The NESTED Procedure
Overview: NESTED Procedure
The NESTED procedure performs random-effects analysis of variance for data from an experiment with a nested (hierarchical) structure.1 A random-effects model for data from a completely nested design with two factors has the form
 |
where
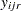
is the value of the dependent variable observed at the
 th replication with the first factor at its
th replication with the first factor at its 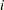 th level and the second factor at its
th level and the second factor at its 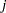 th level.
th level. 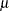
is the overall (fixed) mean of the sampling population.

are mutually uncorrelated random effects with zero means and respective variances
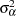 ,
, 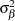 , and
, and 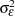 (the variance components).
(the variance components).
This model is appropriate for an experiment with a multistage nested sampling design. An example of this is given in Example 61.1, where four turnip plants are randomly chosen (the first factor), then three leaves are randomly chosen from each plant (the second factor nested within the first), and then two samples are taken from each leaf (the different replications at fixed levels of the two factors).
Note that PROC NESTED is appropriate for models with only classification effects; it does not handle models that contain continuous covariates. For random effects models with covariates, use either the GLM or MIXED procedure.
