| The ROBUSTREG Procedure |
| PROC ROBUSTREG Statement |
The PROC ROBUSTREG statement invokes the procedure. You can specify the following options in the PROC ROBUSTREG statement.
- COVOUT
saves the estimated covariance matrix in the OUTEST= data set. This option is not supported for LTS estimation.
- DATA=SAS-data-set
specifies the input SAS data set used by PROC ROBUSTREG. By default, the most recently created SAS data set is used.
- FWLS
requests that final weighted least squares estimates be computed. These estimates are equivalent to the least squares estimates after the detected outliers are deleted.
- INEST=SAS-data-set
specifies an input SAS data set that contains initial estimates for all the parameters in the model. See the section INEST= Data Set for a detailed description of the contents of the INEST= data set.
- ITPRINT
displays the iteration history for the iteratively reweighted least squares algorithm used by M and MM estimation. You can also use this option in the MODEL statement.
- NAMELEN=n
specifies the length of effect names in tables and output data sets to be
 characters, where
characters, where  is a value between 20 and 200. The default length is 20 characters.
is a value between 20 and 200. The default length is 20 characters. - ORDER=DATA | FORMATTED | FREQ | INTERNAL
specifies the order in which to sort the levels of the classification variables (which are specified in the CLASS statement). This option applies to the levels for all classification variables, except when you use the (default) ORDER=FORMATTED option with numeric classification variables that have no explicit format. With this option, the levels of such variables are ordered by their internal value.
The ORDER= option can take the following values:
Value of ORDER=
Levels Sorted By
DATA
Order of appearance in the input data set
FORMATTED
External formatted value, except for numeric variables with no explicit format, which are sorted by their unformatted (internal) value
FREQ
Descending frequency count; levels with the most observations come first in the order
INTERNAL
Unformatted value
By default, ORDER=FORMATTED. For FORMATTED and INTERNAL, the sort order is machine-dependent. For more information about sorting order, see the chapter on the SORT procedure in the Base SAS Procedures Guide and the discussion of BY-group processing in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
- OUTEST=SAS-data-set
specifies an output SAS data set that contains the parameter estimates, and, if the COVOUT option is specified, the estimated covariance matrix. See the section OUTEST= Data Set for a detailed description of the contents of the OUTEST= data set.
- PLOT | PLOTS <(global-plot-options)> <=plot-request>
- PLOT | PLOTS<(global-plot-options)> <=(plot-request < ...plot-request > )>
specifies options that control details of the plots. If you have enabled ODS GRAPHICS but do not specify the PLOTS= option, then PROC ROBUSTREG produces the robust fit plot by default when the model includes a single continuous independent variable.
The global-plot-options apply to all plots generated by the ROBUSTREG procedure. The following global-plot-option is available:
- ONLY
suppresses the default robust fit plot. Only plots specifically requested are displayed.
You can specify more than one plot-request within the parentheses after PLOTS=. For a single plot request, you can omit the parentheses. The following plot-requests are available.
- ALL
creates all appropriate plots.
- DDPLOT<(LABEL=ALL | LEVERAGE | NONE | OUTLIER)>
creates a plot of robust distance against Mahalanobis distance. See the section Leverage Point and Outlier Detection for details about robust distance. The LABEL= option specifies how the points on this plot are to be labeled, as summarized by the following table.
Table 75.1 Options for Label Value of LABEL=
Label Method
ALL
Label all points
LEVERAGE
Label leverage points
NONE
No labels
OUTLIERS
Label outliers
By default, the ROBUSTREG procedure labels both outliers and leverage points.
If you specify ID variables in the ID statement, the values of the first ID variable are used as labels; otherwise, observation numbers are used as labels.
- FITPLOT<(NOLIMITS)>
creates a plot of robust fit against the single independent continuous variable specified in the model. You can request this plot when only a single independent continuous variable is specified in the model. Confidence limits are added on the plot by default. The NOLIMITS option suppresses these limits.
- HISTOGRAM
creates a histogram for the standardized robust residuals. The histogram is superimposed with a normal density curve and a kernel density curve.
- NONE
suppresses all plots.
- QQPLOT
creates the normal quantile-quantile plot for the standardized robust residuals.
- RDPLOT<(LABEL=ALL | LEVERAGE | NONE | OUTLIER)>
creates the plot of standardized robust residual against robust distance. See the section Leverage Point and Outlier Detection for details about robust distance. The LABEL= option specifies a label method for points on this plot. These label methods are described in Table 75.1.
If you specify ID variables in the ID statement, the values of the first ID variable are used as labels; otherwise, observation numbers are used as labels.
- SEED=number
specifies the seed for the random number generator used to randomly select the subgroups and subsets for LTS and S estimation. By default or if you specify zero, the ROBUSTREG procedure generates a random seed.
