| The SEQTEST Procedure |
| PROC SEQTEST Statement |
Table 78.1 summarizes the options in the PROC SEQTEST statement.
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Input Data Sets |
|
BOUNDARY= |
specifies data set for boundary information |
DATA= |
specifies data set for parameter estimates and information levels |
PARMS= |
specifies data set for parameter estimates and standard errors |
Boundaries |
|
BETAOVERLAP= |
checks for overlapping of the lower and upper |
at the current and subsequent interim stages in a two-sided design |
|
BOUNDARYADJ= |
specifies boundary adjustment for information levels |
BOUNDARYKEY= |
specifies boundary key to maintain Type I and II error probability levels |
BOUNDARYSCALE= |
specifies boundary scale |
ERRSPENDMIN= |
specifies minimum error spending for the boundaries |
NSTAGES= |
specifies number of stages |
|
|
DATA( TESTVAR= ) |
specifies test variable in DATA= data set |
PARMS( TESTVAR= ) |
specifies test variable in PARMS= data set |
|
|
CIALPHA= |
specifies significance levels for the confidence interval |
CITYPE= |
specifies types of confidence interval |
ORDER= |
specifies the ordering of the sample space used to derive |
the |
|
Table Output |
|
CONDPOWER |
displays conditional powers |
ERRSPEND |
displays cumulative error spending at each stage |
PREDPOWER |
displays predictive powers |
PSS |
displays powers and expected sample sizes |
RCI |
displays repeated confidence intervals |
STOPPROB |
displays expected cumulative stopping probabilities |
Graphics Output |
|
PLOTS=ASN |
displays expected sample numbers plot |
PLOTS=CONDPOWER |
displays conditional powers plot |
PLOTS=ERRSPEND |
displays error spending plot |
PLOTS=POWER |
displays powers plot |
PLOTS=RCI |
displays repeated confidence intervals plot |
PLOTS=TEST |
displays boundary plot with test statistics |
The BOUNDARY= option provides the information for the design and is required in the PROC SEQTEST statement. By default, the SEQTEST procedure displays tables of design information and test information. If the ODS GRAPHICS ON statement is specified, the procedure also displays a sequential test plot.
The following options can be used in the PROC SEQTEST statement. They are listed in alphabetical order.
- BETAOVERLAP=ADJUST | NOADJUST
- OVERLAP=ADJUST | NOADJUST
specifies whether to check for overlapping of the lower and upper
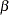 boundaries for the two corresponding one-sided tests at the current and subsequent interim stages. This option applies to two-sided designs with early stopping to accept
boundaries for the two corresponding one-sided tests at the current and subsequent interim stages. This option applies to two-sided designs with early stopping to accept 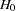 , or to either accept or reject
, or to either accept or reject 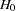 . This type of overlapping might result from a small
. This type of overlapping might result from a small 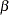 spending at an interim stage. When you specify BETAOVERLAP=ADJUST, the procedure checks for this type of overlapping at the current and subsequent interim stages. If such overlapping is found, the
spending at an interim stage. When you specify BETAOVERLAP=ADJUST, the procedure checks for this type of overlapping at the current and subsequent interim stages. If such overlapping is found, the 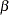 boundaries for the two-sided design at that stage are set to missing, and the
boundaries for the two-sided design at that stage are set to missing, and the 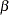 spending values at subsequent stages are adjusted, as described in the section Boundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper
spending values at subsequent stages are adjusted, as described in the section Boundary Adjustments for Overlapping Lower and Upper 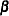 Boundaries.
Boundaries. You can specify BETAOVERLAP=NOADJUST to request that no adjustment be made. The default is BETAOVERLAP=ADJUST.
- BOUNDARY=SAS-data-set
names the required SAS data set that contains the design boundary information. At stage
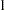 , the data set is usually created from the "Boundary Information" table created by the SEQDESIGN procedure. At each subsequent stage, the data set is usually created from the "Test Information" table created by the SEQTEST procedure at the previous stage. The data set includes the variables _Scale_ for the boundary scale, _Stop_ for the stopping criterion, and _ALT_ for the type of alternative hypothesis. It also includes _Stage_ for the stage number, Info_Prop for the information proportion, and a set of the boundary variables from Bound_LA, Bound_LB, Bound_UB, and Bound_UA for boundary values at each stage.
