| The CALIS Procedure |
| Counting the Degrees of Freedom |
In a regression problem, the number of degrees of freedom for the error estimate is the number of observations in the data set minus the number of parameters. The NOBS=, DFR= (RDF=), and DFE= (EDF=) options refer to degrees of freedom in this sense. However, these values are not related to the degrees of freedom of a test statistic used in a covariance or correlation structure analysis. The NOBS=, DFR=, and DFE= options should be used in PROC CALIS to specify only the effective number of observations in the input DATA= data set.
In general, the number of degrees of freedom in a covariance or correlation structure analysis is defined as the difference between the number of nonredundant values  in the observed
in the observed 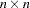 correlation or covariance matrix
correlation or covariance matrix 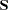 and the number
and the number  of free parameters
of free parameters  used in the fit of the specified model,
used in the fit of the specified model,  . Both values,
. Both values,  and
and  , are counted differently in different situations by PROC CALIS.
, are counted differently in different situations by PROC CALIS.
The number of nonredundant values  is generally equal to the number of lower triangular elements in the
is generally equal to the number of lower triangular elements in the 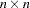 moment matrix
moment matrix 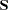 including all diagonal elements, minus a constant
including all diagonal elements, minus a constant  dependent upon special circumstances,
dependent upon special circumstances,
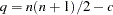 |
The number  is evaluated by adding the following quantities:
is evaluated by adding the following quantities:
If you specify a linear structural equation model containing exogenous manifest variables by using the RAM or LINEQS statement, PROC CALIS adds to
 the number of variances and covariances among these manifest exogenous variables, which are automatically set in the corresponding locations of the central model matrices (see the section Exogenous Manifest Variables).
the number of variances and covariances among these manifest exogenous variables, which are automatically set in the corresponding locations of the central model matrices (see the section Exogenous Manifest Variables). If you specify the DFREDUCE=
 option, PROC CALIS adds the specified number
option, PROC CALIS adds the specified number  to
to  . The number
. The number  can be a negative integer.
can be a negative integer. If you specify the NODIAG option to exclude the fit of the diagonal elements of the data matrix
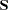 , PROC CALIS adds the number
, PROC CALIS adds the number  of diagonal elements to
of diagonal elements to  .
. If all the following conditions hold, then PROC CALIS adds to
 the number of the diagonal locations:
the number of the diagonal locations: NODIAG and DFREDUC= options are not specified.
A correlation structure is being fitted.
The predicted correlation matrix contains constants on the diagonal.
In some complicated models, especially those use programming statements, PROC CALIS might not be able to detect all the constant predicted values. In such cases, you must specify the DFREDUCE= option to get the correct degrees of freedom.
The number  is the number of different parameter names used in constructing the model if you do not use programming statements to impose constraints on the parameters. Using programming statements in general introduces two kinds of parameters:
is the number of different parameter names used in constructing the model if you do not use programming statements to impose constraints on the parameters. Using programming statements in general introduces two kinds of parameters:
independent parameters, which are used only on the right-hand side of the expressions
dependent parameters, which are used at least once on the left-hand side of the expressions
The independent parameters belong to the parameters involved in the estimation process, whereas the dependent parameters are fully defined by the programming statements and can be computed from the independent parameters. In this case, the number  is the number of different parameter names used in the model specification, but not used in the programming statements, plus the number of independent parameters. The independent parameters and their initial values can be defined in a model specification statement or in a PARMS statement.
is the number of different parameter names used in the model specification, but not used in the programming statements, plus the number of independent parameters. The independent parameters and their initial values can be defined in a model specification statement or in a PARMS statement.
The degrees of freedom are automatically increased by the number of active constraints in the solution. Similarly, the number of parameters are decreased by the number of active constraints. This affects the computation of many fit statistics and indices. Refer to Dijkstra (1992) for a discussion of the validity of statistical inferences with active boundary constraints. If the researcher believes that the active constraints will have a small chance of occurrence in repeated sampling, it might be more suitable to turn off the automatic adjustment by using the NOADJDF option.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.