The SEQTEST Procedure
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Syntax

-
Details
 Input Data Sets Boundary Variables Information Level Adjustments at Future Stages Boundary Adjustments for Information Levels Boundary Adjustments for Minimum Error Spending Boundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper beta Boundaries Stochastic Curtailment Repeated Confidence Intervals Analysis after a Sequential Test Available Sample Space Orderings in a Sequential Test Applicable Tests and Sample Size Computation Table Output ODS Table Names Graphics Output ODS Graphics Acknowledgments
Input Data Sets Boundary Variables Information Level Adjustments at Future Stages Boundary Adjustments for Information Levels Boundary Adjustments for Minimum Error Spending Boundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper beta Boundaries Stochastic Curtailment Repeated Confidence Intervals Analysis after a Sequential Test Available Sample Space Orderings in a Sequential Test Applicable Tests and Sample Size Computation Table Output ODS Table Names Graphics Output ODS Graphics Acknowledgments -
Examples
 Testing the Difference between Two Proportions Testing an Effect in a Regression Model Testing an Effect with Early Stopping to Accept H0 Testing a Binomial Proportion Comparing Two Proportions with a Log Odds Ratio Test Comparing Two Survival Distributions with a Log-Rank Test Testing an Effect in a Proportional Hazards Regression Model Testing an Effect in a Logistic Regression Model
Testing the Difference between Two Proportions Testing an Effect in a Regression Model Testing an Effect with Early Stopping to Accept H0 Testing a Binomial Proportion Comparing Two Proportions with a Log Odds Ratio Test Comparing Two Survival Distributions with a Log-Rank Test Testing an Effect in a Proportional Hazards Regression Model Testing an Effect in a Logistic Regression Model - References
| Table Output |
The SEQTEST procedure displays the "Design Information" and "Test Information" tables by default.
Conditional Power
The "Conditional Power Information" table displays the following information under a hypothetical reference:
stopping stage
MLE, observed maximum likelihood estimate
conditional power under the hypothetical reference
For a one-sided test, the power are derived under hypothetical references 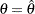 and
and 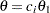 , where
, where 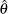 is the observed statistic,
is the observed statistic, 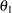 is the alternative reference, and
is the alternative reference, and 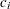 are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided test, the power are derived under the hypothetical references
are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided test, the power are derived under the hypothetical references 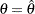 ,
, 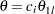 , and
, and 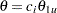 , where
, where 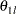 is the lower alternative reference and
is the lower alternative reference and 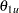 is the upper alternative reference. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5.
is the upper alternative reference. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5.
Design Information
The "Design Information" table displays the design specifications and derived statistics. The derived Max Information (Percent Fixed-Sample) is the maximum information for the sequential design in percentage of the corresponding fixed-sample information.
The Null Ref ASN (Percent Fixed-Sample) is the average sample size required under the null hypothesis for the group sequential design in percentage of the corresponding fixed-sample design. Similarly, the Alt Ref ASN (Percent Fixed-Sample) is the average sample size required under the alternative reference for the group sequential design in percentage of the corresponding fixed-sample design.
Error Spending Information
The "Error Spending Information" table displays the following information at each stage:
proportion of information
actual information level, if the maximum information is either specified or derived
cumulative error spending for each boundary
Parameter Estimates
The "Parameter Estimates" table displays the following information at the conclusion of a sequential trial:
stopping stage
parameter estimate
median and confidence limits based on the specified ordering
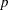 -value for the hypothesis
-value for the hypothesis  based on the specified ordering
based on the specified ordering
Powers and Expected Sample Sizes
The "Powers and Expected Sample Sizes" table displays the following information under each of the specified hypothetical references 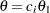 , where
, where 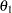 is the alternative reference and
is the alternative reference and 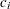 are values specified in the CREF= option.
are values specified in the CREF= option.
coefficient
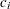 for the hypothetical references. The value
for the hypothetical references. The value 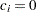 corresponds to the null hypothesis and
corresponds to the null hypothesis and 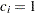 corresponds to the alternative hypothesis
corresponds to the alternative hypothesis power
expected sample size, as percentage of fixed-sample size
For a one-sided design, the power and expected sample sizes under the hypothetical references 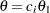 are displayed.
are displayed.
