-
ABSFCONV=r
ABSFTOL=r
-
specifies an absolute function difference convergence criterion. Termination requires a small change of the function value
in successive iterations,
where 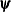 denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization and
denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization and 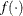 is the objective function. This criterion is not used by the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm. By default, r = 0.
is the objective function. This criterion is not used by the expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm. By default, r = 0.
-
ABSGCONV=r
ABSGTOL=r
-
specifies an absolute gradient convergence criterion. Termination requires the maximum absolute gradient element to be small,
where 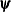 denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization and
denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization and 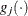 is the gradient of the objective function with respect to the jth parameter. This criterion is not used by the EM algorithm. By default, r = 1E–5.
is the gradient of the objective function with respect to the jth parameter. This criterion is not used by the EM algorithm. By default, r = 1E–5.
-
ABSPCONV=r
ABSPTOL=r
-
specifies a maximum absolute parameter difference convergence criterion. This criterion is used only by the EM algorithm.
Termination requires the maximum absolute parameter change in successive iterations to be small,
where 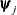 denotes the jth parameter that participates in the optimization. By default, r = 1E–4.
denotes the jth parameter that participates in the optimization. By default, r = 1E–4.
-
DATA=SAS-data-set
-
specifies the SAS-data-set to be read by PROC IRT. The default value is the most recently created data set.
-
DESCENDING
DESC
-
reverses the sorting order for the levels of the response variables. If both the DESCENDING and RORDER= options are specified,
PROC IRT orders the levels according to the RORDER= option and then reverses that order.
-
FCONV=r
FTOL=r
-
specifies a relative function convergence criterion. Termination requires a small relative change of the function value in
successive iterations,
where 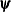 denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization and
denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization and 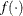 is the objective function. This criterion is not used by the EM algorithm. By default, r
is the objective function. This criterion is not used by the EM algorithm. By default, r 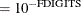 , where FDIGITS is, by default,
, where FDIGITS is, by default, 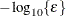 and
and  is the machine precision.
is the machine precision.
-
GCONV=r
GTOL=r
-
specifies a relative gradient convergence criterion. For all techniques except CONGRA, termination requires the normalized
predicted function reduction to be small,
where 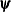 denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization,
denotes the vector of parameters that participate in the optimization, 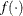 is the objective function, and
is the objective function, and 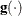 is the gradient. For the CONGRA technique (for which a reliable Hessian estimate
is the gradient. For the CONGRA technique (for which a reliable Hessian estimate 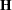 is not available), the following criterion is used:
is not available), the following criterion is used:
This criterion is not used by the EM algorithm. By default, r = 1E–8.
-
ITEMFIT
-
calculates and displays the item fit statistics. These item fit statistics apply only to binary items that have one latent
factor.
-
LINK=name
-
specifies the link function. You can specify the following link functions:
- LOGIT
-
requests the logistic link function.
- PROBIT
-
requests the probit link function.
By default, LINK=LOGIT.
-
MAXFUNC=n
MAXFU=n
-
specifies the maximum number of function calls in the optimization process. This option is not used by the EM algorithm. The
default values are as follows, depending on the optimization technique:
-
NRRIDG: 125
-
QUANEW: 500
-
CONGRA: 1000
The optimization can terminate only after completing a full iteration. Therefore, the number of function calls that are actually
performed can exceed the number that is specified by this option. You can select the optimization technique by specifying
the TECHNIQUE= option.
-
MAXITER=n
MAXIT=n
-
specifies the maximum number of iterations in the optimization process. The default values are as follows, depending on the
optimization technique:
-
NRRIDG: 50
-
QUANEW: 200
-
CONGRA: 400
-
EM: 500
-
MAXMITER=n
MAXMIT=n
-
specifies the maximum number of iterations in the maximization step of the EM algorithm. By default, n = 1.
