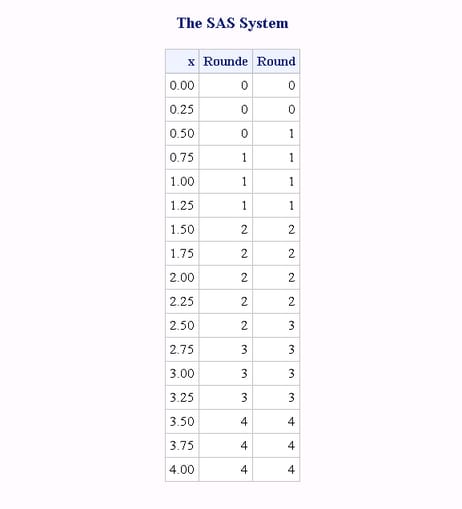
ROUNDE Function
Rounds the first argument to the nearest multiple of the second argument, and returns an even multiple when the first argument is halfway between the two nearest multiples.
| Category: | Truncation |
Comparisons
The ROUND, ROUNDE, and
ROUNDZ functions are similar with four exceptions:
-
When the rounding unit is less than one and not the reciprocal of an integer, the result that is returned by ROUNDZ might not agree exactly with the result from decimal arithmetic. ROUND and ROUNDE perform extra computations, called fuzzing, to try to make the result agree with decimal arithmetic in the most common situations. ROUNDZ does not fuzz the result.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.