| Language Reference |
VARMACOV Call
computes the theoretical cross-covariance matrices for
a stationary VARMA(![]() ) model
) model
- CALL VARMACOV( cov, phi, theta, sigma <, p, q, lag> );
The inputs to the VARMACOV subroutine are as follows:
- phi
- specifies a
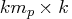 matrix,
matrix, 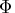 ,
containing the autoregressive coefficient matrices,
where
,
containing the autoregressive coefficient matrices,
where 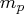 is the number of elements in the subset
of the AR order and
is the number of elements in the subset
of the AR order and 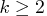 is the number of variables.
All the roots of
is the number of variables.
All the roots of 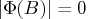 should be greater than one in absolute value,
where
should be greater than one in absolute value,
where 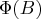 is the finite order matrix polynomial in the backshift
operator
is the finite order matrix polynomial in the backshift
operator 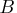 , such that
, such that 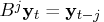 .
You must specify either phi or theta.
.
You must specify either phi or theta.
- theta
- specifies a
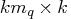 matrix
containing the moving-average coefficient matrices,
where
matrix
containing the moving-average coefficient matrices,
where 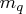 is the number of the elements in the subset
of the MA order.
You must specify either phi or theta.
is the number of the elements in the subset
of the MA order.
You must specify either phi or theta.
- sigma
- specifies a
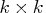 symmetric positive-definite covariance matrix
of the innovation series.
If sigma is not specified, then an identity matrix is used.
symmetric positive-definite covariance matrix
of the innovation series.
If sigma is not specified, then an identity matrix is used.
- p
- specifies the subset of the AR order. The quantity
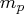 is defined as
is defined as
If you do not specify p, the default subset is p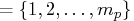 .
.
For example, consider a 4-dimensional vector time series, and phi is a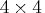 matrix.
If you specify p=1 (the default, since
matrix.
If you specify p=1 (the default, since 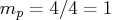 ),
the VARMACOV subroutine computes the theoretical
cross-covariance matrices of VAR(1) as
),
the VARMACOV subroutine computes the theoretical
cross-covariance matrices of VAR(1) as
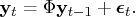
If you specify p=2, the VARMACOV subroutine computes the cross-covariance matrices of VAR(2) as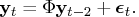
Let phi![= [ \phi_1', \phi_2' ]'](images/langref_langrefeq1354.gif) be an
be an 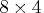 matrix.
If you specify p
matrix.
If you specify p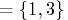 , the VARMACOV subroutine computes
the cross-covariance matrices of VAR(3) as
, the VARMACOV subroutine computes
the cross-covariance matrices of VAR(3) as
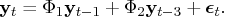 If you do not specify p, the VARMACOV subroutine computes
the cross-covariance matrices of VAR(2) as
If you do not specify p, the VARMACOV subroutine computes
the cross-covariance matrices of VAR(2) as
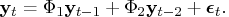
- q
- specifies the subset of the MA order. The quantity
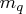 is defined as
is defined as
If you do not specify q, the default subset is q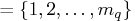 .
.
The usage of q is the same as that of p. - lag
- specifies the length of lags, which must be a positive number.
If
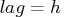 , the VARMACOV computes the cross-covariance matrices
from lag zero to lag
, the VARMACOV computes the cross-covariance matrices
from lag zero to lag 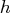 .
By default, lag = 12.
.
By default, lag = 12.
The VARMACOV subroutine returns the following value:
- cov
- is a
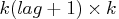 matrix that contains the theoretical
cross-covariance matrices of the VARMA(
matrix that contains the theoretical
cross-covariance matrices of the VARMA(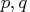 ) model.
) model.
Consider the following bivariate (
phi = { 1.2 -0.5, 0.6 0.3 };
theta= {-0.6 0.3, 0.3 0.6 };
sigma= { 1.0 0.5, 0.5 1.25};
call varmacov(cov, phi, theta, sigma) lag=5;
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.