For a two-sided symmetric design, the power and expected sample sizes under each of the hypothetical references 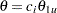 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 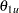 is the upper alternative reference.
is the upper alternative reference.
For a two-sided asymmetric design, the power and expected sample sizes under each of the hypothetical references 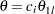 and
and 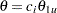 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 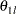 and
and 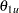 are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively.
are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively.
For a two-sided design, the power is the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis for the correct alternative. Thus, under the null hypothesis, the displayed power corresponds to a one-sided Type I error probability level—that is, the lower  level or the upper
level or the upper  level.
level.
The expected sample size as a percentage of the corresponding fixed-sample design is
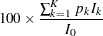 |
where 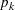 is the stopping probability at stage
is the stopping probability at stage 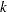 ,
, 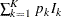 is the expected information level, and
is the expected information level, and 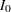 is the information level for the fixed-sample design.
is the information level for the fixed-sample design.
Predictive Power
The "Predictive Power Information" table displays the following information:
stopping stage
MLE, observed maximum likelihood estimate
predictive power
Repeated Confidence Intervals
The "Repeated Confidence Intervals" table displays the following information for the observed statistic at each stage:
information level
parameter estimate
rejection confidence limits. The null hypothesis is rejected for the upper alternative if the lower rejection confidence limit is greater than the null parameter value. Similarly, the null hypothesis is rejected for the lower alternative if the upper rejection confidence limit is less than the null parameter value.
acceptance confidence limits. The upper alternative hypothesis is rejected if the upper acceptance confidence limit is less than the upper alternative value. Similarly, the lower alternative hypothesis is rejected if the lower acceptance confidence limit is greater than the upper alternative value. For a two-sided design, if both upper and lower alternative hypothesis are rejected, the null hypothesis is accepted.
Stopping Probabilities
The "Expected Cumulative Stopping Probabilities" table displays the following information under each of the specified hypothetical references 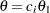 , where
, where 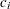 are values specified in the CREF= option, and
are values specified in the CREF= option, and 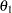 is the alternative reference:
is the alternative reference:
coefficient
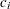 for the hypothetical references. The value
for the hypothetical references. The value 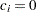 corresponds to the null hypothesis, and
corresponds to the null hypothesis, and 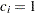 corresponds to the alternative hypothesis
corresponds to the alternative hypothesis expected stopping stage
source of the stopping probability: reject
 (with STOP=REJECT or STOP=BOTH), accept
(with STOP=REJECT or STOP=BOTH), accept  (with STOP=ACCEPT or STOP=BOTH), or either reject or accept
(with STOP=ACCEPT or STOP=BOTH), or either reject or accept  (with STOP=BOTH)
(with STOP=BOTH) expected cumulative stopping probabilities at each stage
For a one-sided design, the expected cumulative stopping probabilities under the hypothetical references 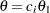 are displayed.
are displayed.
For a two-sided design, the expected cumulative stopping probabilities under each of the hypothetical references 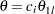 and
and 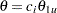 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 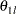 and
and 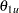 are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively.
are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively.
Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only the expected cumulative stopping probabilities under the hypothetical references 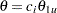 are derived.
are derived.
The expected stopping stage is given by 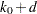 and is derived from the expected information level
and is derived from the expected information level
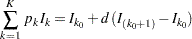 |
where 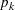 is the stopping probability at stage
is the stopping probability at stage 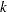 and
and 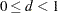 .
.
For equally spaced information levels, the expected stopping stage is reduced to the weighted average
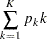 |
Test Information
The "Test Information" table displays the following information at each stage:
proportion of information
actual information level, if the maximum information is available from the input BOUNDARY= data set
alternative references with the specified statistic scale. If a
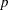 -value scale is specified, the standardized
-value scale is specified, the standardized 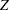 scale is used.
scale is used. boundary values with the specified statistic scale to reject or accept the null hypothesis
Note that implicitly, the test information table also contains variables for the boundary scale, stopping criterion, and type of alternative hypothesis. That is, if an ODS statement is used to save the table, the data set also contains the variables _Scale_ for the boundary scale, _Stop_ for the stopping criterion, and _ALT_ for the type of alternative hypothesis.
If the test variable is specified, the table also displays the following:
test statistic
resulting action of test statistic: continue to the next stage, accept the null hypothesis
 , or reject
, or reject 