The SURVEYLOGISTIC Procedure
- Overview
- Getting Started
-
Syntax
 PROC SURVEYLOGISTIC StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCLUSTER StatementCONTRAST StatementDOMAIN StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementOUTPUT StatementREPWEIGHTS StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementSTRATA StatementTEST StatementUNITS StatementWEIGHT Statement
PROC SURVEYLOGISTIC StatementBY StatementCLASS StatementCLUSTER StatementCONTRAST StatementDOMAIN StatementEFFECT StatementESTIMATE StatementFREQ StatementLSMEANS StatementLSMESTIMATE StatementMODEL StatementOUTPUT StatementREPWEIGHTS StatementSLICE StatementSTORE StatementSTRATA StatementTEST StatementUNITS StatementWEIGHT Statement -
Details
 Missing ValuesModel SpecificationModel FittingSurvey Design InformationLogistic Regression Models and ParametersVariance EstimationDomain AnalysisHypothesis Testing and EstimationLinear Predictor, Predicted Probability, and Confidence LimitsOutput Data SetsDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics
Missing ValuesModel SpecificationModel FittingSurvey Design InformationLogistic Regression Models and ParametersVariance EstimationDomain AnalysisHypothesis Testing and EstimationLinear Predictor, Predicted Probability, and Confidence LimitsOutput Data SetsDisplayed OutputODS Table NamesODS Graphics -
Examples

- References
Getting Started: SURVEYLOGISTIC Procedure
The SURVEYLOGISTIC procedure is similar to the LOGISTIC procedure and other regression procedures in the SAS System. See Chapter 72: The LOGISTIC Procedure, for general information about how to perform logistic regression by using SAS. PROC SURVEYLOGISTIC is designed to handle sample survey data, and thus it incorporates the sample design information into the analysis.
The following example illustrates how to use PROC SURVEYLOGISTIC to perform logistic regression for sample survey data.
In the customer satisfaction survey example in the section Getting Started: SURVEYSELECT Procedure in Chapter 115: The SURVEYSELECT Procedure, an Internet service provider conducts a customer satisfaction survey. The survey population consists of the company’s current
subscribers from four states: Alabama (AL), Florida (FL), Georgia (GA), and South Carolina (SC). The company plans to select
a sample of customers from this population, interview the selected customers and ask their opinions on customer service, and
then make inferences about the entire population of subscribers from the sample data. A stratified sample is selected by using
the probability proportional to size (PPS) method. The sample design divides the customers into strata depending on their
types ('Old' or 'New') and their states (AL, FL, GA, SC). There are eight strata in all. Within each stratum, customers are
selected and interviewed by using the PPS with replacement method, where the size variable is Usage. The stratified PPS sample contains 192 customers. The data are stored in the SAS data set SampleStrata. Figure 111.1 displays the first 10 observations of this data set.
Figure 111.1: Stratified PPS Sample (First 10 Observations)
| Customer Satisfaction Survey |
| Stratified PPS Sampling |
| (First 10 Observations) |
| Obs | State | Type | CustomerID | Rating | Usage | SamplingWeight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AL | New | 24394278 | Neutral | 13.17 | 26.358 |
| 2 | AL | New | 64798692 | Extremely Unsatisfied | 15.53 | 22.352 |
| 3 | AL | New | 75375074 | Unsatisfied | 99.11 | 3.501 |
| 4 | AL | New | 262831809 | Neutral | 5.40 | 64.228 |
| 5 | AL | New | 294428658 | Extremely Satisfied | 1.17 | 297.488 |
| 6 | AL | New | 336222949 | Unsatisfied | 38.69 | 8.970 |
| 7 | AL | New | 351929023 | Extremely Satisfied | 2.72 | 127.475 |
| 8 | AL | New | 366142640 | Satisfied | 2.61 | 132.958 |
| 9 | AL | New | 371478614 | Neutral | 14.36 | 24.173 |
| 10 | AL | New | 477172230 | Neutral | 4.06 | 85.489 |
In the SAS data set SampleStrata, the variable CustomerID uniquely identifies each customer. The variable State contains the state of the customer’s address. The variable Type equals 'Old' if the customer has subscribed to the service for more than one year; otherwise, the variable Type equals 'New'. The variable Usage contains the customer’s average monthly service usage, in hours. The variable Rating contains the customer’s responses to the survey. The sample design uses an unequal probability sampling method, with the
sampling weights stored in the variable SamplingWeight.