, the data set is usually created from the "Boundary Information" table created by the SEQDESIGN procedure. At each subsequent stage, the data set is usually created from the "Test Information" table created by the SEQTEST procedure at the previous stage. The data set includes the variables _Scale_ for the boundary scale, _Stop_ for the stopping criterion, and _ALT_ for the type of alternative hypothesis. It also includes _Stage_ for the stage number, Info_Prop for the information proportion, and a set of the boundary variables from Bound_LA, Bound_LB, Bound_UB, and Bound_UA for boundary values at each stage. The data set might also include _Info_ for the actual information level, NObs for the number of observation, and Events for the number of events required at each stage.
- BOUNDARYADJ=method
- BOUNDARYADJ(boundary)=method
- ERRSPENDADJ=method
- ERRSPENDADJ(boundary)=method
specifies methods for boundary adjustments if the observed information level at a stage does not match the information level in the design specified with the BOUNDARY= data set. The default is BOUNDARYADJ=ERRLINE.
The following options specify available methods for the boundary adjustment:
- NONE
specifies that the cumulative error spending at each interim stage not be changed, even if the corresponding information level has been changed.
- ERRLINE
specifies the linear interpolation method for the adjustment.
-
ERRFUNCGAMMA < ( GAMMA=
 ) >
) >
specifies the gamma function method for the adjustment. The GAMMA= suboption specifies the
 parameter in the function, where
parameter in the function, where  . The default is GAMMA=
. The default is GAMMA= .
. - ERRFUNCOBF
specifies the approximate O’Brien-Fleming cumulative error spending function for the adjustment.
- ERRFUNCPOC
specifies the approximate Pocock cumulative error spending function for the adjustment.
-
ERRFUNCPOW < ( RHO=
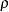 ) >
) >
specifies the power function method for the adjustment. The RHO= suboption specifies the power parameter
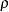 in the function, where
in the function, where  . The default is RHO=
. The default is RHO=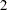 .
.
See the section Boundary Adjustments for Information Levels for a detailed description of the available boundary adjustment methods in the SEQTEST procedure.
If a boundary adjustment method is used for all boundaries in the design, you can use the BOUNDARYADJ=method option to specify the method. Otherwise, you can use the following BOUNDARYADJ(boundary)=method options to specify different methods for the boundaries.
- BOUNDARYADJ(ALPHA)=method
- BOUNDARYADJ(REJECT)=method
specifies the adjustment method for the
 (rejection) boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper
(rejection) boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper  boundaries of a two-sided design.
boundaries of a two-sided design. - BOUNDARYADJ(LOWERALPHA)=method
- BOUNDARYADJ(LOWERREJECT)=method
specifies the adjustment method for the lower
 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design. - BOUNDARYADJ(UPPERALPHA)=method
- BOUNDARYADJ(UPPERREJECT)=method
specifies the adjustment method for the upper
 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design. - BOUNDARYADJ(BETA)=method
- BOUNDARYADJ(ACCEPT)=method
specifies the adjustment method for the
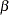 (acceptance) boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper
(acceptance) boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper 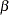 boundaries of a two-sided design.
boundaries of a two-sided design. - BOUNDARYADJ(LOWERBETA)=method
- BOUNDARYADJ(LOWERACCEPT)=method
specifies the adjustment method for the lower
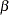 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design. - BOUNDARYADJ(UPPERBETA)=method
- BOUNDARYADJ(UPPERACCEPT)=method
specifies the adjustment method for the upper
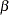 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design.
- BOUNDARYKEY=ALPHA | BETA | BOTH
specifies the boundary key to be maintained in the boundary adjustments. The BOUNDARYKEY=ALPHA option maintains the Type I
 level and derives the Type II error probability, and the BOUNDARYKEY=BETA option maintains the Type II
level and derives the Type II error probability, and the BOUNDARYKEY=BETA option maintains the Type II 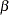 level and derives the Type I error probability. The BOUNDARYKEY=BOTH option maintains both
level and derives the Type I error probability. The BOUNDARYKEY=BOTH option maintains both  and
and 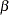 levels simultaneously by deriving a new maximum information. The default is BOUNDARYKEY=ALPHA.
