| Introduction |
Where Are the Data?
Stat Studio runs in a Microsoft Windows operating environment, but it can communicate with SAS running on other computers. The PC running Stat Studio is called the client. The computer running SAS is called the SAS server. If SAS is running on the same PC that is running Stat Studio, then the client and server machines are the same.
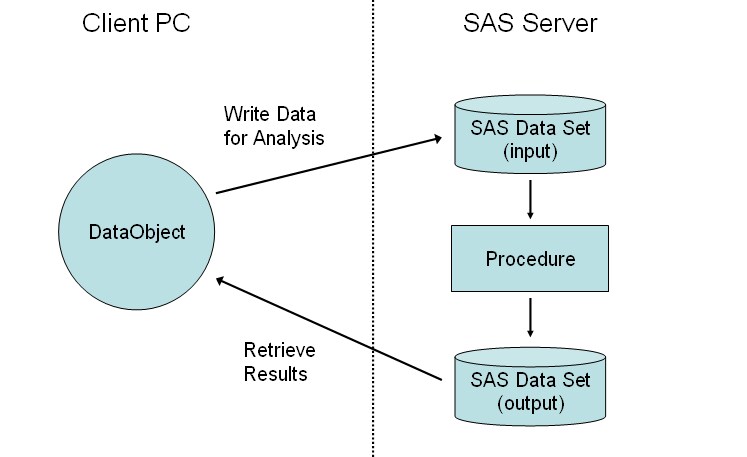
There is a fundamental difference between the Stat Studio graphics and the Stat Studio analyses. The DataObject class, which coordinates all of the dynamically linked graphics and tables, runs on the client and keeps its data in memory on the client. Similarly, the graphics and tables run on the client. The analyses, by contrast, are performed using SAS procedures, and so the analyses run on the SAS server. The SAS procedures must read from a SAS data set in a library on the server.
To perform an analysis, you must get data out of the DataObject and
write the data to a SAS data set in a server library. Similarly, after an
analysis is complete, you might want to get the results (such as
observation-wise statistics) out of a server data set and add them to the
in-memory DataObject. Figure 1.5 illustrates this idea.
|
Figure 1.5: Data Flow
Thus it is important to know how to pass data between a DataObject
and SAS data sets on the server. In Chapter 2, "Reading and Writing Data," you learn
how to move variables between a DataObject and a server data set. You
also learn how to read and write SAS data sets on the
client or on the server, and how to create a DataObject from
various sources of data.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.