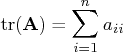| Language Reference |
EIGEN Call
computes eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- CALL EIGEN( eigenvalues, eigenvectors,
 )
<VECL="vl">;
)
<VECL="vl">;
where
The EIGEN call returns the following values:
- eigenvalues
- a matrix to contain the eigenvalues of the input matrix.
- eigenvectors
- names a matrix to contain the right eigenvectors of the input matrix.
- vl
- is an optional
 matrix containing
the left eigenvectors of
matrix containing
the left eigenvectors of  in the same
manner that eigenvectors contains the right eigenvectors.
in the same
manner that eigenvectors contains the right eigenvectors.
The EIGEN subroutine computes eigenvalues, a matrix containing the eigenvalues of
If
The EIGEN subroutine also computes eigenvectors, a matrix. If
The eigenvalues of a matrix
The trace of
An eigenvector is a nonzero vector,
The following are properties of the unsymmetric real eigenvalue problem, in which the real matrix
- The eigenvalues of an unsymmetric
matrix
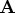 can be complex.
If
can be complex.
If 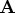 has a complex
eigenvalue
has a complex
eigenvalue 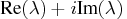 , then the
conjugate complex value
, then the
conjugate complex value  is also an eigenvalue of
is also an eigenvalue of 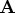 .
. - The right and left eigenvectors corresponding
to a real eigenvalue of
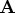 are real.
The right and left eigenvectors corresponding to conjugate
complex eigenvalues of
are real.
The right and left eigenvectors corresponding to conjugate
complex eigenvalues of 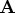 are also conjugate complex.
are also conjugate complex.
- The left eigenvectors of
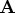 are the same as the
complex conjugate right eigenvectors of
are the same as the
complex conjugate right eigenvectors of  .
.
The three routines, EIGEN, EIGVAL, and EIGVEC, use the following test of symmetry for a square argument matrix
- Select the entry of
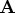 with the largest magnitude:
with the largest magnitude:
- Multiply the value of
 by the square
root of the machine precision
by the square
root of the machine precision 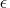 .
(The value of
.
(The value of 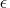 is the largest value
stored in double precision that, when added
to 1 in double precision, still results in 1.)
is the largest value
stored in double precision that, when added
to 1 in double precision, still results in 1.)
- The matrix
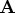 is considered unsymmetric
if there exists at least one pair of symmetric entries
that differs in more than
is considered unsymmetric
if there exists at least one pair of symmetric entries
that differs in more than  ,
,
Consider the following statement:
call eigen(m,e,a);
If In statistical applications, nonsymmetric matrices for which
eigenvalues are desired are usually of the form ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are symmetric.
The eigenvalues
are symmetric.
The eigenvalues ![]() and eigenvectors
and eigenvectors
![]() of
of ![]() can be obtained
by using the GENEIG subroutine or as follows:
can be obtained
by using the GENEIG subroutine or as follows:
f=root(einv);
a=f*h*f';
call eigen(l,w,a);
v=f'*w;
The computation can be checked by forming the residuals. Here
is the code:
r=einv*h*v-v*diag(l);
The values in The following code computes the eigenvalues and left and right eigenvectors of a nonsymmetric matrix with four real and four complex eigenvalues:
A = {-1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0,
-2 -1 0 0 0 0 0 0,
0 0 0.2379 0.5145 0.1201 0.1275 0 0,
0 0 0.1943 0.4954 0.1230 0.1873 0 0,
0 0 0.1827 0.4955 0.1350 0.1868 0 0,
0 0 0.1084 0.4218 0.1045 0.3653 0 0,
0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2,
0 0 0 0 0 0 -2 0 };
call eigen(val,rvec,A) levec='lvec';
The sorted eigenvalues of this matrix are as follows:
VAL
1 1.7320508
1 -1.732051
1 0
0.2087788 0
0.0222025 0
0.0026187 0
-1 2
-1 -2
You can verify the correctness of the left and right eigenvector
computation by using the following code:
/* verify right eigenvectors are correct */
vec = rvec;
do j = 1 to ncol(vec);
/* if eigenvalue is real */
if val[j,2] = 0. then do;
v = a * vec[,j] - val[j,1] * vec[,j];
if any( abs(v) > 1e-12 ) then
badVectors = badVectors || j;
end;
/* if eigenvalue is complex with positive imaginary part */
else if val[j,2] > 0. then do;
/* the real part */
rp = val[j,1] * vec[,j] - val[j,2] * vec[,j+1];
v = a * vec[,j] - rp;
/* the imaginary part */
ip = val[j,1] * vec[,j+1] + val[j,2] * vec[,j];
u = a * vec[,j+1] - ip;
if any( abs(u) > 1e-12 ) | any( abs(v) > 1e-12 ) then
badVectors = badVectors || j || j+1;
end;
end;
if ncol( badVectors ) > 0 then
print "Incorrect right eigenvectors:" badVectors;
else print "All right eigenvectors are correct";
Similar code can be written to verify the left eigenvectors, using the
fact that the left eigenvectors of ![]() are the same as the complex
conjugate right eigenvectors of
are the same as the complex
conjugate right eigenvectors of ![]() . Here is the code:
. Here is the code:
/* verify left eigenvectors are correct */
vec = lvec;
do j = 1 to ncol(vec);
/* if eigenvalue is real */
if val[j,2] = 0. then do;
v = a` * vec[,j] - val[j,1] * vec[,j];
if any( abs(v) > 1e-12 ) then
badVectors = badVectors || j;
end;
/* if eigenvalue is complex with positive imaginary part */
else if val[j,2] > 0. then do;
/* Note the use of complex conjugation */
/* the real part */
rp = val[j,1] * vec[,j] + val[j,2] * vec[,j+1];
v = a` * vec[,j] - rp;
/* the imaginary part */
ip = val[j,1] * vec[,j+1] - val[j,2] * vec[,j];
u = a` * vec[,j+1] - ip;
if any( abs(u) > 1e-12 ) | any( abs(v) > 1e-12 ) then
badVectors = badVectors || j || j+1;
end;
end;
if ncol( badVectors ) > 0 then
print "Incorrect left eigenvectors:" badVectors;
else print "All left eigenvectors are correct";
The EIGEN call performs most of its computations in the memory allocated for returning the eigenvectors.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.