levels simultaneously by deriving a new maximum information. The default is BOUNDARYKEY=ALPHA. - BOUNDARYSCALE=MLE | SCORE | STDZ | PVALUE
- BSCALE=MLE | SCORE | STDZ | PVALUE
specifies the boundary scale to be displayed in the output boundary table and plot. The BOUNDARYSCALE=MLE, BOUNDARYSCALE=SCORE, BOUNDARYSCALE=STDZ, and BOUNDARYSCALE=PVALUE options correspond to the boundary with the maximum likelihood estimator scale, score statistic scale, standardized normal
 scale, and
scale, and  -value scale, respectively. The default is BOUNDARYSCALE=STDZ.
-value scale, respectively. The default is BOUNDARYSCALE=STDZ. With the BOUNDARYSCALE=MLE or BOUNDARYSCALE=SCORE option, either the MAXINFO= option must be specified or the _Info_ variable must be in the BOUNDARY= data set to provide the necessary information level at each stage to derive the boundary values. Usually, these values are obtained from analysis output in SAS procedures.
Note that for a two-sided design, the
 -value scale displays the one-sided fixed-sample
-value scale displays the one-sided fixed-sample  -value under the null hypothesis with a lower alternative hypothesis.
-value under the null hypothesis with a lower alternative hypothesis. -
CIALPHA=
 <( <LOWER=
<( <LOWER=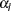 > <UPPER=
> <UPPER=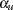 > )>
> )>
specifies the significance levels for the confidence interval, where
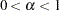 ,
, 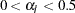 , and
, and  . The default is CIALPHA= 0.05.
. The default is CIALPHA= 0.05. For a lower confidence interval (CITYPE=LOWER), the CIALPHA=
 option produces a
option produces a 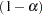 lower confidence interval. For an upper confidence interval (CITYPE=UPPER), the CIALPHA=
lower confidence interval. For an upper confidence interval (CITYPE=UPPER), the CIALPHA= option produces a
option produces a 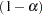 upper confidence interval. The LOWER= and UPPER= suboptions are applicable only for a two-sided confidence interval (CITYPE=TWOSIDED). The LOWER= suboption specifies the lower significance level
upper confidence interval. The LOWER= and UPPER= suboptions are applicable only for a two-sided confidence interval (CITYPE=TWOSIDED). The LOWER= suboption specifies the lower significance level 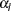 and the upper significance level
and the upper significance level 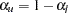 . The UPPER= suboption specifies the upper significance level
. The UPPER= suboption specifies the upper significance level 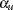 and the lower significance level
and the lower significance level  . If both LOWER= and UPPER= suboptions are not specified,
. If both LOWER= and UPPER= suboptions are not specified, 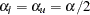 . The significance levels
. The significance levels 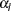 and
and 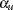 are then used for the
are then used for the 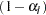 lower confidence limit and
lower confidence limit and 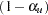 upper confidence limit, respectively.
upper confidence limit, respectively. - CITYPE=LOWER | UPPER | TWOSIDED
specifies the type of confidence interval. The CITYPE=LOWER, CITYPE=UPPER, and CITYPE=TWOSIDED options correspond to the lower confidence interval, upper confidence interval, and two-sided confidence interval, respectively. The default is CITYPE=LOWER for the design with an upper alternative, CITYPE=UPPER for the design with a lower alternative, and CITYPE=TWOSIDED for the design with a two-sided alternative.
- DATA <(TESTVAR=variable)>=SAS-data-set
names the SAS data set that contains the test statistic and its associated information level for the stage. The data set includes the stage variable _Stage_ and a variable to identify or derive the information level: _Info_ for the information level, NObs for the number of observation, or Events for the number of events. If the information level that corresponds to the test statistic is not available, the information level derived in the BOUNDARY= data set is used.
If the TESTVAR= option is specified, the data set also includes the test variable specified in the TESTVAR= option and the scale variable _Scale_ for the test statistic. Usually, these test variable values are obtained from analysis output in SAS procedures.
- ERRSPENDMIN=numbers
- ERRSPENDMIN(boundary)=numbers
specifies the minimum error spending values at the current observed and future interim stages for the boundaries specified in the BOUNDARYKEY= option. The default is ERRSPENDMIN=0.
