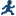Time Series Exploration Task
About the Time Series Exploration Task
The Time Series Exploration task creates graphs and statistics that enable you to
view and analyze your time series data.
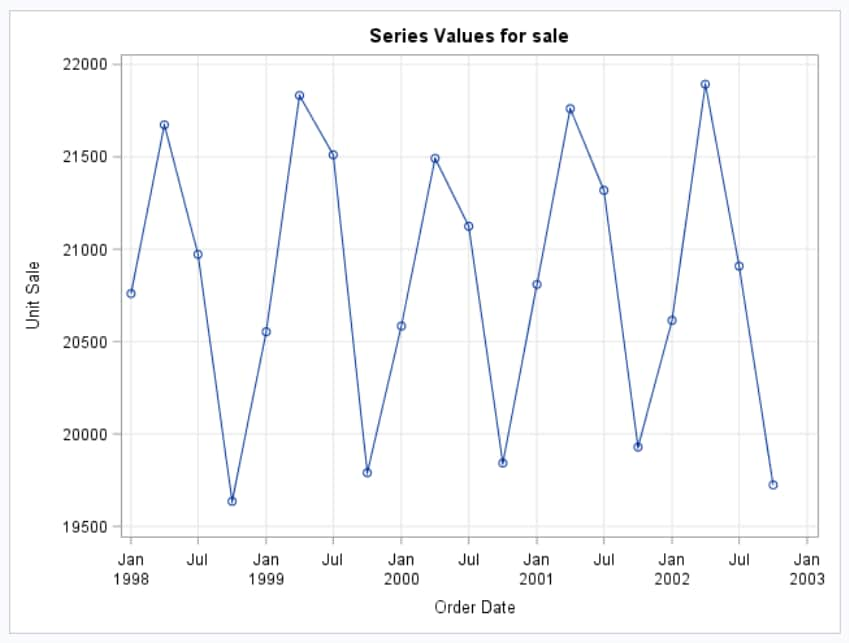
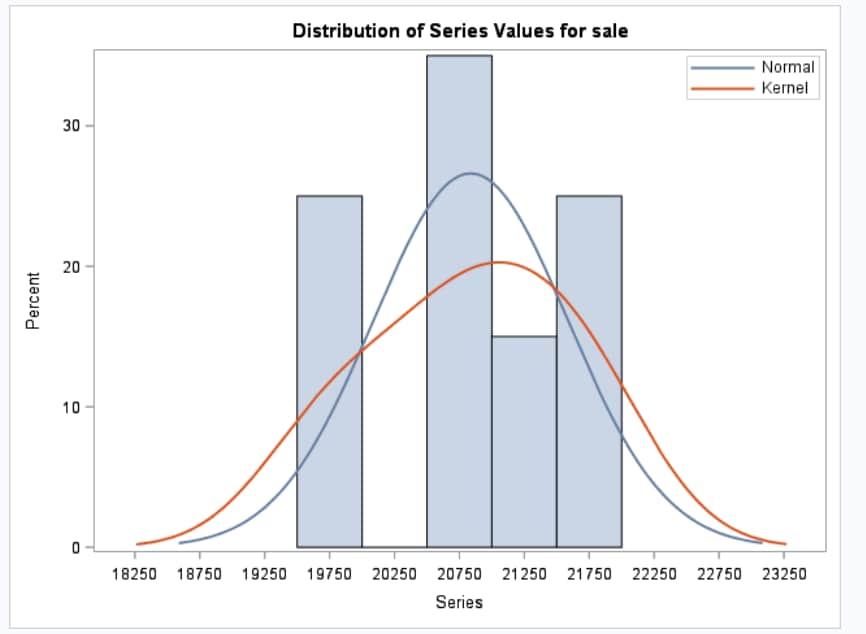
Example: Exploring the SASHELP.PRICEDATA Data Set
To create this example:
-
-
-
Under the Roles heading, locate the Transformations table. For the sale variable, find the Accumulation drop-down list, and select Sum as the accumulation method.