-
NFACTOR=i
NFACT=i
-
specifies the number of factors, i, in the model. You must specify the number of factors only for exploratory analysis, in which all the slope parameters of
the items are freely estimated without being explicitly constrained by using the FACTOR statement. By default, NFACTOR=1. When you use the FACTOR statement to specify the confirmatory factor pattern, the number of factors is implicitly defined by the number of distinctive
factor names that you specify in the statement.
-
NOAD
-
requests that the Gaussian quadrature be nonadaptive.
-
NOITPRINT
-
suppresses the display of the “Iteration History” table.
-
NOPRINT
-
suppresses all output displays.
-
TECHNIQUE=CONGRA | EM | NONE | NRRIDG | QUANEW
TECH=CONGRA | EM | NONE | NRRIDG | QUANEW
OMETHOD=CONGRA | EM | NONE | NRRIDG | QUANEW
-
specifies the optimization technique to obtain maximum likelihood estimates. You can specify the following techniques:
- CONGRA
-
performs a conjugate-gradient optimization.
- EM
-
performs an EM optimization.
- NONE
-
performs no optimization.
- NRRIDG
-
performs a Newton-Raphson optimization with ridging.
- QUANEW
-
performs a dual quasi-Newton optimization.
By default, TECHNIQUE=QUANEW.
For more information about these optimization methods (except EM), see the section Choosing an Optimization Algorithm in Chapter 19: Shared Concepts and Topics. For more information about the EM algorithm, see “Expectation-Maximization (EM) Algorithm” in the section Details: IRT Procedure.
-
OUT=SAS-data-set
-
creates an output data set that contains all the data in the DATA= data set plus estimated factor scores. For exploratory analysis, the factor scores are named _Factor1, _Factor2, and so on. For confirmatory analysis, user-specified factor names are used.
PROC IRT provides three estimation methods for factor scores. You can specify the method by using the SCOREMETHOD option. The default estimation method, maximum a posteriori (MAP), is used if the SCOREMETHOD option is not specified.
-
PINITIAL
-
displays the initial parameter estimates.
-
PLOTS <(global-plot-options)> <= plot-request <(options)>>
PLOTS <(global-plot-options)> <= (plot-request <(options)> <…plot-request <(options)>>)>
-
controls the plots that are produced through ODS Graphics. When you specify only one plot-request, you can omit the parentheses around it. For example:
plots=all
plots=ICC(unpack)
plots(unpack)=(scree ICC)
ODS Graphics must be enabled before plots can be requested. For example:
ods graphics on;
proc irt plots=all;
run;
ods graphics off;
For more information about enabling and disabling ODS Graphics, see the section Enabling and Disabling ODS Graphics in Chapter 21: Statistical Graphics Using ODS.
You can specify the following global-plot-option, which applies to all plots that the IRT procedure generates:
-
UNPACK |UNPACKPANEL
-
suppresses paneling. By default, multiple plots can appear in some output panels. Specify UNPACK to display each plot individually.
You can also specify UNPACK as a suboption in the ICC and SCREE options.
You can specify the following plot-requests:
-
ALL
-
displays all default plots.
-
SCREE <(UNPACK |UNPACKPANEL)>
-
displays the scree and variance explained plots in the same panel. You can display these plots individually by specifying
the UNPACK suboption.
-
ICC <(UNPACK |UNPACKPANEL)>
-
displays item characteristic curve (ICC) plots. By default, multiple ICC plots appear in some output panels. You can request
an individual ICC plot for each item by specifying the UNPACK suboption.
-
NONE
-
suppresses all plots.
-
QPOINTS=i
-
specifies the number of quadrature points in each dimension of the integral. Note that if there are d latent factors and n quadrature points, the IRT procedure evaluates 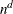 conditional log likelihoods for each observation to compute one value of the objective function. Increasing the number of
quadrature nodes can substantially increase the computational burden. If you do not specify the number of quadrature points,
it is determined adaptively by using the initial parameter estimates.
conditional log likelihoods for each observation to compute one value of the objective function. Increasing the number of
quadrature nodes can substantially increase the computational burden. If you do not specify the number of quadrature points,
it is determined adaptively by using the initial parameter estimates.
