HTML Links and References Produced by the HTML Destination
What Are Links and References?
An HTML link is a place in a document that enables you
to jump to another specific place in the same document or in another
document. A browser typically highlights the text that is between
the tags that begin and end the link. When you click on the highlighted
text, the browser displays the text at the link target. The browser
might then display the contents of the target in the active window,
or it might open another browser window that displays the contents
of the target.
An HTML reference names a file for the browser to display.
When a browser reads a reference, it displays the referenced file
as if it were part of the file that it is displaying. You can't tell
by looking at the browser's display that some of the material is in
the file that you are actually viewing and that some is referenced.
Implementing HTML Links and References
Note: This simplified
discussion of HTML links and references is designed to provide information
that will help you understand what ODS does when it builds links and
references for you. For a complete discussion of HTML tagging, consult
one of the many reference books that are available on the subject.
Each link in HTML is
implemented with a combination of two sets of
<A> (anchor) tags. One anchor tag, which is the starting point of the
link, has an HREF attribute that identifies
the anchor tag to link to. The other anchor tag, which is the target
of the link, has a NAME attribute. This NAME attribute is what the HREF attribute in the first anchor tag points to. The value of each NAME attribute in a file must be unique so that each
value of HREF points to a single, unambiguous
location. The following figure illustrates linking within a file.
The browser highlights the word link. When you click on link, the browser
positions the target right here in
the active window.
When a link points to
a target outside the file that is being displayed, the
HREF attribute must include the path to that file. The
path can be the path within the file system or the uniform resource
locator (URL) of the file. The following figure illustrates a link
from one file to another file that is specified with a URL. The browser
highlights the word link. When you
click on link, the browser positions
the target right here in the active
window or opens another window that displays the target.
ODS provides features
that enable you to customize the text that precedes the pound sign
and the text that follows the pound sign. For information on how to
do this, see the discussions of file-specification, ANCHOR=, BASE=,
PATH=, and GPATH= in the ODS HTML Statement as well as How ODS Constructs Links and References.
HTML implements references
in much the same way as it implements links. The main difference is
that a link points to a particular location within a file and that
a reference points to the file itself. HTML uses the
SRC attribute to identify a file to reference. The value of the SRC attribute is constructed the same way that the value
of the HREF attribute is constructed except
that there is no pound sign and no text following it.
How ODS Constructs Links and References
Several options in the ODS
HTML statement affect how ODS constructs the links and references
that point from the frame to the table of contents, table of pages,
and body file and from the table of contents or table of pages to
the body file. Links are made as
HREF attributes
on <A> (anchor) tags inside the HTML
files. Each HREF attribute points to the NAME attribute on another <A> tag. The HREF must identify both the file
that contains the target and the name of the anchor within that file.
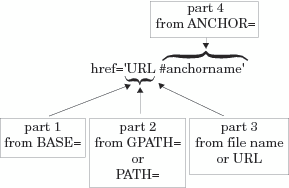
The value of HREF must be a valid target
in a valid URL. It uses the following form:
<A href="URL#anchor-name">
ODS constructs the
value of an
HREF attribute based on information
that you provide in the ODS HTML statement.
Note: HTML references to files
use other tags, but the logic for creating the string that identifies
the file is the same as the logic for creating an
HREF attribute (see How ODS Constructs Links and References).
-
If you specify GPATH= or PATH=, then the next part of the URL in an
HREFattribute comes from that option.If the file that you are linking to is a high-resolution graphic, then ODS uses information from the GPATH= option as the next part of theHREF. For information on these options, see the discussion of GPATH= and the discussion of PATH= in the ODS HTML Statement . The following table shows how ODS uses information from the GPATH= option in the URL inHREFattributes:Building an HREF Attribute from the GPATH= OptionInformation ODS Uses in the Second Part of the URL in the HREF attribute11If you do not specify GPATH=, then ODS uses the value of PATH= to create this part of the HREF. If the file that you are linking to is not a high-resolution graphic, then ODS uses information from the PATH= option as the next part of theHREF. The following table shows how ODS uses information from the PATH= option in the URL inHREFattributes:Note: If you use a fileref as the file specification in the BODY=, CONTENTS=, or PAGE= option in the ODS HTML statement, and you do not use the URL= suboption in that option, then ODS does not use information from GPATH= or PATH= when it creates the complete URL for any correspondingHREFattributes. -
The last part of the URL that is used in an
HREFattribute is, by default, the name of the file that contains the target. ODS determines the name of the file from the file-specification that you use in the BODY=, CONTENTS=, or PAGE= option. (ODS does not create links or references to frame files.) For more information on these options, see ODS MARKUP Statement.