Publishing Models to a Database
About Publishing Models to a Database
SAS Model Manager enables
you to publish the project champion model and challenger models that
are associated with the DATA Step score code
type to a configured database. SAS Model Manager uses the SAS Scoring
Accelerator and SAS/ACCESS interface to the database to publish models
to the database. The Scoring Accelerator takes the models from SAS
Model Manager and translates them into scoring files or functions
that can be deployed inside the database. After the scoring functions
are published using the SAS/ACCESS interface to the database, the
functions extend the database’s SQL language and can be used
in SQL statements such as other database functions. After the scoring
files are published, they are used by the SAS Embedded Process to
run the scoring model.
If the scoring function
publish method is chosen, the scoring metadata tables in the database
are populated with information about the project and pointers to the
scoring function. This feature enables users to review descriptions
and definitions of the published model. The audit logs track the history
of the model's usage and any changes that are made to the scoring
project.
For more information
about the SAS Scoring Accelerator, see the SAS In-Database Technology page available
at
http://support.sas.com.
Note: For more information about
the prerequisites before publishing models to a database, see Prerequisites for Publishing to a Database.
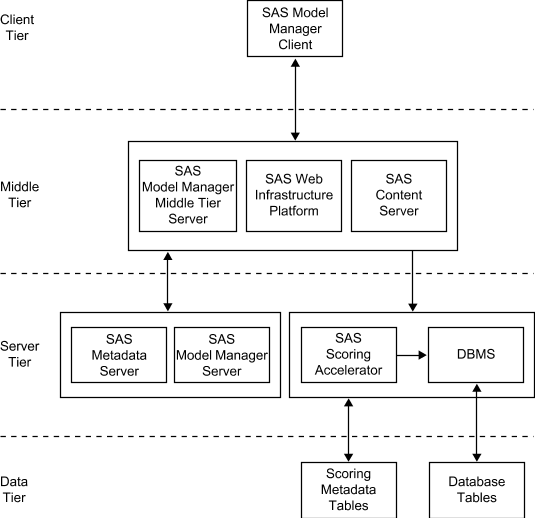
Here
is a diagram that represents the relationship between SAS Model Manager
and SAS Model Manager In-Database Support.
Here are descriptions
of the diagram's components.
SAS Model Manager Client
The SAS Model Manager
Client handles communication to and from SAS Model Manager. You use
the SAS Model Manager Client to create projects and versions, import
models, connect with data sources, validate models, run modeling reports,
run scoring tasks, set project status, declare the champion model,
and run performance tests.
SAS Model Manager Middle Tier Server
The SAS Model Manager
Middle Tier Server is a collection of services that are hosted by
an application server that orchestrates the communication and movement
of data between all servers and components in the SAS Model Manager
operational environment.
SAS Web Infrastructure Platform
The SAS Web Infrastructure
Platform (or WIP) is a collection of middle tier services and applications
that provides basic integration services. It is delivered as part
of the Integration Technologies package. As such, all Business Intelligence
applications, Data Integration applications, and SAS Solutions have
access to the Web Infrastructure Platform as part of their standard
product bundling.
SAS Content Server
The SAS Model Manager
model repository and SAS Model Manager project tree configuration
data and metadata are stored in the SAS Content Server. Communication
between SAS Model Manager and the SAS Content Server uses the WebDAV
communication protocol.
SAS Model Manager Server
The SAS Model Manager
Server is a collection of macros on the SAS Workspace Server that
generate SAS code to perform SAS Model Manager tasks.
SAS Scoring Accelerator
The SAS Scoring Accelerator
creates scoring functions or model files that can be deployed inside
a database. The scoring functions or model files are based on the
project's champion model score code or challenger model score
code.
DBMS
The relational databases
in the database management system (DBMS) serve as output data sources
for SAS Model Manager.
Process Flow
This is an example of
the process flow to publish a scoring model to a database. For more information,
see How to Publish Models to a Database.
-
From SAS Model Manager, you select the Publish Models
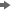 to a Database for the project
that contains the champion model or challenger model that you want
to publish to a specific database. For more information,
see How to Publish Models to a Database.
to a Database for the project
that contains the champion model or challenger model that you want
to publish to a specific database. For more information,
see How to Publish Models to a Database. -
After you select the publish method and complete all the required information to publish the model to a database, SAS Model Manager establishes a connection to the database using the credentials that were entered. The publish name is validated against the target database. If the publish name is not unique, an error message is displayed.
-
The middle-tier server updates the scoring metadata tables (for example, table project_metadata). For more information see, Scoring Function Metadata Tables.
-
The middle-tier server updates the project user-defined properties with the publish name that was entered in the Publish Models to a Database window.Note: For more information about the user-defined properties that are created when publishing, see SAS User-Defined Properties.
