The VARIOGRAM Procedure
Semivariance Computation
With the classification of a point pair  into an angle/distance class, as shown earlier in this section, the semivariance computation proceeds as follows.
into an angle/distance class, as shown earlier in this section, the semivariance computation proceeds as follows.
Denote all pairs that  belong to angle class
belong to angle class 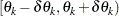 and distance class
and distance class 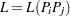 as
as 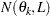 . For example, based on Figure 98.20 and Figure 98.21,
. For example, based on Figure 98.20 and Figure 98.21, 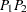 belongs to
belongs to  .
.
Let 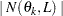 denote the number of such pairs. The component of the standard (or method of moments) semivariance that correspond to angle/distance class
denote the number of such pairs. The component of the standard (or method of moments) semivariance that correspond to angle/distance class 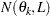 is given by
is given by
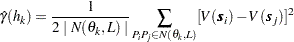 |
where 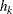 is the average distance in class
is the average distance in class 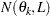 ; that is,
; that is,
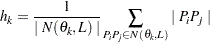 |
The robust version of the semivariance is given by
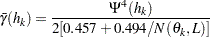 |
where
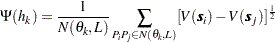 |
This robust version of the semivariance is computed when you specify the ROBUST option in the COMPUTE statement in PROC VARIOGRAM.
PROC VARIOGRAM computes and writes to the OUTVAR= data set the quantities 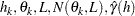 , and
, and 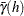 .
.