If a set of numbers is used for each boundary in the design, you can use the ERRSPENDMIN=numbers option. Otherwise, you can use the following ERRSPENDMIN(boundary)=numbers options to specify different sets of minimum error spending values for the boundaries. For a boundary, the error spending value at stage
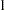 is identical to its nominal
is identical to its nominal  -value.
-value. - ERRSPENDMIN(ALPHA)=numbers
- ERRSPENDMIN(REJECT)=numbers
specifies the minimum error spending values for the
 boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper
boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper  boundaries of a two-sided design.
boundaries of a two-sided design. - ERRSPENDMIN(LOWERALPHA)=numbers
- ERRSPENDMIN(LOWERREJECT)=numbers
specifies the minimum error spending values for the lower
 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design. - ERRSPENDMIN(UPPERALPHA)=numbers
- ERRSPENDMIN(UPPERREJECT)=numbers
specifies the minimum error spending values for the upper
 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design. - ERRSPENDMIN(BETA)=numbers
- ERRSPENDMIN(ACCEPT)=numbers
specifies the minimum error spending values for the
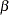 boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper
boundary of a one-sided design or the lower and upper 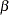 boundaries of a two-sided design.
boundaries of a two-sided design. - ERRSPENDMIN(LOWERBETA)=numbers
- ERRSPENDMIN(LOWERACCEPT)=numbers
specifies the minimum error spending values for the lower
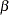 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design. - ERRSPENDMIN(UPPERBETA)=numbers
- ERRSPENDMIN(UPPERACCEPT)=numbers
specifies the minimum error spending values for the upper
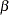 boundary of a two-sided design.
boundary of a two-sided design.
- NSTAGES=number
specifies the number of stages for the clinical trial. The default is the number derived from the BOUNDARY= data set.
The specified NSTAGES= number might or might not be the same as the number derived in the BOUNDARY= data set. You can use the NSTAGES= option to set the next stage as the final stage to compute the conditional power, as described in the section Conditional Power Approach.
- ORDER=LR | MLE | STAGEWISE
specifies the ordering of the sample space
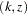 , where
, where 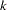 is the stage number and
is the stage number and  is the observed standardized
is the observed standardized  statistic. The ordering is used to derive the
statistic. The ordering is used to derive the  -values for the observed
-values for the observed 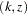 statistic and to create unbiased median estimate and confidence limits from the statistic. The ORDER=LR option specifies the LR ordering that compares the distances between observed standardized
statistic and to create unbiased median estimate and confidence limits from the statistic. The ORDER=LR option specifies the LR ordering that compares the distances between observed standardized  statistics and their corresponding hypothetical values, the ORDER=MLE option specifies the MLE ordering that compares values in the MLE scale, and the ORDER=STAGEWISE specifies the stagewise ordering that uses counterclockwise ordering around the continuation region. The default is ORDER=STAGEWISE. See the section Available Sample Space Orderings in a Sequential Test for a detailed description of these sample space orderings.
statistics and their corresponding hypothetical values, the ORDER=MLE option specifies the MLE ordering that compares values in the MLE scale, and the ORDER=STAGEWISE specifies the stagewise ordering that uses counterclockwise ordering around the continuation region. The default is ORDER=STAGEWISE. See the section Available Sample Space Orderings in a Sequential Test for a detailed description of these sample space orderings. - PARMS <(TESTVAR=variable)> =SAS-data-set
names the SAS data set that contains the parameter estimate and its associated standard error for the stage. The data set includes the stage variable _Stage_, the test statistic Estimate, the standard error of the estimate StdErr, and the test statistic scale variable _Scale_. The standard error is are used to derive the information level. If the standard error is not available, the information level derived in the BOUNDARY= data set is used.
The data set also includes the variable Parameter, Effect, Variable, or Parm that contains the test variable specified in the TESTVAR= option. Usually, these test variable values are obtained from analysis output in SAS procedures.
Table Output Options
The following options can be used in the PROC SEQTEST statement to display additional table output. They are listed in alphabetical order.
- CONDPOWER <( CREF=numbers )>
displays conditional powers given the most recently observed statistic under specified hypothetical references, where the numbers
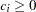 . In the SEQTEST procedure, the conditional power is the probability that the test statistic at the final stage would exceed the rejection critical value given the observed statistic.