-
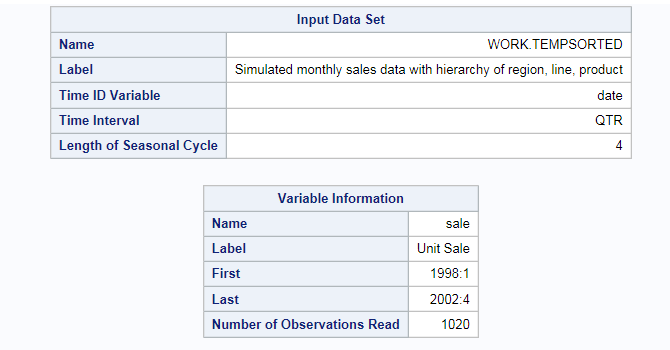
The first part of the
results describes the input data set. This information shows the name
and interval of the time ID variable and information about the dependent
variable.
Assigning Data to Roles
To run the Time Series
Exploration task, you must assign a column to the Dependent
variable role.
|
Role
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Roles
|
|
|
Dependent
variable
|
specifies the dependent variable.
|
|
Independent
variables
|
specifies any explanatory, input, predictor, or causal factor variables. You can assign
only numeric variables to this role.
|
|
Transformations
|
specifies the transformations and simple differencing for the dependent and independent variables. If you assign a variable to the Time ID role, you can also specify an accumulation method. If the season length is greater
than 1, you can specify seasonal differencing.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Time ID
|
specifies the column
that contains the time ID values.
|
|
Properties
|
|
|
Interval
|
specifies the interval
for the time ID variable. For
more information about SAS time intervals, see Understanding SAS Time Intervals.
|
|
Multiplier
|
specifies the multiplier for the time interval. By default, the multiplier is 1. This value cannot be negative.
|
|
Shift
|
specifies the shift
for the time interval. By default, the shift is 1. This value cannot
be negative.
|
|
Season length
|
specifies the seasonality of the time interval. The default value depends on the time interval.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Season length
|
enables you to specify
the seasonality of the data when you do not assign a time ID variable.
|
|
Group analysis
by
|
lists the variable or
variables that you want to use as the classification (BY) variables.
|
Setting the Analyses Options
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Series Plots
|
|
|
You can include these series plots in your results:
|
|
|
Statistics
|
|
|
You can include these
statistics in your results:
|
|
|
Autocorrelation Analysis
|
|
|
Perform
autocorrelation analysis
|
specifies to include an autocorrelation analysis in the results.
|
|
Select plots
to display
|
specifies the plots to display in the results. By default, the results show the autocorrelation analysis
panel. However, you can select whether to include these plots in the results as well:
|
|
Number of
lags
|
specifies the lag values.
By default, the number of lags is 0.
|
|
Cross-Correlation Analysis
Note: To perform a cross-correlation
analysis, you must assign a variable to the Independent
variables role.
|
|
|
Perform
cross-correlation analysis
|
specifies to include a cross-correlation analysis in the results.
|
|
Plots
|
specifies the plots to include in the results. A cross-series plot is included by default. You can also include a cross-correlation function plot and a normalized cross-correlation function plot.
|
|
Decomposition Analysis
Note: To perform a decomposition
analysis, the seasonal cycle length must be greater than 1.
|
|
|
Perform
decomposition analysis
|
specifies to include a decomposition analysis in the results.
|
|
Select plots
to display
|
specifies the plots to include in the results. By default, the decomposition panel is included. You can choose to include these plots as well:
|
|
Decomposition
method
|
specifies the decomposition method to use when creating the selected decomposition analysis plots.
|
|
Spectral Density Analysis
|
|
|
Spectral
density estimate plot
|
specifies whether to include a spectral density plot in the results.
|
|
Minimum
period
|
specifies the minimum period to include in the spectral density plot. This value must
be an integer greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 32,767.
|
|
Details
|
|
|
Adjust the
series by its mean prior to the analysis
|
specifies whether the series should be adjusted by its mean before performing the
Fourier decomposition.
|
|
Analysis
domain
|
specifies how the smoothing
function is interpreted. You can choose from these options:
|
|
Kernel Specifications
|
|
|
Kernel function
|
specifies the kernel function to use in the analysis. By default, no kernel function is specified. You can choose
from these options:
|
|
Scale coefficient
|
specifies the scale coefficient for the kernel function.
|
|
Exponent
|
specifies the exponent for the kernel function.
|
|
Unit Root Test Analysis
|
|
|
Perform
augmented Dickey-Fuller test
|
specifies whether to
perform an augmented Dickey-Fuller test.
|
|
Augmenting
order
|
specifies the augmenting order for the Dickey-Fuller test. This value must be an integer
greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1,000.
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.