| The PHREG Procedure |
| CLASS Statement |
The CLASS statement names the categorical variables to be used in the analysis. The CLASS statement must precede the MODEL statement. You can specify various options for each variable by enclosing them in parentheses after the variable name. You can also specify global options for the CLASS statement by placing them after a slash (/). Global options are applied to all the variables specified in the CLASS statement. If you specify more than one CLASS statement, the global options specified in any one CLASS statement apply to all CLASS statements. However, individual CLASS variable options override the global options.
- CPREFIX= n
specifies that, at most, the first n characters of a CLASS variable name be used in creating names for the corresponding dummy variables. The default is
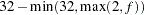 , where
, where 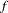 is the formatted length of the CLASS variable.
is the formatted length of the CLASS variable. - DESCENDING
- DESC
- LPREFIX= n
specifies that, at most, the first n characters of a CLASS variable label be used in creating labels for the corresponding dummy variables.
- MISSING
allows a missing value (for example,‘.’ for a numeric variable and blanks for a character variable) as a valid value for the CLASS variable.
- ORDER=DATA | FORMATTED | FREQ | INTERNAL
specifies the sorting order for the categories of cateogrical variables. This ordering determines which parameters in the model correspond to each level in the data, so the ORDER= option can be useful when you use the CONTRAST statement. When the default ORDER=FORMATTED is in effect for numeric variables for which you have supplied no explicit format, the levels are ordered by their internal values. The following table shows how PROC PHREG interprets values of the ORDER= option.
Value of ORDER=
Levels Sorted By
DATA
order of appearance in the input data set
FORMATTED
external formatted value, except for numeric variables with no explicit format, which are sorted by their unformatted (internal) value
FREQ
descending frequency count; levels with the most observations come first in the order
INTERNAL
unformatted value
By default, ORDER=FORMATTED. For FORMATTED and INTERNAL, the sort order is machine dependent. For more information about sorting order, see the chapter on the SORT procedure in the Base SAS Procedures Guide and the discussion of BY-group processing in SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
- PARAM=keyword
- specifies the parameterization method for the categorical variable or variables. Design matrix columns are created from CLASS variables according to the following coding schemes. The default is PARAM=REF. If PARAM=ORTHPOLY or PARAM=POLY, and the CLASS levels are numeric, then the ORDER= option in the CLASS statement is ignored, and the internal, unformatted values are used. See the section CLASS Variable Parameterization for further details.
- EFFECT
specifies effect coding.
- GLM
specifies less-than-full-rank, reference-cell coding; this option can be used only as a global option.
- ORDINAL
specifies the cumulative parameterization for an ordinal CLASS variable.
- POLYNOMIAL | POLY
specifies polynomial coding.- REFERENCE | REF
specifies reference cell coding.- ORTHEFFECT
orthogonalizes PARAM=EFFECT
- ORTHORDINAL
orthogonalizes PARAM=ORDINAL.
- ORTHPOLY
orthogonalizes PARAM=POLYNOMIAL.
- ORTHREF
orthogonalizes PARAM=REFERENCE.
The EFFECT, POLYNOMIAL, REFERENCE, and ORDINAL coding schemes and their orthogonal parameterizations are full-rank parameterization. The REF= option in the CLASS statement determines the reference level for the EFFECT, REFERENCE, and their orthogonal parameterizations.
Parameter names for a CLASS predictor variable are constructed by concatenating the CLASS variable name with the CLASS levels. However, for the POLYNOMIAL and orthogonal parameterizations, parameter names are formed by concatenating the CLASS variable name and keywords that reflect the parameterization.
- REF=’level’ | keyword
specifies the reference level for PARAM=EFFECT or PARAM=REF. For an individual variable, you can specify a specific level of the variable in the REF= option. For a global or individual variable REF= option, you can use one of the following keywords. The default is REF=LAST.
- FIRST
designates the first ordered level as reference.
- LAST
designates the last ordered level as reference.
- TRUNCATE
specifies that class levels should be determined using no more than the first 16 characters of the formatted values of CLASS variables. This is a global option, not an individual CLASS variable option.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.