Prerequisites for Publishing to a Database
Make User-Defined Formats Available When Publishing Models to a Database
In order to publish
models with user-defined formats to a database using the Publish Models
to a Database feature, you must make the user-defined formats available
to SAS Model Manager.
-
Send a request to the SAS administrator and ask them to either put the user-defined formats SAS data set (formats.sas7bcat) in the \\SASConfigDirectory\Lev1\SASApp\SASEnvironment\SASFormats directory or add the LIBNAME definition for the formats library to the \\SASConfigDirectory\Lev1\SASApp\appserver_autoexec_usermods file.
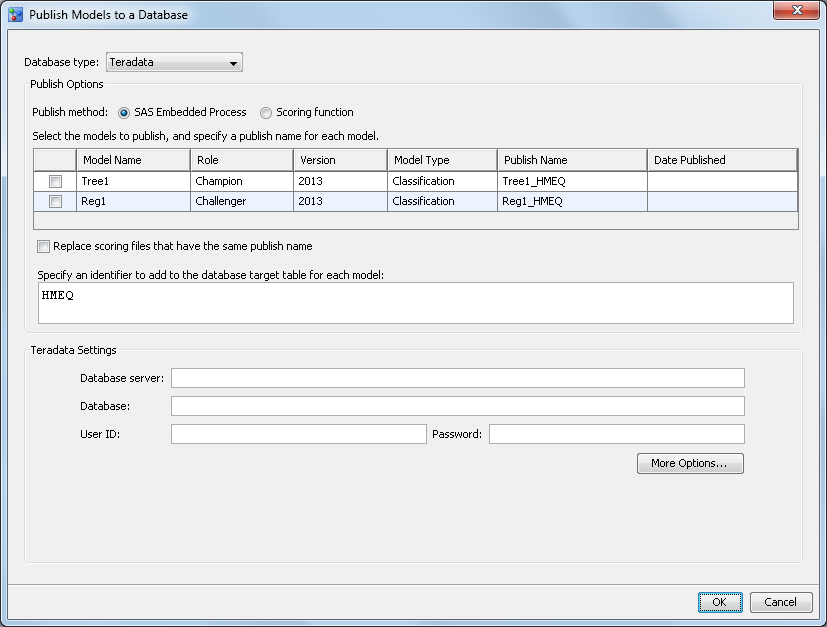
Publish Models to a Database Field Descriptions
Database type
specifies the type
of database to which the scoring function or model scoring files are
published.
Publish method
specifies the method
to use when publishing the scoring function or model files to the
database.
Publish name
specifies the name
to use when publishing a scoring function or model files to the database.
The publish name is a user-defined value that can be modified. The
SAS Embedded Process publish method uses the publish name as
the model name to publish the model files to the database. The scoring
function publish method has a system-generated prefix and
the publish name that makes up the scoring
function name. These are used to publish the model scoring function.
The prefix portion
of the scoring function name is 11 characters long and is in the format
of Yyymmddnnn_.
The yymmdd value
in the prefix is the GMT timestamp that identifies the date on which
you selected the Publish Models to a Database menu option.
An example of a function name is Y081107001_user_defined_value.
Here are the naming convention requirements:
to a Database menu option.
An example of a function name is Y081107001_user_defined_value.
Here are the naming convention requirements:
Here are the naming
convention requirements for the publish name:
Replace scoring files that have the same publish
name
specifies to replace
the model scoring files that have the same publish name when you are
using the SAS Embedded Process publish method. The value of the publish
name is validated against the target database when this option is
not selected. If the publish name is not unique, an error message
is displayed.
Specify an identifier to add to the database table
for each model
specifies the value
of the identifier that is added to each model in the database so that
the Database administrator or other users can query the database.
The default value is the project name. This option is available only
for the SAS Embedded Process publish method.
Server user ID (DB2 only)
specifies the user
ID for SAS SFTP. This value enables you to access the machine on which
you have installed the DB2 database. If you do not specify a value
for Server user ID, the value of User
ID is used as the user ID for SAS SFTP.
Schema(Greenplum, Oracle, and DB2)
specifies the schema
name for the database. The schema name is owned by the user that is
specified in the User ID field. The schema
must be created by your database administrator.
Compile database (Netezza only)
specifies the name
of the database where the SAS_COMPILEUDF function is published.
See Also: For
more information about publishing the SAS_COMPILEUDF function, see
the SAS In-Database Products: Administrator's Guide.
