SQL Procedure
- Syntax
 Procedure SyntaxPROC SQL StatementALTER TABLE StatementCONNECT StatementCREATE INDEX StatementCREATE TABLE StatementCREATE VIEW StatementDELETE StatementDESCRIBE StatementDISCONNECT StatementDROP StatementEXECUTE StatementINSERT StatementRESET StatementSELECT StatementUPDATE StatementVALIDATE Statement
Procedure SyntaxPROC SQL StatementALTER TABLE StatementCONNECT StatementCREATE INDEX StatementCREATE TABLE StatementCREATE VIEW StatementDELETE StatementDESCRIBE StatementDISCONNECT StatementDROP StatementEXECUTE StatementINSERT StatementRESET StatementSELECT StatementUPDATE StatementVALIDATE Statement - Overview
- Examples
 Creating a Table and Inserting Data into ItCreating a Table from a Query's ResultUpdating Data in a PROC SQL TableJoining Two TablesCombining Two TablesReporting from DICTIONARY TablesPerforming an Outer JoinCreating a View from a Query's Result Joining Three TablesQuerying an In-Line View Retrieving Values with the SOUNDS-LIKE Operator Joining Two Tables and Calculating a New ValueProducing All the Possible Combinations of the Values in a ColumnMatching Case Rows and Control RowsCounting Missing Values with a SAS Macro
Creating a Table and Inserting Data into ItCreating a Table from a Query's ResultUpdating Data in a PROC SQL TableJoining Two TablesCombining Two TablesReporting from DICTIONARY TablesPerforming an Outer JoinCreating a View from a Query's Result Joining Three TablesQuerying an In-Line View Retrieving Values with the SOUNDS-LIKE Operator Joining Two Tables and Calculating a New ValueProducing All the Possible Combinations of the Values in a ColumnMatching Case Rows and Control RowsCounting Missing Values with a SAS Macro
Overview
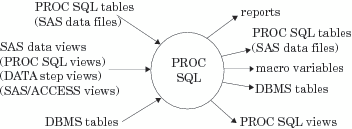
What Is the SQL Procedure?
The SQL procedure implements
Structured Query Language (SQL) for SAS. SQL is a standardized, widely
used language that retrieves data from and updates data in tables
and the views that are based on those tables.
What Are PROC SQL Tables?
A PROC SQL table is synonymous with a SAS data file
and has a member type of DATA. You can use PROC SQL tables as input
into DATA steps and procedures.
You create PROC SQL
tables from SAS data files, from SAS views, or from DBMS tables by
using PROC SQL's pass-through facility or the
SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME statement. The pass-through
facility is described in Connecting to a DBMS by Using the SQL Procedure Pass-Through Facility.
The SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME statement
is described in Connecting to a DBMS by Using the LIBNAME Statement.
What Are Views?
A SAS
view defines a virtual data set that is named and stored
for later use. A view contains no data but describes or defines data
that is stored elsewhere. There are three types of SAS views:
You can refer to views
in queries as if they were tables. The view derives its data from
the tables or views that are listed in its FROM clause. The data that
is accessed by a view is a subset or superset of the data that is
in its underlying tables or views.
A PROC SQL view is a
SAS data set of type VIEW that is created by PROC SQL. A PROC SQL
view contains no data. It is a stored query expression that reads
data values from its underlying files, which can include SAS data
files, SAS/ACCESS views,
DATA step views, other PROC SQL views, or DBMS data. When executed,
a PROC SQL view's output can be a subset or superset of one or
more underlying files.
SAS/ACCESS views and DATA step views are similar to PROC SQL
views in that they are both stored programs of member type VIEW. SAS/ACCESS views describe data
in DBMS tables from other software vendors. DATA step views are stored
DATA step programs.
Note: Starting in SAS System 9,
PROC SQL views, the pass-through facility, and the SAS/ACCESS LIBNAME statement are the preferred
ways to access relational DBMS data; SAS/ACCESS views are no longer recommended. You can convert existing SAS/ACCESS views to PROC SQL views
by using the CV2VIEW procedure. For more information,
see Chapter 33, “CV2VIEW Procedure” in SAS/ACCESS for Relational Databases: Reference.
You can update data
through a PROC SQL or SAS/ACCESS
view with certain restrictions. See Updating PROC SQL and SAS/ACCESS Views.
Note: In this chapter, the term view collectively
refers to PROC SQL views, DATA step views, and SAS/ACCESS views, unless otherwise noted.
Note: When
the contents of an SQL view are processed (by a DATA step or a procedure),
the referenced data set must be opened to retrieve information about
the variables that is not stored in the view. If that data set has
a libref associated with it that is not defined in the current SAS
code, then an error will result. You can avoid this error by specifying
a USING clause in the CREATE VIEW statement. See CREATE VIEW Statement for details.
SQL Procedure Coding Conventions
Because PROC SQL implements Structured
Query Language, it works somewhat differently from other Base SAS
procedures, as described here:
-
When a PROC SQL statement is executed, PROC SQL continues to run until a QUIT statement, a DATA step, or another SAS procedure is executed. Therefore, you do not need to repeat the PROC SQL statement with each SQL statement. You need to repeat the PROC SQL statement only if you execute a QUIT statement, a DATA step, or another SAS procedure between SQL statements.
-
SQL procedure statements are divided into clauses. For example, the most basic SELECT statement contains the SELECT and FROM clauses. Items within clauses are separated with commas in SQL, not with blanks as in other SAS code. For example, if you list three columns in the SELECT clause, then the columns are separated with commas.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.