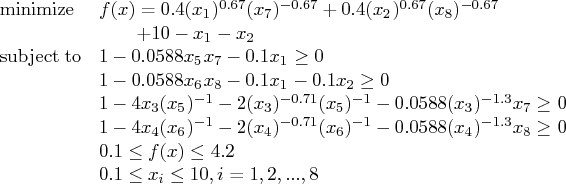| The Interior Point Nonlinear Programming Solver -- Experimental |
Example 7.1: Solving Highly Nonlinear Optimization Problems
This example demonstrates the use of the IPNLP solver to solve the following highly nonlinear optimization problem, which appears in Hock and Schittkowski (1981).
The initial point used is ![]() . You can call the IPNLP solver within PROC OPTMODEL
to solve the problem by writing the following SAS code:
. You can call the IPNLP solver within PROC OPTMODEL
to solve the problem by writing the following SAS code:
proc optmodel;
var x{1..8} >=.1 <=10;
minimize obj = 0.4*x[1]^.67*x[7]^-.67+.4*x[2]^.67*x[8]^-.67
+10-x[1]-x[2];
con c1: 1-.0588*x[5]*x[7]-.1*x[1]>=0;
con c2: 1-.0588*x[6]*x[8]-.1*x[1]-.1*x[2]>=0;
con c3: 1-4*x[3]/x[5]-2/(x[3]^.71*x[5])-.0588*x[7]/x[3]^1.3>=0;
con c4: 1-4*x[4]/x[6]-2/(x[4]^.71*x[6])-.0588*x[8]/x[4]^1.3>=0;
con c5: .4*x[1]^.67*x[7]^-.67+.4*x[2]^.67*x[8]^-.67+10
-x[1]-x[2]>=.1;
con c6: .4*x[1]^.67*x[7]^-.67+.4*x[2]^.67*x[8]^-.67+10
-x[1]-x[2]<=4.2;
/* starting point */
x[1] = 6;
x[2] = 3;
x[3] = .4;
x[4] = .2;
x[5] = 6;
x[6] = 6;
x[7] = 1;
x[8] = .5;
solve with ipnlp;
print x;
quit;
The summaries and the optimal solution are shown in Output 7.1.1.
Output 7.1.1: Summaries and the Optimal Solution
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.