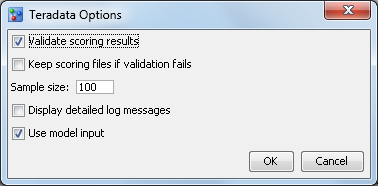
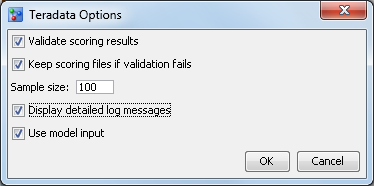
Options
Validate scoring results
specifies to validate
the scoring results when publishing a model scoring function or model
scoring files. This option creates a benchmark scoring result on the
SAS Workspace Server using the DATA Step score code. The scoring input
data set is used to create an equivalent database table. Scoring is
performed using the new scoring function or model scoring files and
database table. The scoring results are then compared.
Keep scoring function if validation fails(scoring
function) or Keep scoring files if validation fails (SAS
Embedded Process)
specifies to save the
scoring function or model scoring files if the validation of the scoring
results fails. Saving the scoring function or model scoring files
is useful for debugging if validation fails.
Use model input
specifies to use the
selected model input when publishing the scoring function or model
files instead of using the project input, which is the default. This
is useful when the project input variables exceed the limitations
for a database.
Protected mode (Teradata only)
specifies the mode
of operation to use when publishing a model using the scoring function
publish method. There are two modes of operation, protected and unprotected.
You specify the mode by selecting or deselecting the Protected
mode option. The default mode of operation is protected.
Protected mode means that the macro code is isolated in a separate
process from the Teradata database, and an error does not cause database
processing to fail. You should run the Publish Scoring Function in
protected mode during validation. When the model is ready for production,
you can run the Publish Scoring Function in unprotected mode. You
might see a significant performance advantage when you run the Publish
Scoring Function in unprotected mode.
Fenced mode (DB2 and Netezza only)
specifies the mode
of operation to use when publishing a model using the scoring function
publish method. There are two modes of operation, fenced and unfenced.
You specify the mode by selecting or deselecting the Fenced
mode option. The default mode of operation is fenced.
Fenced mode means that the macro code is isolated in a separate process
from the DB2 database, and an error does not cause database processing
to fail. You should run the Publish Scoring Function in fenced mode
during validation. When the model is ready for production, you can
run the Publish Scoring Function in unfenced mode. You might see a
significant performance advantage when you run the Publish Scoring
Function in unfenced mode.
How to Publish Models to a Database
-
Verify that you have set the champion model and challenger models that you want to publish. For more information, see Set a Champion Model.
-
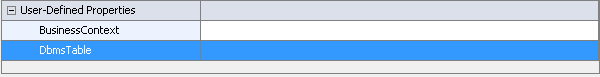
Note: If you plan to use scoring application or SQL Code to score this project, you can set the DbmsTable property to the name of input table in your database that you want to use for scoring the champion model. When you publish a scoring function or model files, the information that is associated with the input table in the database is updated to contain the value of the DbmsTable property. The scoring application or SQL code can then query the database for the input table name to use as the scoring input table.For more information, see User-Defined Properties.
-
Select a database type and publish method. The type of database and the publish method that you choose determine which database settings and options are required.Operating Environment Information: The SAS Embedded Process can be used with the SAS Scoring Accelerator for Netezza to run scoring models with the release of SAS 9.4. The SAS Administrator can enable Netezza support for SAS Model Manager so that the Netezza database type appears when using the SAS Embedded Process publish method. For more information, see the SAS Model Manager: Administrator's Guide.
-
Enter a publish name for each model that you selected to publish. The scoring function publish method has a system-generated prefix and the publish name. These are used to publish the model scoring function. The SAS Embedded Process publish method uses only the publish name to publish the model files to the database. The publish name is a user-defined value that can be modified.Here are the naming convention requirements:
-
The maximum length of the publish name for the SAS Embedded Process publish method is 128 alphanumeric characters for all databases. However, the recommended maximum length of the publish name is 32 alphanumeric characters for all database types. The database types that are currently supported by SAS Model Manager are Teradata, Oracle, Netezza, Greenplum, and DB2.
-
Click OK. A message is displayed to indicate whether the models were published to the database successfully or not.
Log Messages
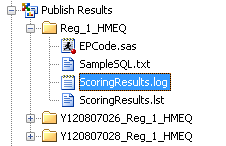
A user can view the
log file after publishing a scoring model to a database. The Publish
Results folder in the Project Tree contains a folder
for each model that was published. The publish name is used to create
a folder for each model that is published. That folder contains the
ScoringResults.log file. The time at which the process started, details
about who initiated the process, and the time at which the project
was published are recorded. Error messages are also recorded in the
log file. The log file provides an audit trail of all relevant actions
in the publishing process.
Scoring Function Metadata Tables
If the metadata tables
are created and configured for use in SAS Management Console, the
following tables are populated in the database when you are publishing
a scoring function:
model_metadata
provides information
about the champion model, such as the function name and signature
that are stored within this table.
project_model_info
maps a project to the
champion model, as well as provides information about the current
active scoring model.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.