Using Graphs to Display Results
Overview of the Graph Types
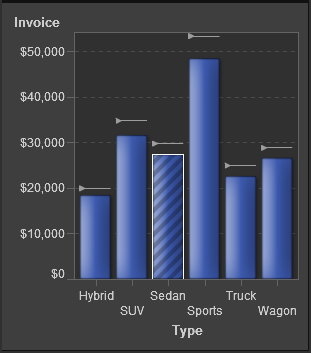
About Targeted Bar Charts
A targeted
bar chart is a variation
of the bar chart that has pointers to target values. In A Targeted Bar Chart, the pointers appear above each bar.
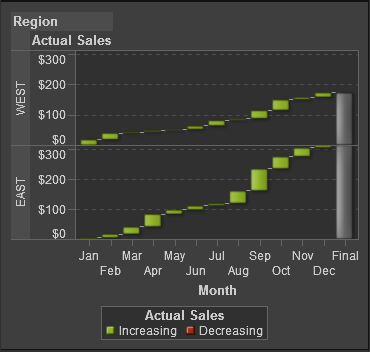
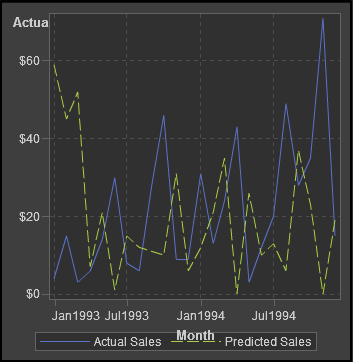
About Waterfall Charts
A waterfall
chart shows how the initial value of a measure increases
or decreases during a series of operations or transactions. (This
chart is also called a progressive bar chart.) The first bar begins
at the initial value, and each subsequent bar begins where the previous
bar ends. The length and direction of a bar indicates the magnitude
and type (positive or negative, for example) of the operation or transaction.
The resulting chart is a stepped cascade that shows how the transactions
or operations lead to the final value of the measure.
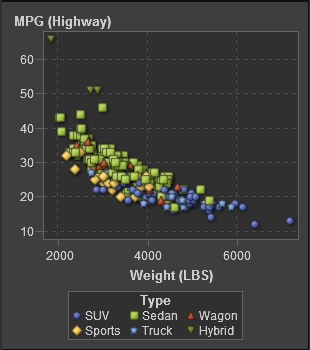
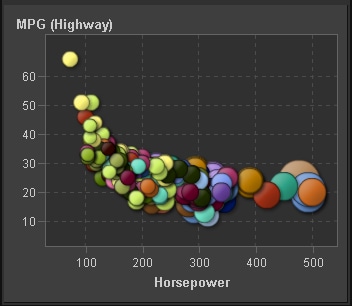
About Bubble Plots
A bubble
plot is a variation of a scatter plot in which the markers
are replaced with bubbles. In a bubble plot, each bubble represents
an observation. The location of the bubble represents the value for
the two measure axes; the size of the bubble represents the value
for the third measure. A bubble plot is useful for data sets with
dozens to hundreds of values or when the values differ by several
orders of magnitude. You can also use a bubble plot when you want
specific values to be visually represented by different bubble sizes.
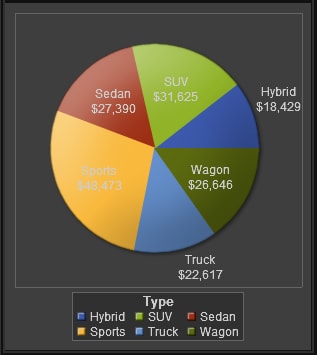
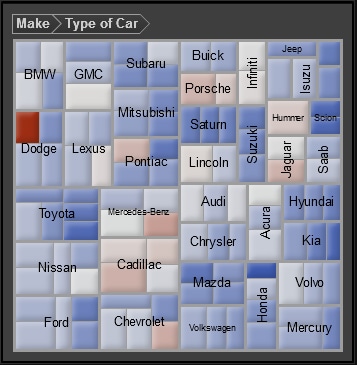
About Treemaps
A treemap is
divided into rectangular areas called tiles. The color of each tile
represents the value of the first measure in the query. The size of
each tile represents the value of the second measure in the query. For
example, a treemap might be used to represent sales data where the
tile sizes vary according to the number of orders invoiced and the
tile colors are derived from a color gradient that represents low
to high sales figures.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.