The SURVEYPHREG Procedure
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Syntax
 PROC SURVEYPHREG Statement BY Statement CLASS Statement CLUSTER Statement DOMAIN Statement ESTIMATE Statement FREQ Statement LSMEANS Statement LSMESTIMATE Statement MODEL Statement NLOPTIONS Statement OUTPUT Statement Programming Statements REPWEIGHTS Statement SLICE Statement STORE Statement STRATA Statement TEST Statement WEIGHT Statement
PROC SURVEYPHREG Statement BY Statement CLASS Statement CLUSTER Statement DOMAIN Statement ESTIMATE Statement FREQ Statement LSMEANS Statement LSMESTIMATE Statement MODEL Statement NLOPTIONS Statement OUTPUT Statement Programming Statements REPWEIGHTS Statement SLICE Statement STORE Statement STRATA Statement TEST Statement WEIGHT Statement -
Details
 Notation and Estimation Failure Time Distribution Time and CLASS Variables Usage Partial Likelihood Function for the Cox Model Specifying the Sample Design Missing Values Variance Estimation Domain Analysis Hypothesis Tests, Confidence Intervals, and Residuals Output Data Sets Displayed Output ODS Table Names ODS Graphics
Notation and Estimation Failure Time Distribution Time and CLASS Variables Usage Partial Likelihood Function for the Cox Model Specifying the Sample Design Missing Values Variance Estimation Domain Analysis Hypothesis Tests, Confidence Intervals, and Residuals Output Data Sets Displayed Output ODS Table Names ODS Graphics -
Examples

- References
| ESTIMATE Statement |
- ESTIMATE <'label'> estimate-specification <(divisor=n)>
<, ...<'label'> estimate-specification <(divisor=n)> >
< / options> ;
The ESTIMATE statement provides a mechanism for obtaining custom hypothesis tests. Estimates are formed as linear estimable functions of the form 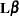 . You can perform hypothesis tests for the estimable functions, construct confidence limits, and obtain specific nonlinear transformations.
. You can perform hypothesis tests for the estimable functions, construct confidence limits, and obtain specific nonlinear transformations.
Table 89.2 summarizes important options in the ESTIMATE statement.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Construction and Computation of Estimable Functions |
|
Specifies a list of values to divide the coefficients |
|
Suppresses the automatic fill-in of coefficients for higher-order effects |
|
Tunes the estimability checking difference |
|
Degrees of Freedom and p-values |
|
Determines the method for multiple comparison adjustment of estimates |
|
Determines the confidence level ( |
|
Performs one-sided, lower-tailed inference |
|
Adjusts multiplicity-corrected p-values further in a step-down fashion |
|
Specifies values under the null hypothesis for tests |
|
Performs one-sided, upper-tailed inference |
|
Statistical Output |
|
Constructs confidence limits |
|
Displays the correlation matrix of estimates |
|
Displays the covariance matrix of estimates |
|
Prints the |
|
Produces a joint |
|
Specifies the seed for computations that depend on random numbers |
|
For details about the syntax of the ESTIMATE statement, see the section ESTIMATE Statement of Chapter 19, Shared Concepts and Topics.

 )
) 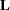 matrix
matrix  or chi-square test for the estimable functions
or chi-square test for the estimable functions