| The BOM Procedure |
STRUCTURE Statement
- STRUCTURE / options ;
The STRUCTURE statement lists the variables in the Product Structure and the Part Master input data sets. The main variable in the Part Master data set is the Part variable; the main variables in the Product Structure data set are the Parent and Component variables. If all the part master data are contained in the Product Structure data set, you need not specify a Part Master data set.
If two separate input data sets are specified, you must specify both a Part variable and a Parent variable. Otherwise, you may specify either a Parent variable or a Part variable, or both. You must always specify at least one Component variable. The number of Component variables specified must be equal to the number of the product structure records (number of relationships specified) in each observation of the Product Structure data set. All other variables are optional. However, if you specify the Quantity, Offset, or Factor variables, you must have the same number of these variables as the number of Component variables.
In this statement, you can also explicitly specify the items that are to be used as the end (level-0) items.
- COMPONENT=(variables)
- COMP=(variables)
-
specifies variables in the Product Structure
input data set that contain the part numbers (identifications) of the
components that are directly used in the common parent
item identified by the Parent variable.
These variables are also referred to as Component variables.
The Component variables must be of the same type, format,
and length as the Part variable in the
Part Master data set.
At least one Component variable must be specified.
Note: This variable is case-sensitive when it is in character format. - ENDITEM=(enditems)
-
specifies the items that are to be used as the highest level or
level-0 items (also referred to as end items) in the indented bills
of material. In other words, this option can be used to construct
indented bills of material and summarized parts list for sub-assemblies.
The values for enditems must be either numbers
(if the Part variable is numeric) or quoted strings (if the
Part variable is character). If you do not specify this option,
the procedure assumes every final product (finished good) is an end item
and builds an indented bill of material for it.
- FACTOR=(variables)
- SFACTOR=(variables)
-
identifies variables in the Product Structure data set
that contain the scrap factor information for each product structure record
with the parent item identified by the Parent
variable and the component identified by each of the
Component variables; the
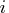 th factor variable
corresponds to the
th factor variable
corresponds to the 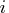 th Component variable.
The scrap factor is used to increase the gross requirement to
account for anticipated loss within
the manufacture of a particular parent
item (Cox and Blackstone, J. H., Jr. 1998). These variables are also
referred to as the Factor variables. The variables specified must
be numeric and the number of Factor variables must be equal to
the number of Component variables.
If you do not specify this option, PROC BOM
assumes the scrap factors for all product structure records
to be 0.
th Component variable.
The scrap factor is used to increase the gross requirement to
account for anticipated loss within
the manufacture of a particular parent
item (Cox and Blackstone, J. H., Jr. 1998). These variables are also
referred to as the Factor variables. The variables specified must
be numeric and the number of Factor variables must be equal to
the number of Component variables.
If you do not specify this option, PROC BOM
assumes the scrap factors for all product structure records
to be 0.
- ID=(variables)
-
identifies all variables in the Part Master data set
that are not specified in the
LEADTIME=,
PART=, QTYONHAND=,
or REQUIREMENT=
options, and are to be included in the
Indented BOM and the Summarized Parts
output data sets. These variables
are also referred to as ID variables.
An ID variable cannot be named as: Gros_Req,
_Level_, L_Offset, Low_Code, Net_Req,
On_Hand, _Parent_,
Paren_ID, _Part_, Part_ID, _Prod_,
Qty_Per, Qty_Prod,
S_Factor,
Tot_Lead, or Tot_Off. This option
is useful for carrying any identifying and descriptive information
(part description, unit of measure, etc.) and control values (lot size,
unit cost, etc.) about each
item (identified by the Part variable)
from the Part Master data set to the output data sets.
