



|
Setting Up a COM/DCOM Server |


|
Follow the configuration instructions for configuring permissions on either for Windows NT 4, or for Windows 2000 and XP.
On your remote IOM server, start dcomcnfg.
Select SAS: IOM DCOM Servers, and then select Properties.
Select the Security tab, and add launch and access permissions for the following users:
If your DCOM IOM server is on Windows NT 4, this configuration is sufficient.
If your DCOM IOM server is on Windows 2000 or XP, you must change the identity of the user that will run the DCOM server process. The NT Anonymous Logon user account on Windows NT 4 does not have sufficient permission to run SAS on a Windows 2000 or XP server.
For Windows 2000 or XP, to change the user that will run the DCOM server process:
If you select This user, enter a valid user account that has permission to run SAS on your server.
For Windows 2000 and XP, IIS processes are configured as COM+ Applications. Therefore, you must configure an additional layer of security prior to accessing a remote IOM DCOM server from an ASP.
By default, an application in IIS 5 uses Medium (Pooled) application protection, and, as a result, it runs under the IIS Out of Process Pooled Applications COM+ application. In a typical IIS 5 installation, this application is launched by the IWAM _<machine_name> account.
The IWAM_<machine name> account exists on the \\<machine name>* domain on which IIS is running. But, when the IWAM_<machine name> attempts to authenticate on the remote server as the IWAM_<machine name> user, access is denied because the account does not exist on the remote server. The COM+ application must run under an account that exists on both machines. There are two ways to achieve this access:
Important Note: It is recommended that you DO NOT change the launching user of the IIS Out of Process Pooled Applications. Changing the launching user will cause all of your pooled IIS applications to launch as a specific user and could cause problems. In addition, if you change the launching user from the IWAM account to another user, it is difficult to revert back to the IWAM account. You might want to revert back to the IWAM account if another application fails because you changed this launching user. For these reasons, we recommend that you change to High (Isolated) Application Protection for the IIS Application that will access SAS using DCOM. This will create a new COM+ Application that you can configure independently, without affecting any other pooled applications. If you change the launching user of the IIS Out of Process Pooled Application, it is possible to revert back to the IWAM account. For more information about resetting the IWAM password, see PRB: Configured Identity is Incorrect for IWAM Account (Q297989) on the Microsoft Web site. |
To set up remote DCOM and COM+:
To run your application as an isolated process:
Start Internet Services Manager by clicking
Start  Settings
Settings
 Control Panel.
Open Administrative Tools and click Internet Services Manager.
Control Panel.
Open Administrative Tools and click Internet Services Manager.
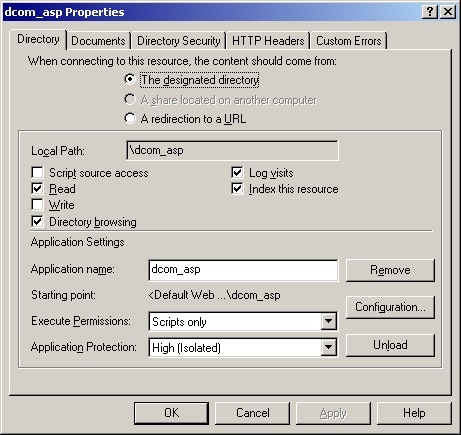
Select the directory where your ASP is located.
Right-click, and select Properties to view the properties for your directory.
On the Directory tab under Application Settings, change Application Protection to High (Isolated).
Note: Be sure to read the Important Note under Configuring Windows 2000 or XP with IIS 5 Remote DCOM and COM+ Settings. It is recommended that you do NOT change the launching user of the IIS Out-Of-Process Pooled Applications.
To configure the COM+ application:
 Settings
Settings
 Control Panel.
Control Panel. 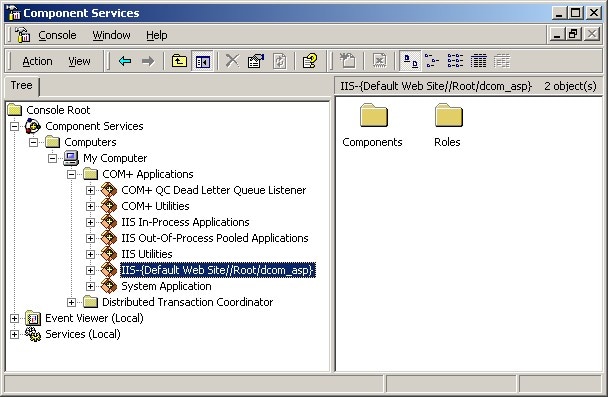
Right-click the appropriate COM+ application, and select Properties.
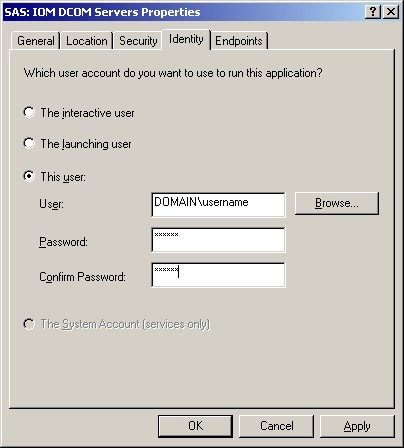
Select the Identity tab, and do one of the following:
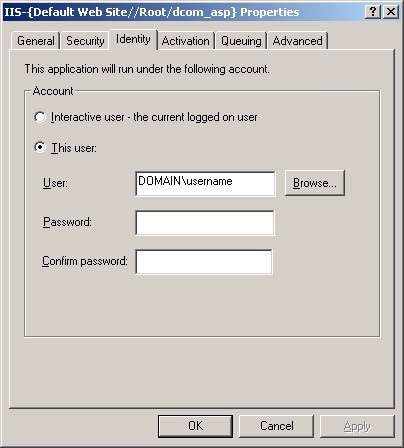
You must give the user who launches the IIS COM+ application permission to access and launch the remote IOM DCOM server. To set the permissions:
On your remote IOM DCOM server, start dcomcnfg.
Select SAS: IOM DCOM Servers, and then select Properties.
Select the Security tab, and add launch and access permissions for the user who is launching your IIS COM+ application.
Add access permissions for
Network (users accessing this object remotely)
found in the \\<machine name>* domain.
These COM/DCOM configurations will work for most simple setups. There are many other ways to configure IIS, DCOM and COM+ that might better suit your specific needs. The following documents and books on the World Wide Web provide additional information about IIS, DCOM, COM+ as well as information about developing ASP applications that use COM objects. There are also many other resources for Active Server Page developers available on the MSDN Web site.

|
Setting Up a COM/DCOM Server |


|