- METHOD=method type <( options )>
specifies the estimation method and some additional options for the estimation method. PROC ROBUSTREG provides four estimation methods: M estimation, LTS estimation, S estimation, and MM estimation. The default method is M estimation.
Note:Since the LTS and S methods use subsampling algorithms, these methods are not suitable in an analysis with variables that have only a few unequal values or a few unequal values within one BY group. For example, indicator variables that correspond to a classification variable often fall into this type. The same issue also applies to the initial LTS and S estimates in the MM method. In case of a model that includes classification independent variables or continuous independent variables with a few unequal values, the M method is recommended.
Options with METHOD=M
With METHOD=M, you can specify the following additional options:
- ASYMPCOV=H1 | H2 | H3
specifies the type of asymptotic covariance computed for the M estimate. The three types are described in the section Asymptotic Covariance and Confidence Intervals. By default, ASYMPCOV= H1.
- CONVERGENCE=criterion <(EPS=value)>
specifies a convergence criterion for the M estimate. The three criteria listed in the following table are available.
Table 75.2 Options to Specify Convergence Criteria Type
Option
Coefficient
CONVERGENCE=COEF
Residual
CONVERGENCE=RESID
Weight
CONVERGENCE=WEIGHT
By default, CONVERGENCE = COEF. You can specify the precision of the convergence criterion with the EPS= option. By default, EPS=1.E
 8.
8. - MAXITER=n
sets the maximum number of iterations during the parameter estimation. By default, MAXITER=1,000.
- SCALE=scale type | value
specifies the scale parameter or a method for estimating the scale parameter. These methods and options are summarized in the following table.
Table 75.3 Options to Specify Scale Scale
Option
Default d
Fixed constant
SCALE=value
Huber estimate
SCALE=HUBER<(D=d)>
2.5
Median estimate
SCALE=MED
Tukey estimate
SCALE=TUKEY<(D=d)>
2.5
By default, SCALE = MED.
- WF | WEIGHTFUNCTION=function type
specifies the weight function used for the M estimate. The ROBUSTREG procedure provides 10 weight functions, which are listed in the following table. You can specify the parameters in these functions with the A=, B=, and C= options. These functions are described in the section M Estimation. The default weight function is bisquare.
Table 75.4 Options to Specify Weight Functions Weight Function
Option
Default a, b, c
Andrews
WF=ANDREWS<(C=c)>
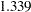
Bisquare
WF=BISQUARE<(C=c)>
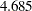
Cauchy
WF=CAUCHY<(C=c)>
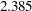
Fair
WF=FAIR<(C=c)>
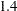
Hampel
WF=HAMPEL<( <A=a> <B=b> <C=c>)>
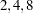
Huber
WF=HUBER<(C=c)>
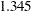
Logistic
WF=LOGISTIC<(C=c)>

Median
WF=MEDIAN<(C=c)>

Talworth
WF=TALWORTH<(C=c)>
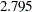
Welsch
WF=WELSCH<(C=c)>

Options with METHOD=LTS
With METHOD=LTS, you can specify the following additional options:
- CSTEP=n
specifies the number of concentration steps (C-steps) for the LTS estimate. See the section LTS Estimate for information about how the default value is determined.
- H=n
specifies the quantile for the LTS estimate. See the section LTS Estimate for information about how the default value is determined.
- IADJUST=ALL | NONE
requests (IADJUST=ALL) or suppresses (IADJUST=NONE) the intercept adjustment for all estimates in the LTS algorithm. By default, the intercept adjustment is used for data sets with fewer than 10,000 observations. See the section Algorithm for details.
- NBEST=n
specifies the number of best solutions kept for each subgroup during the computation of the LTS estimate. The default number is 10, which is the maximum number allowed.
- NREP=n
specifies the number of times to repeat least squares fit in subgroups during the computation of the LTS estimate. See the section LTS Estimate for information about how the default number is determined.
- SUBANALYSIS
requests a display of the subgrouping information and parameter estimates within subgroups. This option generates the ODS tables shown in Table 75.5.
Table 75.5 ODS Tables Available with SUBANALYSIS Option ODS Table Name
Description
BestEstimates
Best final estimates for LTS
BestSubEstimates
Best estimates for each subgroup
CStep
C-step information for LTS
Groups
Grouping information for LTS
- SUBGROUPSIZE=n
specifies the data set size of the subgroups in the computation of the LTS estimate. The default number is 300.
Options with METHOD=S
With METHOD=S, you can specify the following additional options:
- ASYMPCOV=H1 | H2 | H3 | H4
specifies the type of asymptotic covariance computed for the S estimate. The four types are described in the section Asymptotic Covariance and Confidence Intervals. By default, ASYMPCOV= H4.
