| Language Reference |
EIGVAL Function
computes eigenvalues
- EIGVAL(
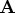 )
)
where ![]() is a square numeric matrix.
is a square numeric matrix.
The EIGVAL function returns a column vector
of the eigenvalues of ![]() .
See the description of the EIGEN subroutine for more details.
.
See the description of the EIGEN subroutine for more details.
The following code computes Example 7.1.1 from Golub and Van Loan (1989):
a = { 67.00 177.60 -63.20 ,
-20.40 95.88 -87.16 ,
22.80 67.84 12.12 };
val = EIGVAL(a);
print val;
The matrix produced containing the eigenvalues is as follows:
VAL
75 100
75 -100
25 0
Notice that A symmetric example follows:
x={1 1,1 2,1 3,1 4};
xpx=t(x)*x;
a=eigval(xpx); /* xpx is a symmetric matrix */
The matrix produced containing the eigenvalues is as follows:
A 2 rows 1 col (numeric)
33.401219
0.5987805
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.