RCHART Statement: SHEWHART Procedure
Saving Control Limits
[See SHWRCHR in the SAS/QC Sample Library]You can save the control limits for an 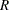 chart in a SAS data set; this enables you to apply the control limits to future data (see Reading Preestablished Control Limits) or modify the limits with a DATA step program.
chart in a SAS data set; this enables you to apply the control limits to future data (see Reading Preestablished Control Limits) or modify the limits with a DATA step program.
The following statements read measurements from the data set Disks (see Creating Range Charts from Raw Data) and save the control limits displayed in Figure 15.72 in a data set named Disklim:
title 'Control Limits for Disk Times';
proc shewhart data=Disks;
rchart Time*Lot / outlimits = Disklim
nochart;
run;
The OUTLIMITS= option names the data set containing the control limits, and the NOCHART option suppresses the display of the chart. The data set Disklim is listed in Figure 15.76.
| Control Limits for Disk Times |
| _VAR_ | _SUBGRP_ | _TYPE_ | _LIMITN_ | _ALPHA_ | _SIGMAS_ | _LCLX_ | _MEAN_ | _UCLX_ | _LCLR_ | _R_ | _UCLR_ | _STDDEV_ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Lot | ESTIMATE | 6 | .004447667 | 3 | 7.94314 | 8.00307 | 8.06299 | 0 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 |
The data set Disklim contains one observation with the limits for process Time. The variables _LCLR_ and _UCLR_ contain the lower and upper control limits, and the variable _R_ contains the central line. The value of _MEAN_ is an estimate of the process mean, and the value of _STDDEV_ is an estimate of the process standard deviation  . The value of _LIMITN_ is the nominal sample size associated with the control limits, and the value of _SIGMAS_ is the multiple of
. The value of _LIMITN_ is the nominal sample size associated with the control limits, and the value of _SIGMAS_ is the multiple of  associated with the control limits. The variables _VAR_ and _SUBGRP_ are bookkeeping variables that save the process and subgroup-variable. The variable _TYPE_ is a bookkeeping variable that indicates whether the values of _MEAN_ and _STDDEV_ are estimates or standard values. The variables _LCLX_ and _UCLX_, which contain the lower and upper control limits for subgroup means, are included so that the data set Disklim can be used to create an
associated with the control limits. The variables _VAR_ and _SUBGRP_ are bookkeeping variables that save the process and subgroup-variable. The variable _TYPE_ is a bookkeeping variable that indicates whether the values of _MEAN_ and _STDDEV_ are estimates or standard values. The variables _LCLX_ and _UCLX_, which contain the lower and upper control limits for subgroup means, are included so that the data set Disklim can be used to create an 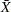 chart (see XRCHART Statement: SHEWHART Procedure). For more information, see OUTLIMITS= Data Set.
chart (see XRCHART Statement: SHEWHART Procedure). For more information, see OUTLIMITS= Data Set.
You can create an output data set containing both control limits and summary statistics with the OUTTABLE= option, as illustrated by the following statements:
title 'Summary Statistics and Control Limit Information';
proc shewhart data=Disks;
rchart Time*Lot / outtable=Disktab
nochart;
run;
The data set Disktab is listed in Figure 15.77.
| Summary Statistics and Control Limit Information |
| _VAR_ | Lot | _SIGMAS_ | _LIMITN_ | _SUBN_ | _LCLR_ | _SUBR_ | _R_ | _UCLR_ | _STDDEV_ | _EXLIM_ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 1 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 2 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 3 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.07 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 4 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 5 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.16 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 6 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.12 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 7 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 8 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 9 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 10 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 11 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 12 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 13 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.13 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 14 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 15 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.13 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 16 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.09 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 17 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 18 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 19 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.18 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 20 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 21 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.14 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 22 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.20 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 23 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 24 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 | |
| Time | 25 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.124 | 0.24847 | 0.048927 |
This data set contains one observation for each subgroup sample. The variables _SUBR_ and _SUBN_ contain the subgroup ranges and subgroup sample sizes. The variables _LCLR_ and _UCLR_ contain the lower and upper control limits, and the variable _R_ contains the central line. The variables _VAR_ and Batch contain the process name and values of the subgroup-variable, respectively. For more information, see OUTTABLE= Data Set. An OUTTABLE= data set can be read later as a TABLE= data set. For example, the following statements read Disktab and display an 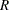 chart (not shown here) identical to the chart in Figure 15.72:
chart (not shown here) identical to the chart in Figure 15.72:
title 'Range Chart for Disk Drive Test Times'; proc shewhart table=Disktab; rchart Time*Lot; run;
Because the SHEWHART procedure simply displays the information in a TABLE= data set, you can use TABLE= data sets to create specialized control charts (see Specialized Control Charts: SHEWHART Procedure). For more information, see TABLE= Data Set.