- CHIF= TUKEY | YOHAI
specifies the
 function for the S estimate. PROC ROBUSTREG provides two
function for the S estimate. PROC ROBUSTREG provides two  functions, Tukey’s bisquare function and Yohai’s optimal function, which you can request with CHIF=TUKEY and CHIF=YOHAI, respectively. The default is Tukey’s bisquare function.
functions, Tukey’s bisquare function and Yohai’s optimal function, which you can request with CHIF=TUKEY and CHIF=YOHAI, respectively. The default is Tukey’s bisquare function. - EFF=value
specifies the efficiency (as a fraction) for the S estimate. The parameter
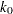 in the
in the  function is determined by this efficiency. The default efficiency is determined such that the consistent S estimate has the breakdown value of
function is determined by this efficiency. The default efficiency is determined such that the consistent S estimate has the breakdown value of 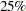 . This option is overwritten by the K0= option if both of them are used.
. This option is overwritten by the K0= option if both of them are used. - K0=value
specifies the
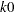 parameter in the
parameter in the  function of the S estimate. For CHIF=TUKEY, the default is 1.548. For CHIF=YOHAI, the default is 0.66. These default values correspond to a
function of the S estimate. For CHIF=TUKEY, the default is 1.548. For CHIF=YOHAI, the default is 0.66. These default values correspond to a 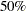 breakdown value of the consistent S estimate.
breakdown value of the consistent S estimate. - MAXITER=n
sets the maximum number of iterations for computing the scale parameter of the S estimate. By default, MAXITER=1000.
- NREP=n
specifies the number of repeats of subsampling in the computation of the S estimate. See the section Algorithm for information about how the default number of repeats is determined.
- NOREFINE
suppresses the refinement for the S estimate. See the section Algorithm for details.
- SUBSETSIZE=n
specifies the size of the subset for the S estimate. See the section Algorithm for information about how the default value is determined.
- TOLERANCE=value
specifies the tolerance for the S estimate of the scale. The default value is 0.001.
Options with METHOD=MM
With METHOD=MM, you can specify the following additional options:
- ASYMPCOV=H1 | H2 | H3 | H4
specifies the type of asymptotic covariance computed for the MM estimate. The four types are described in the section Details: ROBUSTREG Procedure. By default, ASYMPCOV= H4.
- BIASTEST<(ALPHA=number)>
requests the bias test for the final MM estimate. See the section Bias Test for details about this test.
- CHIF= TUKEY | YOHAI
selects the
 function for the MM estimate. PROC ROBUSTREG provides two
function for the MM estimate. PROC ROBUSTREG provides two  functions: Tukey’s bisquare function and Yohai’s optimal function, which you can request with CHIF=TUKEY and CHIF=YOHAI, respectively. The default is Tukey’s bisquare function. This
functions: Tukey’s bisquare function and Yohai’s optimal function, which you can request with CHIF=TUKEY and CHIF=YOHAI, respectively. The default is Tukey’s bisquare function. This  function is also used by the initial S estimate if you specify the INITEST=S option.
function is also used by the initial S estimate if you specify the INITEST=S option. - CONVERGENCE=criterion<(EPS=number)>
specifies a convergence criterion for the MM estimate. The three criteria listed in Table 75.6 are available.
Table 75.6 Options to Specify Convergence Criteria Type
Option
Coefficient
CONVERGENCE=COEF
Residual
CONVERGENCE=RESID
Weight
CONVERGENCE=WEIGHT
By default, CONVERGENCE = COEF. You can specify the precision of the convergence criterion with the EPS= option. By default, EPS=1.E
 8.
8. - EFF=value
specifies the efficiency (as a fraction) for the MM estimate. The parameter
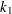 in the
in the  function is determined by this efficiency. The default efficiency is set to 0.85, which corresponds to
function is determined by this efficiency. The default efficiency is set to 0.85, which corresponds to  for CHIF=TUKEY or
for CHIF=TUKEY or 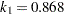 for CHIF=YOHAI.
for CHIF=YOHAI. - INITH=h
specifies the integer
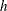 for the initial LTS estimate used by the MM estimator. See the section Algorithm for how to specify
for the initial LTS estimate used by the MM estimator. See the section Algorithm for how to specify 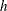 and how the default is determined.
and how the default is determined. - INITEST=LTS | S
specifies the initial estimator for the MM estimator. By default, the LTS estimator with its default settings is used as the initial estimator for the MM estimator.
- K0=number
specifies the parameter
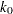 in the
in the  function for the MM estimate. For CHIF=TUKEY, the default is
function for the MM estimate. For CHIF=TUKEY, the default is 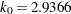 . For CHIF=YOHAI, the default is
. For CHIF=YOHAI, the default is 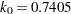 . These default values correspond to the
. These default values correspond to the 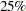 breakdown value of the MM estimator.
breakdown value of the MM estimator. - MAXITER=n
sets the maximum number of iterations during the parameter estimation. By default, MAXITER=1,000.
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.