. In the SEQTEST procedure, the conditional power is the probability that the test statistic at the final stage would exceed the rejection critical value given the observed statistic. If interim stages exist between the current stage and the final stage, the conditional power is not the conditional probability to reject the null hypothesis
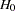 . In this case, you can set the next stage as the final stage, and the conditional power is the conditional probability to reject
. In this case, you can set the next stage as the final stage, and the conditional power is the conditional probability to reject 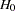 .
. For a one-sided test, the powers are derived under the hypothetical references
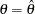 and
and 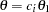 , where
, where 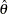 is the observed statistic,
is the observed statistic, 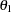 is the alternative reference, and
is the alternative reference, and 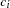 are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided test, the powers are derived under hypothetical references
are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided test, the powers are derived under hypothetical references 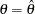 ,
, 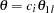 , and
, and 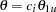 , where
, where 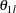 is the lower alternative reference and
is the lower alternative reference and 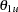 is the upper alternative reference. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5.
is the upper alternative reference. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5. - ERRSPEND
displays the error spending at each stage for each sequential boundary.
- PREDPOWER
displays predictive powers given the most recently observed statistic. The predictive power is the posterior probability that the test statistic at the final stage would exceed the rejection critical value given the observed statistic and a prior distribution of the hypothetical reference. A noninformative prior is used in the procedure.
- PSS <( CREF=numbers ) >
displays powers and expected sample sizes under various hypothetical references, where the numbers
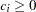 .
. For a one-sided design with the null reference
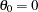 , the power and expected sample sizes under hypotheses
, the power and expected sample sizes under hypotheses 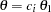 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 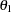 is the alternative reference and
is the alternative reference and 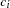 are the values specified in the CREF= option.
are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided design, the power and expected sample sizes under hypotheses
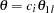 and
and 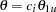 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 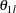 and
and 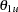 are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5.
are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5. Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only the power and expected sample sizes under hypotheses
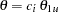 are derived.
are derived. - RCI
displays repeated confidence intervals for the parameter from the observed statistic at each stage. Repeated confidence intervals include both rejection and acceptance confidence intervals.
With the STOP=REJECT or STOP=BOTH option, rejection confidence limits can be derived, and the null hypothesis
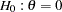 is rejected if the lower rejection confidence limit is greater than
is rejected if the lower rejection confidence limit is greater than 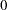 or the upper rejection confidence limit is less than
or the upper rejection confidence limit is less than 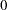 .
. With the STOP=ACCEPT or STOP=BOTH option, acceptance confidence limits can be derived, and the null hypothesis is accepted with alternative hypotheses
 and
and 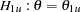 if the upper acceptance confidence limit is less than
if the upper acceptance confidence limit is less than 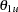 and the lower acceptance confidence limit is greater than
and the lower acceptance confidence limit is greater than 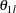 .
. - STOPPROB <( CREF=numbers ) >
displays expected cumulative stopping probabilities under various hypothetical references, where the numbers
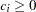 .
. For a one-sided design, expected cumulative stopping probabilities at each stage under hypotheses
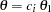 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 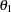 is the alternative reference and
is the alternative reference and 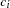 are the values specified in the CREF= option.
are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided design, expected cumulative stopping probabilities at each stage under hypotheses
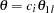 and
and 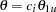 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 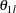 and
and 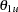 are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only expected cumulative stopping probabilities under hypotheses
are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only expected cumulative stopping probabilities under hypotheses 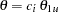 are derived. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5.
are derived. The default is CREF= 0 0.5 1.0 1.5.
Graphics Output Options
This section describes the options for using ODS Graphics with the SEQTEST procedure to create plots. To request these plots, you must specify the ODS GRAPHICS ON statement in addition to the following options in the PROC SEQTEST statement. For more information about the ODS GRAPHICS statement, see Chapter 21, Statistical Graphics Using ODS.
The following options can be used in the PROC SEQTEST statement to display plots with ODS Graphics. They are listed in alphabetical order.
- PLOTS <( ONLY )> <= plot-request>
- PLOTS <( ONLY )> <= ( plot-request < ...plot-request> ) >
specifies options that control the details of the plots. The default is PLOTS=TEST. The global plot option ONLY suppresses the default plots and displays only plots specifically requested.