- LEADTIME=variable
- DUR=variable
-
identifies the variable in the Part Master data set
that contains
the lead time information for the item identified by the
Part variable. The lead time of an item
is the length of time between recognition of the need for an order
and the receipt of the goods. Individual components of lead time can
include order preparation time, queue time, processing time, move or
transportation time, and receiving and inspection
time (Cox and Blackstone, J. H., Jr. 1998). This variable is also referred
to as the LeadTime variable. The variable specified
must be numeric. If you do not specify this option, PROC BOM
assumes the lead time for each item to be 0.
On the other hand, if this option is specified,
the procedure creates a new variable, Tot_Lead, in the
Indented BOM data set to contain the total
lead time. See the section "Indented BOM Data Set" for details about the calculation
of the total lead time.
- OFFSET=(variables)
- LTOFFSET=(variables)
-
identifies variables in the Product Structure data set
that contain the lead-time offset information for each product structure
record with the parent item identified by the Parent
variable and the component identified by each of the
Component variables; the
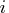 th offset variable
corresponds to the
th offset variable
corresponds to the 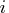 th Component variable.
The lead-time offset
can be used to control when materials are issued to a work center as
well as to determine the need date when planning, purchasing, or
manufacturing a particular
component (Clement, Coldrick, and Sari 1992).
These variables are also referred to
as the Offset variables. The variables specified must be
numeric and the number of Offset variables must
be equal to the number of Component variables.
If you do not specify this option, PROC BOM
assumes the lead-time offsets for all product structure records
to be 0.
On the other hand, if this option is specified, the procedure creates
a variable, Tot_Off, in the
Indented BOM data set to contain the total offset.
See the section "Indented BOM Data Set" for details about the calculation of the total offset.
th Component variable.
The lead-time offset
can be used to control when materials are issued to a work center as
well as to determine the need date when planning, purchasing, or
manufacturing a particular
component (Clement, Coldrick, and Sari 1992).
These variables are also referred to
as the Offset variables. The variables specified must be
numeric and the number of Offset variables must
be equal to the number of Component variables.
If you do not specify this option, PROC BOM
assumes the lead-time offsets for all product structure records
to be 0.
On the other hand, if this option is specified, the procedure creates
a variable, Tot_Off, in the
Indented BOM data set to contain the total offset.
See the section "Indented BOM Data Set" for details about the calculation of the total offset.
Note: The lead-time offset and the total offset can be expressed in units that are different from the lead time. - PARENT=variable
-
specifies the variable in the Product Structure
data set that contains the part number or identification for the
immediate parent item of the components identified by the
Component variables.
This variable is also referred to as the Parent
variable. The Parent variable must be of the same type, format,
and length as the Part variable in the
Part Master data set.
You must specify this option whenever a
Part Master data set is explicitly
specified in addition to the Product Structure
data set. On the other hand, if a Part Master
data set is not specified, the Parent variable is not
necessary; if this variable is not specified, the procedure assumes that
it is the same as the variable specified in the
PART= option.
Note: This variable is case-sensitive when it is in character format. - PART=variable
- ITEM=variable
-
specifies the variable in the Part Master data set
that contains the part number or identification.
This variable is also referred to as the Part
variable. The Part variable can be either character or numeric.
You must specify this option whenever a Part Master
data set is specified in addition to the
Product Structure data set. Otherwise, the
Part variable is not necessary; if this variable is not specified,
the procedure assumes that
it is the same as the variable specified in the
PARENT= option.
Note: This variable is case-sensitive when it is in character format. - QTYONHAND=variable
- INVENTORY=variable
-
identifies the variable in the Part Master data set
that contains the quantity currently on hand for the item identified by the
Part variable. This variable is also
referred to as the QtyOnHand variable. The QtyOnHand
variable must be numeric. If you do not specify the QtyOnHand
variable, the procedure assumes that you do not have any items on hand.
- QUANTITY=(variables)
- QTYPER=(variables)
-
identifies variables in the Product Structure data set
that contain the quantity per assembly information for each product
structure record with the parent item identified by the
Parent
variable and the components identified by each of the
Component variables; the
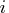 th quantity
variable corresponds to the
th quantity
variable corresponds to the 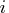 th Component
variable. The quantity per assembly for a given parent-component
relationship is the quantity of the component to be used in the
production of 1 unit of the parent item. These variables
are also referred to as the Quantity or QtyPer variables.