The following SAS statements fit a cumulative logistic model between the satisfaction levels and the Internet usage by using the stratified PPS sample:
title 'Customer Satisfaction Survey'; proc surveylogistic data=SampleStrata; strata state type/list; model Rating (order=internal) = Usage; weight SamplingWeight; run;
The PROC SURVEYLOGISTIC statement invokes the SURVEYLOGISTIC procedure. The STRATA statement specifies the stratification
variables State and Type that are used in the sample design. The LIST option requests a summary of the stratification. In the MODEL statement, Rating is the response variable and Usage is the explanatory variable. The ORDER=internal is used for the response variable Rating to ask the procedure to order the response levels by using the internal numerical value (1–5) instead of the formatted character
value. The WEIGHT statement specifies the variable SamplingWeight that contains the sampling weights.
The results of this analysis are shown in the following figures.
Figure 111.2: Stratified PPS Sample, Model Information
| Customer Satisfaction Survey |
| Model Information | ||
|---|---|---|
| Data Set | WORK.SAMPLESTRATA | |
| Response Variable | Rating | |
| Number of Response Levels | 5 | |
| Stratum Variables | State | |
| Type | ||
| Number of Strata | 8 | |
| Weight Variable | SamplingWeight | Sampling Weight |
| Model | Cumulative Logit | |
| Optimization Technique | Fisher's Scoring | |
| Variance Adjustment | Degrees of Freedom (DF) | |
PROC SURVEYLOGISTIC first lists the following model fitting information and sample design information in Figure 111.2:
-
The link function is the logit of the cumulative of the lower response categories.
-
The Fisher scoring optimization technique is used to obtain the maximum likelihood estimates for the regression coefficients.
-
The response variable is
Rating, which has five response levels. -
The stratification variables are
StateandType. -
There are eight strata in the sample.
-
The weight variable is
SamplingWeight. -
The variance adjustment method used for the regression coefficients is the default degrees of freedom adjustment.
Figure 111.3 lists the number of observations in the data set and the number of observations used in the analysis. Since there is no missing value in this example, observations in the entire data set are used in the analysis. The sums of weights are also reported in this table.
Figure 111.3: Stratified PPS Sample, Number of Observations
The "Response Profile" table in Figure 111.4 lists the five response levels, their ordered values, and their total frequencies and total weights for each category. Due
to the ORDER=INTERNAL option for the response variable Rating, the category "Extremely Unsatisfied" has the Ordered Value 1, the category "Unsatisfied" has the Ordered Value 2, and so
on.
Figure 111.4: Stratified PPS Sample, Response Profile
Figure 111.5 displays the output of the stratification summary. There are a total of eight strata, and each stratum is defined by the customer types within each state. The table also shows the number of customers within each stratum.
Figure 111.5: Stratified PPS Sample, Stratification Summary
Figure 111.6 shows the chi-square test for testing the proportional odds assumption. The test is highly significant, which indicates that the cumulative logit model might not adequately fit the data.
Figure 111.6: Stratified PPS Sample, Testing the Proportional Odds Assumption
Figure 111.7 shows the iteration algorithm converged to obtain the MLE for this example. The "Model Fit Statistics" table contains the
Akaike information criterion (AIC), the Schwarz criterion (SC), and the negative of twice the log likelihood (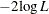 ) for the intercept-only model and the fitted model. AIC and SC can be used to compare different models, and the ones with
smaller values are preferred.
) for the intercept-only model and the fitted model. AIC and SC can be used to compare different models, and the ones with
smaller values are preferred.
Figure 111.7: Stratified PPS Sample, Model Fitting Information
The table "Testing Global Null Hypothesis: BETA=0" in Figure 111.8 shows the likelihood ratio test, the efficient score test, and the Wald test for testing the significance of the explanatory
variable (Usage). All tests are significant.
Figure 111.8: Stratified PPS Sample
Figure 111.9 shows the parameter estimates of the logistic regression and their standard errors.
Figure 111.9: Stratified PPS Sample, Parameter Estimates
| Analysis of Maximum Likelihood Estimates | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate | Standard Error |
t Value | Pr > |t| | |
| Intercept | Extremely Unsatisfied | -2.1252 | 0.3727 | -5.70 | <.0001 |
| Intercept | Unsatisfied | -0.8649 | 0.3616 | -2.39 | 0.0178 |
| Intercept | Neutral | -0.1768 | 0.3645 | -0.49 | 0.6282 |
| Intercept | Satisfied | 1.0953 | 0.5255 | 2.08 | 0.0385 |
| Usage | 0.0441 | 0.0181 | 2.43 | 0.0159 | |
| NOTE: The degrees of freedom for the t tests is 186. | |||||
Figure 111.10 displays the odds ratio estimate and its confidence intervals.
Figure 111.10: Stratified PPS Sample, Odds Ratios