The plot request options include the following.
- ALL
produces all appropriate plots.
- ASN <( CREF=numbers )>
displays a plot of the average sample numbers (expected sample sizes for nonsurvival data or expected number of events for survival data) under various hypothetical references, where the numbers
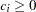 .
. For a one-sided design, expected sample numbers under hypotheses
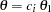 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 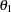 is the alternative reference and
is the alternative reference and 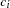 are the values specified in the CREF= option.
are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided design, expected sample numbers under hypotheses
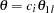 and
and 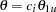 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 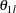 and
and 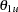 are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only the average sample numbers under hypotheses
are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only the average sample numbers under hypotheses 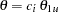 are derived. The default is CREF= 0 to 1.5 by 0.01.
are derived. The default is CREF= 0 to 1.5 by 0.01. - CONDPOWER <( CREF=numbers ) >
displays a plot of conditional powers given the most recently observed statistic under specified hypothetical references, where the numbers
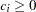 . In the SEQTEST procedure, the conditional power is the probability that the test statistic at the final stage would exceed the rejection critical value given the observed statistic.
. In the SEQTEST procedure, the conditional power is the probability that the test statistic at the final stage would exceed the rejection critical value given the observed statistic. For a one-sided test, the powers are derived under hypothetical references
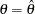 and
and 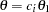 , where
, where 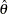 is the observed statistic,
is the observed statistic, 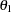 is the alternative reference, and
is the alternative reference, and 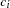 are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided test, the powers are derived under hypothetical references
are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided test, the powers are derived under hypothetical references 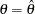 ,
, 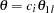 , and
, and 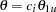 , where
, where 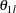 is the lower alternative reference and
is the lower alternative reference and 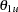 is the upper alternative reference. The default is CREF= 0 to 1.5 by 0.01.
is the upper alternative reference. The default is CREF= 0 to 1.5 by 0.01. - ERRSPEND <( HSCALE=INFO | STAGE ) >
displays a plot of the error spending for all sequential boundaries in the designs simultaneously. You can display the information level (HSCALE=INFO) or the stage number (HSCALE=STAGE) on the horizontal axis. With HSCALE=INFO, the information fractions are used in the plot. The default is HSCALE=STAGE.
- NONE
suppresses all plots.
- POWER <( CREF=numbers ) >
displays a plot of the power curves under various hypothetical references, where the numbers
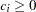 .
. For a one-sided design, powers under hypotheses
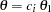 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 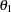 is the alternative reference and
is the alternative reference and 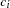 are the values specified in the CREF= option.
are the values specified in the CREF= option. For a two-sided design, powers under hypotheses
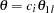 and
and 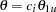 are displayed, where
are displayed, where 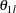 and
and 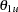 are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only powers under hypotheses
are the lower and upper alternative references, respectively. Note that for a symmetric two-sided design, only powers under hypotheses 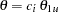 are derived. The default is CREF= 0 to 1.5 by 0.01.
are derived. The default is CREF= 0 to 1.5 by 0.01. - RCI
displays a plot of repeated confidence intervals. Repeated confidence intervals include both rejection and acceptance confidence intervals.
With the STOP=REJECT or STOP=BOTH option, rejection confidence limits can be derived and the null hypothesis
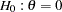 is rejected if the lower rejection confidence limit is greater than
is rejected if the lower rejection confidence limit is greater than 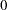 or the upper rejection confidence limit is less than
or the upper rejection confidence limit is less than 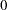 .
. With the STOP=ACCEPT or STOP=BOTH option, acceptance confidence limits can be derived and the null hypothesis is accepted with alternative hypotheses
 and
and 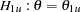 if the upper acceptance confidence limit is less than
if the upper acceptance confidence limit is less than 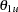 and the lower acceptance confidence limit is greater than
and the lower acceptance confidence limit is greater than 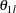 .
. - TEST <( HSCALE=INFO | SAMPLESIZE ) >
displays a plot of the sequential boundaries and test variables. Either the information level (HSCALE=INFO) or the sample size (HSCALE=SAMPLESIZE) is displayed on the horizontal axis. The HSCALE=SAMPLESIZE option is applicable only if the sample size information is available in both the input BOUNDARY= data set and input DATA= data set. The stage number for each stage is displayed inside the plot. The default is HSCALE=INFO.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.