| The NLP Procedure |
PROFILE Statement
- PROFILE parms [ / [ ALPHA= values ] [ options ] ] ;
where parms is given in the format pnam_1 pnam_2 ... pnam_n, and values is the list of
The PROFILE statement
- writes the
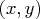 coordinates of profile points for
each of the listed parameters to the
OUTEST= data set
coordinates of profile points for
each of the listed parameters to the
OUTEST= data set
- displays, or writes to the OUTEST= data set,
the profile likelihood confidence limits (PL CLs) for the listed
parameters for the specified
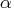 values.
If the approximate standard errors are available, the
corresponding Wald confidence limits can be computed.
values.
If the approximate standard errors are available, the
corresponding Wald confidence limits can be computed.
The keyword PROFILE must be followed by the names of parameters for which the profile or the PL CLs should be computed. If the parameter name list is empty, the profiles and PL CLs for all parameters are computed. Then, optionally, the
profile l11-l15 u1-u5 c /
alpha= .9 to .1 by -.1 .09 to .01 by -.01;
Duplicate A number of additional options can be specified.
- FFACTOR=
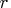
-
specifies the factor relating the discrepancy
function
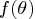 to the
to the 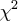 quantile. The default
value is
quantile. The default
value is 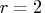 .
.
- FORCHI= F | CHI
-
defines the scale for the
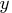 values written to
the OUTEST= data set. For FORCHI=F, the
values written to
the OUTEST= data set. For FORCHI=F, the 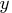 values
are scaled to the values of the log likelihood function
values
are scaled to the values of the log likelihood function 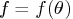 ;
for FORCHI=CHI, the
;
for FORCHI=CHI, the 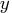 values are scaled so that
values are scaled so that
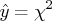 . The default value is FORCHI=F.
. The default value is FORCHI=F.
- FEASRATIO=
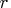
-
specifies a factor of the Wald confidence limit
(or an approximation of it if standard errors are not computed)
defining an upper bound for the search for confidence limits.
In general, the range of
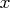 values in the profile graph is
between
values in the profile graph is
between 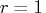 and
and 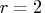 times the length of the corresponding
Wald interval. For many examples, the
times the length of the corresponding
Wald interval. For many examples, the 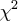 quantiles
corresponding to small
quantiles
corresponding to small 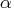 values define a
values define a 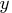 level
level
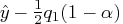 , which is too far away
from
, which is too far away
from 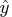 to be reached by
to be reached by 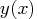 for
for 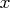 within the
range of twice the Wald confidence limit. The search for an
intersection with such a
within the
range of twice the Wald confidence limit. The search for an
intersection with such a 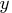 level at a practically infinite
value of
level at a practically infinite
value of 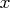 can be computationally expensive.
A smaller
value for
can be computationally expensive.
A smaller
value for 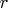 can speed up computation time by restricting
the search for confidence limits to a region closer to
can speed up computation time by restricting
the search for confidence limits to a region closer to 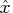 .
The default value of
.
The default value of 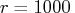 practically disables the
FEASRATIO= option.
practically disables the
FEASRATIO= option.
- OUTTABLE
-
specifies that the complete set
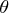 of parameter estimates rather than only
of parameter estimates rather than only 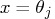 for each
confidence limit is written to the OUTEST= data
set. This output can be helpful for further analyses on how small
changes in
for each
confidence limit is written to the OUTEST= data
set. This output can be helpful for further analyses on how small
changes in 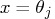 affect the changes in the
affect the changes in the 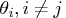 .
.
For some applications, it may be computationally less expensive to compute the PL confidence limits for a few parameters than to compute the approximate covariance matrix of many parameters, which is the basis for the Wald confidence limits. However, the computation of the profile of the discrepancy function and the corresponding CLs in general will be much more time-consuming than that of the Wald CLs.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.