The variables specified must be numeric and the number of
Quantity variables must be equal to the number of
Component variables.
If you do not specify these variables, the procedure assumes
that you need 1 unit of each listed component identified by a
Component variable
to make 1 unit of the parent item identified by the
Parent variable.
th Component
variable. The quantity per assembly for a given parent-component
relationship is the quantity of the component to be used in the
production of 1 unit of the parent item. These variables
are also referred to as the Quantity or QtyPer variables.
The variables specified must be numeric and the number of
Quantity variables must be equal to the number of
Component variables.
If you do not specify these variables, the procedure assumes
that you need 1 unit of each listed component identified by a
Component variable
to make 1 unit of the parent item identified by the
Parent variable.
- REQUIREMENT=variable
- GROSSREQ=variable
-
identifies the variable in the Part Master data set
that contains the gross
requirement (the quantity planned to be produced in a production plan)
for the item identified by the
Part variable.
This variable is also referred to as
the Requirement variable and must be
numeric. If you do not specify this option, the procedure assumes that
the gross requirements for all items are missing except for the
final products or end items. All final products or end items
are assumed to have gross requirements of 1 unit.
In other words, if the Part Master data set
does not contain the production plan information, PROC BOM uses a
default production plan in which each end item has a requirement of
1 unit. The procedure uses the specified
(or assumed) values of the Requirement variable
to calculate the gross requirements for all other items.
These values are saved in the Requirement variable
in the Summarized Parts output data set
if the SUMMARYOUT= option is specified.
If the REQUIREMENT= option is not specified, the
Summarized Parts data set uses the
default name, Gros_Req.
See the section "Summarized Parts Data Set" for details on the calculation of the gross requirements. - RID=(variables)
-
identifies all variables in the Product Structure data
set that are not specified in the COMPONENT=,
FACTOR=, OFFSET=,
PARENT=, or QUANTITY= options,
and are to be included in the Indented BOM data set.
These variables are also referred to as RID variables.
The RID variables cannot be named as:
_Level_, L_Offset, _Parent_,
Paren_ID, _Part_, Part_ID, _Prod_,
Qty_Per, Qty_Prod,
S_Factor, Tot_Lead, or Tot_Off. This option
is useful for carrying other information stored in a product structure
record to the Indented BOM data set. This
typically includes engineering effectivity, operation number,
reference designator, and line sequence number.
The number of RID variables specified must be a multiple of the number of the Component variables. If you specify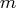 RID and
RID and 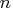 Component
variables as
Component
variables as
component=(COMP1-COMPn) RID=(VAR1-VARm)
the procedure distributes these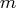 RID variables
to each product structure record with the parent item identified by the
Parent variable and the component identified
by each of the Component variables in the
following manner:
RID variables
to each product structure record with the parent item identified by the
Parent variable and the component identified
by each of the Component variables in the
following manner:
component 1st RID variable 2nd RID variable ... 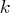 th RID variable
th RID variableCOMP 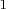
VAR 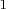
VAR 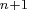
VAR 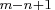
COMP 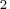
VAR 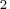
VAR 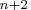
VAR 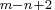
..... COMP 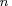
VAR 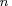
VAR 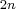
VAR 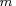
where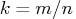 .
Note that the procedure treats the variables VAR
.
Note that the procedure treats the variables VAR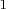 to VAR
to VAR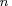 as the first RID variable for each of the
as the first RID variable for each of the 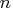 product structure records,
and hence, they must have the same
type, format, and length. The same rules apply to variables VAR
product structure records,
and hence, they must have the same
type, format, and length. The same rules apply to variables VAR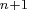 to VAR
to VAR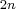 , ..., VAR
, ..., VAR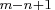 to VAR
to VAR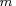 , etc.
, etc.
Copyright © 2008 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.