Validation Framework Overview
The SAS Clinical Standards
Toolkit validation assesses the compliance of data, and the metadata
describing the data, with an accepted reference standard. It assesses
the consistency of values in a specific column, between columns, across
records in a specific data set, and across data sets. The primary
output is a Results data set that itemizes the process findings, and
an optional Metrics data set that summarizes the results.
The SAS Clinical Standards
Toolkit provides a framework to build a process. The process uses
inputs or process controls to evaluate the compliance of source data
with a reference standard. Each SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit process
uses a SAS program file to point to a SASReferences control data set,
and to execute a primary action SAS macro (such as %SDTM_VALIDATE).
This SAS program file is referred to as a driver program in this document.
Generally, validation
is performed by running SAS macros against the standard, which is
represented by SAS files. Validation of some standards, such as CDISC
CRT-DDS, might include validating files that are not SAS files (such
as define.xml).
The following display shows a SAS Clinical
Standards Toolkit validation process:
Components of a SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit Validation Process
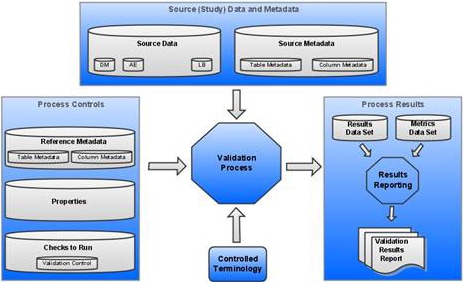
Each component is fully
described in the following sections.
-
Source Data is a set of SAS data sets in one or more libraries that collectively represents a clinical study. These SAS data sets are referred to as study domains or study data sets. One or more source data sets are required by a typical SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit validation process. However, it is possible to test only the structural compliance of source metadata by limiting validation to a subset of validation checks.
-
Source Metadata is a set of SAS data sets in one or more libraries that provide metadata about the source data. The source metadata is typically in a format specific to a standard. For example, metadata about source data sets might be captured in a source_tables data set. Metadata about columns in those source data sets might be captured in a source_columns data set.
-
Process Controls is the set of instructions that each SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit process uses to perform a specific action. These instructions might be provided in a varied number and in various type of files. For a SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit validation process, these files include:
-
Reference Metadata is a set of SAS data sets that provide metadata. This metadata defines a specific standard and is typically in a format specific to a standard. For example, metadata about data sets might be captured in a reference_tables data set. Metadata about columns in those data sets might be captured in a reference_columns data set. For an example, see Sample reference_tables Record (CDISC SDTM 3.2) and Sample reference_columns Record (CDISC SDTM 3.2).
-
Properties are a series of name-value pairs that are translated into SAS global macro variables. These macro variables are available for the duration of the SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit process. Properties might be defined in a varied number of files. Both text file format and SAS data set format are supported. For information about a sample validation.properties file, see Validation Check Metadata: Validation Master. For information about the SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit global macro variables, see Global Macro Variables.
-
Set of Checks to Run is a set of checks that represent all or some of the checks defined for a standard. Each check provides metadata that is used by the validation code to perform a specific compliance assessment.
-
-
Controlled Terminology is an optional set of lookup values against which source data columns can be evaluated. These values can be in the form of SAS format catalogs or SAS data sets.
-
Results are presented in a Results data set that itemizes the process findings, and in a Metrics data set that summarizes the results. The Results data set usually contains a record indicating that each check was run successfully without error, or it contains a record that itemizes the errors detected. Information about the process also might be included. The generation of a Metrics data set is conditional based on property file settings.
The SAS Clinical Standards
Toolkit validation makes these basic assumptions:
-
There is some combination of source data and metadata available as SAS files that you want to validate.
-
A reference standard has been defined with which the source data and metadata are to be compared. The SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit provides representative reference metadata for each supported standard.
-
The source data can be in a varied number of SAS files, and those SAS files can have any form. However, the metadata describing the source data must accurately represent the source data. The metadata must be in a form specific to a supported standard and defined by the SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit.
-
A set of validation checks must be defined, and the validation checks must conform to a generic SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit SAS data set structure. The SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit provides a representative set of validation checks for each supported standard.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.