-
RCONVERGE=p
RCONV=p
-
specifies the convergence criterion for rotation cycles. Rotation stops when the scaled change of the simplicity function
value is less than the RCONVERGE= value. The default convergence criterion is
where 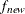 and
and 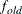 are simplicity function values
of the current cycle and the previous cycle, respectively;
are simplicity function values
of the current cycle and the previous cycle, respectively; 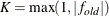 is a scaling factor; and
is a scaling factor; and  is 1E–9 by default and is modified by the RCONVERGE= value.
is 1E–9 by default and is modified by the RCONVERGE= value.
-
RESFUNC=ONEP | TWOP | THREEP | FOURP | GRADED | RASCH
-
specifies the response functions for the variables that are included in the VAR statement. The response functions correspond to different response models. The graded response (GRADED) model is assumed
by default. You can specify the following response functions:
- ONEP
-
specifies the one-parameter model.
- TWOP
-
specifies the two-parameter model.
- THREEP
-
specifies the three-parameter model.
- FOURP
-
specifies the four-parameter model.
- GRADED
-
specifies the graded response model.
- RASCH
-
specifies the Rasch model.
The graded response model assumes that the response variables are ordinal-categorical up to 19 levels. All other models assume
binary responses. For more information about these response models, see “Response Models” in the Details: IRT Procedure section.
-
RITER=n
-
specifies the maximum number of cycles for factor rotation. The default value is the maximum between 10 times the number of
variables and 100.
-
ROTATE=name
R=name
-
specifies the rotation method. You can specify the following orthogonal rotation methods:
- BIQUARTIMAX | BIQMAX
-
specifies orthogonal biquartimax rotation.
- EQUAMAX | E
-
specifies orthogonal equamax rotation.
- NONE | N
-
specifies that no rotation be performed, leaving the original orthogonal solution.
- PARSIMAX | PA
-
specifies orthogonal parsimax rotation.
- QUARTIMAX | QMAX | Q
-
specifies orthogonal quartimax rotation.
- VARIMAX | V
-
specifies orthogonal varimax rotation.
You can specify the following oblique rotation methods:
- OBBIQUARTIMAX | OBIQMAX
-
specifies oblique biquartimax rotation.
- OBEQUAMAX | OE
-
specifies oblique equamax rotation.
- OBPARSIMAX | OPA
-
specifies oblique parsimax rotation.
- OBQUARTIMAX | OQMAX
-
specifies oblique quartimax rotation.
- OBVARIMAX | OV
-
specifies oblique varimax rotation.
By default, ROTATE=VARIMAX.
-
RORDER=DATA | FORMATTED | FREQ | INTERNAL
-
specifies the sort order for the levels of the response variable. This order determines which threshold parameter in the model
corresponds to each level in the data. If RORDER=FORMATTED for numeric variables for which you have supplied no explicit format,
the levels are ordered by their internal values. This option applies to all the responses in the model. When the default,
RORDER=FORMATTED, is in effect for numeric variables for which you have supplied no explicit format, the levels are ordered
by their internal values. You can specify the following sort orders:
|
Value of RORDER=
|
Levels Sorted By
|
|
DATA
|
Order of appearance in the input data set
|
|
FORMATTED
|
External formatted value, except for numeric variables that have no explicit format, which are sorted by their unformatted
(internal) value
|
|
FREQ
|
Descending frequency count; levels that contain the most observations come first in the order
|
|
INTERNAL
|
Unformatted value
|
For FORMATTED and INTERNAL, the sort order is machine-dependent. For more information about sort order, see the chapter on
the SORT procedure in the SAS Procedures Guide and the discussion of BY-group processing in
SAS Language Reference: Concepts.
-
SCOREMETHOD=ML | EAP | MAP
-
specifies the method of factor score estimation. You can specify the following methods:
- ML
-
requests the maximum likelihood method.
- EAP
-
requests the expected a posteriori method.
- MAP
-
requests the maximum a posteriori method.
