| The NLP Procedure |
MATRIX Statement
- MATRIX M_name pattern_definitions ;
The MATRIX statement defines a matrix
The rows and columns in matrix ![]() and vector
and vector ![]() correspond
to the order of decision variables in the DECVAR statement.
correspond
to the order of decision variables in the DECVAR statement.
- Full Matrix Definition:
The MATRIX statement consists of H_name or
g_name followed by an equals sign and all
(nonredundant) numerical values of the matrix
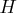 or
vector
or
vector 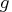 . Assuming symmetry, only the elements of the
lower triangular part of the matrix
. Assuming symmetry, only the elements of the
lower triangular part of the matrix 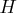 must be listed.
This specification should be used mainly for small
problems with almost dense
must be listed.
This specification should be used mainly for small
problems with almost dense 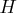 matrices.
matrices.
MATRIX H= 100 10 100 1 10 100 0 1 10 100; MATRIX G= 1 2 3 4; - Band-diagonal Matrix Definition:
This form of pattern definition is useful if the
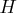 matrix has (almost) constant band-diagonal structure.
The MATRIX statement consists of H_name followed by
empty brackets
matrix has (almost) constant band-diagonal structure.
The MATRIX statement consists of H_name followed by
empty brackets ![[,]](images/nlp_nlpeq168.gif) , an equals sign, and a list of numbers
to be assigned to the diagonal and successive subdiagonals.
, an equals sign, and a list of numbers
to be assigned to the diagonal and successive subdiagonals.
MATRIX H[,]= 100 10 1; MATRIX G= 1 2 3 4; - Sparse Matrix Definitions:
In each of the following three
specification types, the H_name or g_name
is followed by a list of pattern definitions separated
by commas. Each pattern definition consists of
a location specification in brackets on the left side
of an equals sign that is followed by a list of numbers.
- (Sub)Diagonalwise:
This form of pattern definition is useful if the
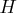 matrix
contains nonzero elements along diagonals or subdiagonals.
The starting location is specified by an index pair in
brackets
matrix
contains nonzero elements along diagonals or subdiagonals.
The starting location is specified by an index pair in
brackets ![[i,j]](images/nlp_nlpeq169.gif) . The expression
. The expression 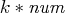 on the right-hand side
specifies that
on the right-hand side
specifies that 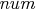 is assigned to the elements
is assigned to the elements ![[i,j], ... ,[i+k-1,j+k-1]](images/nlp_nlpeq172.gif) in a diagonal direction of the
in a diagonal direction of the 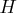 matrix.
The special case
matrix.
The special case 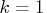 can be used to assign values
to single nonzero element locations in
can be used to assign values
to single nonzero element locations in  .
.
MATRIX H [1,1]= 4 * 100, [2,1]= 3 * 10, [3,1]= 2 * 1; MATRIX G [1,1]= 1 2 3 4; - Columnwise Starting in Diagonal:
This form of pattern definition is useful if the
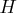 matrix
contains nonzero elements columnwise starting in the diagonal.
The starting location is specified by only one index
matrix
contains nonzero elements columnwise starting in the diagonal.
The starting location is specified by only one index 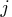 in
brackets
in
brackets ![[,j]](images/nlp_nlpeq175.gif) . The
. The 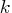 numbers at the right-hand
side are assigned to the elements
numbers at the right-hand
side are assigned to the elements ![[j,j], ... ,[\min(j+k-1,n),j]](images/nlp_nlpeq177.gif) .
.
MATRIX H [,1]= 100 10 1, [,2]= 100 10 1, [,3]= 100 10, [,4]= 100; MATRIX G [,1]= 1 2 3 4; - Rowwise Starting in First Column:
This form of pattern definition is useful if the
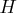 matrix
contains nonzero elements rowwise ending in the diagonal.
The starting location is specified by only one index
matrix
contains nonzero elements rowwise ending in the diagonal.
The starting location is specified by only one index 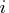 in
brackets
in
brackets ![[i,]](images/nlp_nlpeq178.gif) . The
. The 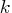 numbers at the right-hand
side are assigned to the elements
numbers at the right-hand
side are assigned to the elements ![[i,1], ... ,[i,\min(k,i)]](images/nlp_nlpeq179.gif) .
.
MATRIX H [1,]= 100, [2,]= 10 100, [3,]= 1 10 100, [4,]= 0 1 10 100; MATRIX G [1,]= 1 2 3 4;
- (Sub)Diagonalwise:
This form of pattern definition is useful if the
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.
![h = [ 100 & 10 & 1 & 0 \ 10 & 100 & 10 & 1 \ 1 & 10 & 100 & 10 \ 0 & 1 & 10 & 100 \ ] g = [ 1 \ 2 \ 3 \ 4 \ ] c = 0](images/nlp_nlpeq167.gif)