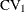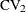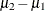The POWER Procedure
- Overview
-
Getting Started

-
Syntax
 PROC POWER StatementCOXREG StatementLOGISTIC StatementMULTREG StatementONECORR StatementONESAMPLEFREQ StatementONESAMPLEMEANS StatementONEWAYANOVA StatementPAIREDFREQ StatementPAIREDMEANS StatementPLOT StatementTWOSAMPLEFREQ StatementTWOSAMPLEMEANS StatementTWOSAMPLESURVIVAL StatementTWOSAMPLEWILCOXON Statement
PROC POWER StatementCOXREG StatementLOGISTIC StatementMULTREG StatementONECORR StatementONESAMPLEFREQ StatementONESAMPLEMEANS StatementONEWAYANOVA StatementPAIREDFREQ StatementPAIREDMEANS StatementPLOT StatementTWOSAMPLEFREQ StatementTWOSAMPLEMEANS StatementTWOSAMPLESURVIVAL StatementTWOSAMPLEWILCOXON Statement -
Details

-
Examples
 One-Way ANOVAThe Sawtooth Power Function in Proportion AnalysesSimple AB/BA Crossover DesignsNoninferiority Test with Lognormal DataMultiple Regression and CorrelationComparing Two Survival CurvesConfidence Interval PrecisionCustomizing PlotsBinary Logistic Regression with Independent PredictorsWilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Test
One-Way ANOVAThe Sawtooth Power Function in Proportion AnalysesSimple AB/BA Crossover DesignsNoninferiority Test with Lognormal DataMultiple Regression and CorrelationComparing Two Survival CurvesConfidence Interval PrecisionCustomizing PlotsBinary Logistic Regression with Independent PredictorsWilcoxon-Mann-Whitney Test - References
PAIREDMEANS Statement
-
PAIREDMEANS <options>;
The PAIREDMEANS statement performs power and sample size analyses for t tests, equivalence tests, and confidence interval precision involving paired samples.
Summary of Options
Table 89.16 summarizes the options available in the PAIREDMEANS statement.
Table 89.18: PAIREDMEANS Statement Options
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Define analysis |
|
|
Specifies an analysis of precision of the confidence interval for the mean difference |
|
|
Specifies the underlying distribution assumed for the test statistic |
|
|
Specifies the statistical analysis |
|
|
Specify analysis information |
|
|
Specifies the significance level |
|
|
Specifies the lower equivalence bound |
|
|
Specifies the null mean difference |
|
|
Specifies the null mean ratio |
|
|
Specifies the number of sides and the direction of the statistical test or confidence interval |
|
|
Specifies the upper equivalence bound |
|
|
Specify effects |
|
|
Specifies the desired confidence interval half-width |
|
|
Specifies the mean difference |
|
|
Specifies the geometric mean ratio, |
|
|
Specifies the two paired means |
|
|
Specify variability |
|
|
Specifies the correlation between members of a pair |
|
|
Specifies the common coefficient of variation |
|
|
Specifies the coefficient of variation for each member of a pair |
|
|
Specifies the standard deviation of each member of a pair |
|
|
Specifies the common standard deviation |
|
|
Specify sample size |
|
|
Enables fractional input and output for sample sizes |
|
|
Specifies the number of pairs |
|
|
Specify power and related probabilities |
|
|
Specifies the desired power of the test |
|
|
Specifies the type of probability for the PROBWIDTH= option |
|
|
Specifies the probability of obtaining a confidence interval half-width less than or equal to the value specified by the HALFWIDTH= |
|
|
Control ordering in output |
|
|
Controls the output order of parameters |
|
Table 89.19 summarizes the valid result parameters for different analyses in the PAIREDMEANS statement.
Table 89.19: Summary of Result Parameters in the PAIREDMEANS Statement
Dictionary of Options
Restrictions on Option Combinations
To define the analysis, choose one of the following parameterizations:
To specify the means, choose one of the following parameterizations:
-
individual means (by using the PAIREDMEANS= option)
-
mean difference (by using the MEANDIFF= option)
-
mean ratio (by using the MEANRATIO= option)
To specify the coefficient of variation, choose one of the following parameterizations:
-
common coefficient of variation (by using the CV= option)
-
individual coefficients of variation (by using the PAIREDCVS= option)
To specify the standard deviation, choose one of the following parameterizations:
-
common standard deviation (by using the STDDEV= option)
-
individual standard deviations (by using the PAIREDSTDDEVS= option)
Option Groups for Common Analyses
This section summarizes the syntax for the common analyses that are supported in the PAIREDMEANS statement.
Paired t Test
You can express effects in terms of the mean difference and variability in terms of a correlation and common standard deviation, as in the following statements. Default values for the DIST= , SIDES= , NULLDIFF= , and ALPHA= options specify a two-sided test for no difference with a normal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=diff
meandiff = 7
corr = 0.4
stddev = 12
npairs = 50
power = .;
run;
You can also express effects in terms of individual means and variability in terms of correlation and individual standard deviations:
proc power;
pairedmeans test=diff
pairedmeans = 8 | 15
corr = 0.4
pairedstddevs = (7 12)
npairs = .
power = 0.9;
run;
Paired t Test of Mean Ratio with Lognormal Data
You can express variability in terms of correlation and a common coefficient of variation, as in the following statements. Defaults for the DIST= , SIDES= , NULLRATIO= and ALPHA= options specify a two-sided test of mean ratio = 1 assuming a lognormal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=ratio
meanratio = 7
corr = 0.3
cv = 1.2
npairs = 30
power = .;
run;
You can also express variability in terms of correlation and individual coefficients of variation:
proc power;
pairedmeans test=ratio
meanratio = 7
corr = 0.3
pairedcvs = 0.8 | 0.9
npairs = 30
power = .;
run;
Additive Equivalence Test for Mean Difference with Normal Data
The following statements demonstrate a sample size computation for a TOST equivalence test for a normal mean difference. Default values for the DIST= and ALPHA= options specify a normal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=equiv_diff
lower = 2
upper = 5
meandiff = 4
corr = 0.2
stddev = 8
npairs = .
power = 0.9;
run;
Multiplicative Equivalence Test for Mean Ratio with Lognormal Data
The following statements demonstrate a power computation for a TOST equivalence test for a lognormal mean ratio. Default values for the DIST= and ALPHA= options specify a lognormal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=equiv_ratio
lower = 3
upper = 7
meanratio = 5
corr = 0.2
cv = 1.1
npairs = 50
power = .;
run;
Confidence Interval for Mean Difference
By default CI= DIFF analyzes the conditional probability of obtaining the desired precision, given that the interval contains the true mean difference, as in the following statements. The defaults of SIDES= 2 and ALPHA= 0.05 specify a two-sided interval with a confidence level of 0.95.
proc power;
pairedmeans ci = diff
halfwidth = 4
corr = 0.35
stddev = 8
npairs = 30
probwidth = .;
run;
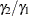

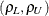
![\begin{align*} \rho _ L & = \frac{\exp \left(-\left[ \log (\mr{CV}_1^2+1) \log (\mr{CV}_2^2+1) \right]^\frac {1}{2} \right) - 1}{\mr{CV}_1 \mr{CV}_2} \\ \rho _ U & = \frac{\exp \left(\left[ \log (\mr{CV}_1^2+1) \log (\mr{CV}_2^2+1) \right]^\frac {1}{2}\right) - 1}{\mr{CV}_1 \mr{CV}_2} \end{align*}](images/statug_power0042.png)