NPCHART Statement: SHEWHART Procedure
Example 17.19 Specifying Standard Average Proportion
See SHWNP3 in the SAS/QC Sample LibraryIn some situations, a standard (known) value (![]() ) is available for the expected proportion of nonconforming items, based on extensive testing or previous sampling. This example
illustrates how you can specify
) is available for the expected proportion of nonconforming items, based on extensive testing or previous sampling. This example
illustrates how you can specify ![]() to create an
to create an ![]() chart.
chart.
An ![]() chart is used to monitor the number of failing circuits in the data set
chart is used to monitor the number of failing circuits in the data set Circuits, which is introduced in Creating np Charts from Count Data. The expected proportion of failing circuits is known to be ![]() . The following statements create an
. The following statements create an ![]() chart, shown in Output 17.19.1, using
chart, shown in Output 17.19.1, using ![]() to compute the control limits:
to compute the control limits:
title1 'np Chart for Failing Circuits';
title2 'Using Data in CIRCUITS and Standard Value P0=0.02';
proc shewhart data=Circuits;
npchart Fail*Batch / subgroupn = 500
p0 = 0.02
npsymbol = np0
nolegend
needles
odstitle = title
odstitle2 = title2;
label Batch ='Batch Number'
Fail ='Fraction Failing';
run;
Output 17.19.1: An ![]() Chart with Standard Value of
Chart with Standard Value of ![]()
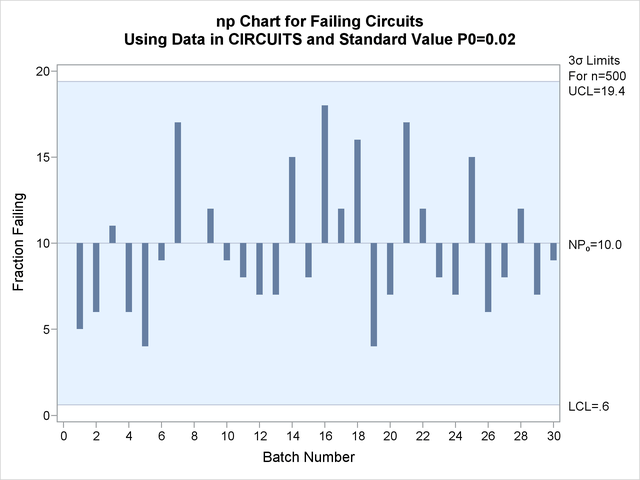
The chart indicates that the process is in control. The P0= option specifies ![]() . The NPSYMBOL= option specifies a label for the central line indicating that the line represents a standard value. The NEEDLES
option connects points to the central line with vertical needles. The NOLEGEND option suppresses the default legend for subgroup
sample sizes. Labels for the vertical and horizontal axes are provided with the LABEL statement. For details concerning axis
labeling, see Axis Labels.
. The NPSYMBOL= option specifies a label for the central line indicating that the line represents a standard value. The NEEDLES
option connects points to the central line with vertical needles. The NOLEGEND option suppresses the default legend for subgroup
sample sizes. Labels for the vertical and horizontal axes are provided with the LABEL statement. For details concerning axis
labeling, see Axis Labels.
Alternatively, you can specify ![]() using the variable
using the variable _P_ in a LIMITS= data set, as follows:
data Climits;
length _var_ _subgrp_ _type_ $8;
_p_ = 0.02;
_subgrp_ = 'Batch';
_var_ = 'Fail';
_type_ = 'STANDARD';
_limitn_ = 500;
proc shewhart data=Circuits limits=Climits;
npchart Fail*Batch / subgroupn = 500
npsymbol = np0
nolegend
needles;
label Batch ='Batch Number'
Fail ='Fraction Failing';
run;
The bookkeeping variable _TYPE_ indicates that _P_ has a standard value. The chart produced by these statements is identical to the chart in Output 17.19.1.
