The ANOVA Procedure
Example 24.2 Alternative Multiple Comparison Procedures
The following is a continuation of the first example in the section One-Way Layout with Means Comparisons. You are studying the effect of bacteria on the nitrogen content of red clover plants, and the analysis of variance shows a highly significant effect. The following statements create the data set and compute the analysis of variance as well as Tukey’s multiple comparisons test for pairwise differences between bacteria strains; the results are shown in Figure 24.1, Figure 24.2, and Figure 24.3
title1 'Nitrogen Content of Red Clover Plants'; data Clover; input Strain $ Nitrogen @@; datalines; 3DOK1 19.4 3DOK1 32.6 3DOK1 27.0 3DOK1 32.1 3DOK1 33.0 3DOK5 17.7 3DOK5 24.8 3DOK5 27.9 3DOK5 25.2 3DOK5 24.3 3DOK4 17.0 3DOK4 19.4 3DOK4 9.1 3DOK4 11.9 3DOK4 15.8 3DOK7 20.7 3DOK7 21.0 3DOK7 20.5 3DOK7 18.8 3DOK7 18.6 3DOK13 14.3 3DOK13 14.4 3DOK13 11.8 3DOK13 11.6 3DOK13 14.2 COMPOS 17.3 COMPOS 19.4 COMPOS 19.1 COMPOS 16.9 COMPOS 20.8 ;
proc anova data=Clover; class Strain; model Nitrogen = Strain; means Strain / tukey; run;
The interactivity of PROC ANOVA enables you to submit further MEANS statements without re-running the entire analysis. For example, the following command requests means of the Strain levels with Duncan’s multiple range test and the Waller-Duncan 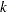 -ratio
-ratio  test.
test.
means Strain / duncan waller; run;
Results of the Waller-Duncan 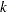 -ratio
-ratio  test are shown in Output 24.2.1.
test are shown in Output 24.2.1.
 -ratio
-ratio  Test
Test
| Nitrogen Content of Red Clover Plants |
| Kratio | 100 |
|---|---|
| Error Degrees of Freedom | 24 |
| Error Mean Square | 11.78867 |
| F Value | 14.37 |
| Critical Value of t | 1.91873 |
| Minimum Significant Difference | 4.1665 |
| Means with the same letter are not significantly different. |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waller Grouping | Mean | N | Strain | |
| A | 28.820 | 5 | 3DOK1 | |
| B | 23.980 | 5 | 3DOK5 | |
| B | ||||
| C | B | 19.920 | 5 | 3DOK7 |
| C | ||||
| C | D | 18.700 | 5 | COMPOS |
| D | ||||
| E | D | 14.640 | 5 | 3DOK4 |
| E | ||||
| E | 13.260 | 5 | 3DOK13 | |
The Waller-Duncan 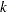 -ratio
-ratio  test is a multiple range test. Unlike Tukey’s test, this test does not operate on the principle of controlling Type I error. Instead, it compares the Type I and Type II error rates based on Bayesian principles (Steel and Torrie; 1980).
test is a multiple range test. Unlike Tukey’s test, this test does not operate on the principle of controlling Type I error. Instead, it compares the Type I and Type II error rates based on Bayesian principles (Steel and Torrie; 1980).
The Waller Grouping column in Output 24.2.1 shows which means are significantly different. From this test, you can conclude the following:
The mean nitrogen content for strain 3DOK1 is higher than the means for all other strains.
The mean nitrogen content for strain 3DOK5 is higher than the means for COMPOS, 3DOK4, and 3DOK13.
The mean nitrogen content for strain 3DOK7 is higher than the means for 3DOK4 and 3DOK13.
The mean nitrogen content for strain COMPOS is higher than the mean for 3DOK13.
Differences between all other means are not significant based on this sample size.
Output 24.2.2 shows the results of Duncan’s multiple range test. Duncan’s test is a result-guided test that compares the treatment means while controlling the comparison-wise error rate. You should use this test for planned comparisons only (Steel and Torrie; 1980). The results and conclusions for this example are the same as for the Waller-Duncan 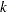 -ratio
-ratio  test. This is not always the case.
test. This is not always the case.
| Alpha | 0.05 |
|---|---|
| Error Degrees of Freedom | 24 |
| Error Mean Square | 11.78867 |
| Number of Means | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Critical Range | 4.482 | 4.707 | 4.852 | 4.954 | 5.031 |
| Means with the same letter are not significantly different. |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duncan Grouping | Mean | N | Strain | |
| A | 28.820 | 5 | 3DOK1 | |
| B | 23.980 | 5 | 3DOK5 | |
| B | ||||
| C | B | 19.920 | 5 | 3DOK7 |
| C | ||||
| C | D | 18.700 | 5 | COMPOS |
| D | ||||
| E | D | 14.640 | 5 | 3DOK4 |
| E | ||||
| E | 13.260 | 5 | 3DOK13 | |
Tukey and Least Significant Difference (LSD) tests are requested with the following MEANS statement. The CLDIFF option requests confidence intervals for both tests.
means Strain/ lsd tukey cldiff ; run;
The LSD tests for this example are shown in Output 24.2.3, and they give the same results as the previous two multiple comparison tests. Again, this is not always the case.
