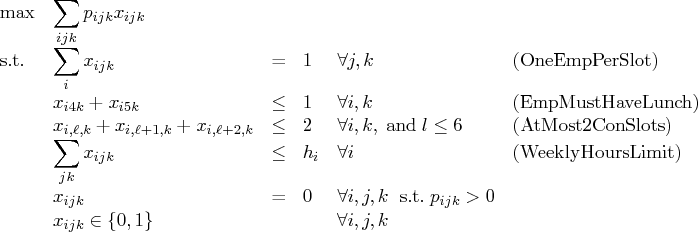| The Mixed Integer Linear Programming Solver |
Example 9.1: Scheduling
The following application has been adapted from Example 3.13.
Scheduling is a common application area where mixed integer linear programming techniques are used. In this example, you have eight one-hour time slots in each of five days. You have to assign four employees to these time slots so that each slot is covered on every day. You allow the employees to specify preference data for each slot on each day. In addition, the following constraints must be satisfied:
- Each employee has some time slots for which he or she is unavailable (OneEmpPerSlot).
- Each employee must have either time slot 4 or time slot 5 off for lunch (EmpMustHaveLunch).
- Each employee can work at most two time slots in a row (AtMost2ConSlots).
- Each employee can work only a specified number of hours in the week (WeeklyHoursLimit).
The following data set preferences gives the preferences for each individual, time slot, and day. A 10 represents the most desirable time slot, and a 1 represents the least desirable time slot. In addition, a 0 indicates that the time slot is not available. The data set maxhours gives the maximum number of hours each employee can work per week.
data preferences;
input name $ slot mon tue wed thu fri;
datalines;
marc 1 10 10 10 10 10
marc 2 9 9 9 9 9
marc 3 8 8 8 8 8
marc 4 1 1 1 1 1
marc 5 1 1 1 1 1
marc 6 1 1 1 1 1
marc 7 1 1 1 1 1
marc 8 1 1 1 1 1
mike 1 10 9 8 7 6
mike 2 10 9 8 7 6
mike 3 10 9 8 7 6
mike 4 10 3 3 3 3
mike 5 1 1 1 1 1
mike 6 1 2 3 4 5
mike 7 1 2 3 4 5
mike 8 1 2 3 4 5
bill 1 10 10 10 10 10
bill 2 9 9 9 9 9
bill 3 8 8 8 8 8
bill 4 0 0 0 0 0
bill 5 1 1 1 1 1
bill 6 1 1 1 1 1
bill 7 1 1 1 1 1
bill 8 1 1 1 1 1
bob 1 10 9 8 7 6
bob 2 10 9 8 7 6
bob 3 10 9 8 7 6
bob 4 10 3 3 3 3
bob 5 1 1 1 1 1
bob 6 1 2 3 4 5
bob 7 1 2 3 4 5
bob 8 1 2 3 4 5
;
data maxhours;
input name $ hour;
datalines;
marc 20
mike 20
bill 20
bob 20
;
Using PROC OPTMODEL, you can model and solve the scheduling problem as follows.
proc optmodel presolver=none;
/* read in the preferences and max hours from the data sets */
set <string,num> DailyEmployeeSlots;
set <string> Employees;
set <num> TimeSlots = (setof {<name,slot> in DailyEmployeeSlots} slot);
set <string> WeekDays = {"mon","tue","wed","thu","fri"};
num WeeklyMaxHours{Employees};
num PreferenceWeights{DailyEmployeeSlots,Weekdays};
num NSlots = card(TimeSlots);
read data preferences into DailyEmployeeSlots=[name slot]
{day in Weekdays} <PreferenceWeights[name,slot,day] = col(day)>;
read data maxhours into Employees=[name] WeeklyMaxHours=hour;
/* declare the binary assignment variable x[i,j,k] */
var Assign{<name,slot> in DailyEmployeeSlots, day in Weekdays} binary;
/* for each p[i,j,k] = 0, fix x[i,j,k] = 0 */
for {<name,slot> in DailyEmployeeSlots, day in Weekdays:
PreferenceWeights[name,slot,day] = 0}
fix Assign[name,slot,day] = 0;
/* declare the objective function */
max TotalPreferenceWeight =
sum{<name,slot> in DailyEmployeeSlots, day in Weekdays}
PreferenceWeights[name,slot,day] * Assign[name,slot,day];
/* declare the constraints */
con OneEmpPerSlot{slot in TimeSlots, day in Weekdays}:
sum{name in Employees} Assign[name,slot,day] = 1;
con EmpMustHaveLunch{name in Employees, day in Weekdays}:
Assign[name,4,day] + Assign[name,5,day] <= 1;
con AtMost2ConsSlots{name in Employees, start in 1..NSlots-2,
day in Weekdays}:
Assign[name,start,day] + Assign[name,start+1,day]
+ Assign[name,start+2,day] <= 2 ;
con WeeklyHoursLimit{name in Employees}:
sum{slot in TimeSlots, day in Weekdays} Assign[name,slot,day]
<= WeeklyMaxHours[name];
/* solve the model */
solve with milp;
/* clean up the solution */
for {<name,slot> in DailyEmployeeSlots, day in Weekdays}
Assign[name,slot,day] = round(Assign[name,slot,day],1e-6);
create data report from [name slot]={<name,slot> in DailyEmployeeSlots:
max {day in Weekdays} Assign[name,slot,day] > 0}
{day in Weekdays} <col(day)=(if Assign[name,slot,day] > 0
then Assign[name,slot,day] else .)>;
quit;
The following code demonstrates how to use the TABULATE procedure to display a schedule showing how the eight time slots are covered for the week.
title 'Reported Solution';
proc format;
value xfmt 1=' xxx ';
run;
proc tabulate data=report;
class name slot;
var mon--fri;
table (slot * name), (mon tue wed thu fri)*sum=' '*f=xfmt.
/misstext=' ';
run;
The output from the preceding code is displayed in Output 9.1.1.
Output 9.1.1: Scheduling Reported Solution
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.