The hypothesis for an effect does not involve parameters of other effects except for containing effects (which it must involve to be estimable).
-
Type II SS are invariant to the ordering of effects in the model.
-
For unbalanced designs, Type II hypotheses for effects that are contained in other effects are not usually the same hypotheses that are tested if the data are balanced. The hypotheses are generally functions of the cell counts.
The Type II estimable functions and associated tests for the example are shown in Figure 45.13.
Figure 45.13: Type II Estimable Functions and Tests
| Type II Estimable Functions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Coefficients | ||
| a | b | a*b | |
| Intercept | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| a 1 | L2 | 0 | 0 |
| a 2 | L3 | 0 | 0 |
| a 3 | -L2-L3 | 0 | 0 |
| b 1 | 0 | L5 | 0 |
| b 2 | 0 | -L5 | 0 |
| a*b 1 1 | 0.619*L2+0.0476*L3 | 0.2857*L5 | L7 |
| a*b 1 2 | 0.381*L2-0.0476*L3 | -0.2857*L5 | -L7 |
| a*b 2 1 | -0.0476*L2+0.381*L3 | 0.2857*L5 | L9 |
| a*b 2 2 | 0.0476*L2+0.619*L3 | -0.2857*L5 | -L9 |
| a*b 3 1 | -0.5714*L2-0.4286*L3 | 0.4286*L5 | -L7-L9 |
| a*b 3 2 | -0.4286*L2-0.5714*L3 | -0.4286*L5 | L7+L9 |
Type III and Type IV sums of squares (SS), sometimes referred to as partial sums of squares, are considered by many to be the most desirable; see Searle (1987, Section 4.6). Using PROC GLM’s singular parameterization, these SS cannot, in general, be computed by comparing model SS
from different models. However, they can sometimes be computed by reduction for methods that reparameterize to full rank,
when such a reparameterization effectively imposes Type III linear constraints on the parameters. In PROC GLM, they are computed
by constructing a hypothesis matrix ![]() and then computing the SS associated with the hypothesis
and then computing the SS associated with the hypothesis ![]() . As long as there are no missing cells in the design, Type III and Type IV SS are the same.
. As long as there are no missing cells in the design, Type III and Type IV SS are the same.
These are properties of Type III and Type IV SS:
-
The hypothesis for an effect does not involve parameters of other effects except for containing effects (which it must involve to be estimable).
-
The hypotheses to be tested are invariant to the ordering of effects in the model.
-
The hypotheses are the same hypotheses that are tested if there are no missing cells. They are not functions of cell counts.
-
The SS do not generally add up to the model SS and, in some cases, can exceed the model SS.
The SS are constructed from the general form of estimable functions. Type III and Type IV tests are different only if the design has missing cells. In this case, the Type III tests have an orthogonality property, while the Type IV tests have a balancing property. These properties are discussed in Chapter 15: The Four Types of Estimable Functions. For this example, since the data contain observations for all pairs of levels of A and B, Type IV tests are identical to the Type III tests that are shown in Figure 45.14. (This combines tables from several pages of output.)
Figure 45.14: Type III Estimable Functions and Tests
| Type III Estimable Functions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Effect | Coefficients | ||
| a | b | a*b | |
| Intercept | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| a 1 | L2 | 0 | 0 |
| a 2 | L3 | 0 | 0 |
| a 3 | -L2-L3 | 0 | 0 |
| b 1 | 0 | L5 | 0 |
| b 2 | 0 | -L5 | 0 |
| a*b 1 1 | 0.5*L2 | 0.3333*L5 | L7 |
| a*b 1 2 | 0.5*L2 | -0.3333*L5 | -L7 |
| a*b 2 1 | 0.5*L3 | 0.3333*L5 | L9 |
| a*b 2 2 | 0.5*L3 | -0.3333*L5 | -L9 |
| a*b 3 1 | -0.5*L2-0.5*L3 | 0.3333*L5 | -L7-L9 |
| a*b 3 2 | -0.5*L2-0.5*L3 | -0.3333*L5 | L7+L9 |