| Nitrogen Content of Red Clover Plants |
| Alpha | 0.05 |
|---|---|
| Error Degrees of Freedom | 24 |
| Error Mean Square | 11.78867 |
| Critical Value of t | 2.06390 |
| Least Significant Difference | 4.4818 |
| Comparisons significant at the 0.05 level are indicated by ***. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain Comparison |
Difference Between Means |
95% Confidence Limits | ||
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK5 | 4.840 | 0.358 | 9.322 | *** |
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK7 | 8.900 | 4.418 | 13.382 | *** |
| 3DOK1 - COMPOS | 10.120 | 5.638 | 14.602 | *** |
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK4 | 14.180 | 9.698 | 18.662 | *** |
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK13 | 15.560 | 11.078 | 20.042 | *** |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK1 | -4.840 | -9.322 | -0.358 | *** |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK7 | 4.060 | -0.422 | 8.542 | |
| 3DOK5 - COMPOS | 5.280 | 0.798 | 9.762 | *** |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK4 | 9.340 | 4.858 | 13.822 | *** |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK13 | 10.720 | 6.238 | 15.202 | *** |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK1 | -8.900 | -13.382 | -4.418 | *** |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK5 | -4.060 | -8.542 | 0.422 | |
| 3DOK7 - COMPOS | 1.220 | -3.262 | 5.702 | |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK4 | 5.280 | 0.798 | 9.762 | *** |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK13 | 6.660 | 2.178 | 11.142 | *** |
| COMPOS - 3DOK1 | -10.120 | -14.602 | -5.638 | *** |
| COMPOS - 3DOK5 | -5.280 | -9.762 | -0.798 | *** |
| COMPOS - 3DOK7 | -1.220 | -5.702 | 3.262 | |
| COMPOS - 3DOK4 | 4.060 | -0.422 | 8.542 | |
| COMPOS - 3DOK13 | 5.440 | 0.958 | 9.922 | *** |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK1 | -14.180 | -18.662 | -9.698 | *** |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK5 | -9.340 | -13.822 | -4.858 | *** |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK7 | -5.280 | -9.762 | -0.798 | *** |
| 3DOK4 - COMPOS | -4.060 | -8.542 | 0.422 | |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK13 | 1.380 | -3.102 | 5.862 | |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK1 | -15.560 | -20.042 | -11.078 | *** |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK5 | -10.720 | -15.202 | -6.238 | *** |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK7 | -6.660 | -11.142 | -2.178 | *** |
| 3DOK13 - COMPOS | -5.440 | -9.922 | -0.958 | *** |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK4 | -1.380 | -5.862 | 3.102 | |
If you only perform the LSD tests when the overall model 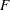 test is significant, then this is called Fisher’s protected LSD test. Note that the LSD tests should be used for planned comparisons.
test is significant, then this is called Fisher’s protected LSD test. Note that the LSD tests should be used for planned comparisons.
The TUKEY tests shown in Output 24.2.4 find fewer significant differences than the other three tests. This is not unexpected, as the TUKEY test controls the Type I experimentwise error rate. For a complete discussion of multiple comparison methods, see the section Multiple Comparisons in Chapter 41, The GLM Procedure.
| Alpha | 0.05 |
|---|---|
| Error Degrees of Freedom | 24 |
| Error Mean Square | 11.78867 |
| Critical Value of Studentized Range | 4.37265 |
| Minimum Significant Difference | 6.7142 |
| Comparisons significant at the 0.05 level are indicated by ***. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain Comparison |
Difference Between Means |
Simultaneous 95% Confidence Limits |
||
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK5 | 4.840 | -1.874 | 11.554 | |
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK7 | 8.900 | 2.186 | 15.614 | *** |
| 3DOK1 - COMPOS | 10.120 | 3.406 | 16.834 | *** |
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK4 | 14.180 | 7.466 | 20.894 | *** |
| 3DOK1 - 3DOK13 | 15.560 | 8.846 | 22.274 | *** |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK1 | -4.840 | -11.554 | 1.874 | |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK7 | 4.060 | -2.654 | 10.774 | |
| 3DOK5 - COMPOS | 5.280 | -1.434 | 11.994 | |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK4 | 9.340 | 2.626 | 16.054 | *** |
| 3DOK5 - 3DOK13 | 10.720 | 4.006 | 17.434 | *** |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK1 | -8.900 | -15.614 | -2.186 | *** |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK5 | -4.060 | -10.774 | 2.654 | |
| 3DOK7 - COMPOS | 1.220 | -5.494 | 7.934 | |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK4 | 5.280 | -1.434 | 11.994 | |
| 3DOK7 - 3DOK13 | 6.660 | -0.054 | 13.374 | |
| COMPOS - 3DOK1 | -10.120 | -16.834 | -3.406 | *** |
| COMPOS - 3DOK5 | -5.280 | -11.994 | 1.434 | |
| COMPOS - 3DOK7 | -1.220 | -7.934 | 5.494 | |
| COMPOS - 3DOK4 | 4.060 | -2.654 | 10.774 | |
| COMPOS - 3DOK13 | 5.440 | -1.274 | 12.154 | |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK1 | -14.180 | -20.894 | -7.466 | *** |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK5 | -9.340 | -16.054 | -2.626 | *** |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK7 | -5.280 | -11.994 | 1.434 | |
| 3DOK4 - COMPOS | -4.060 | -10.774 | 2.654 | |
| 3DOK4 - 3DOK13 | 1.380 | -5.334 | 8.094 | |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK1 | -15.560 | -22.274 | -8.846 | *** |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK5 | -10.720 | -17.434 | -4.006 | *** |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK7 | -6.660 | -13.374 | 0.054 | |
| 3DOK13 - COMPOS | -5.440 | -12.154 | 1.274 | |
| 3DOK13 - 3DOK4 | -1.380 | -8.094 | 5.334 | |
