Creating a Define-XML 2.0 define.xml File from ADaM Source Data
Overview
The SAS Clinical Standards
Toolkit supports the currently published CDISC Analysis Results Metadata
1.0 extension for the Define-XML 2.0 submission standard, which supports
representation of the ADaM 2.1 analysis data sets in metadata form,
including Analysis Results Metadata.
Assumption
You have a library of
CDISC ADaM SAS data sets (which are not read by this process) from
which a set of metadata (in the form of source_study, source_tables,
source_columns, source_codelists, source_values, source_documents,
and source_analysisresults data sets) has been created. This metadata
must contain the expected, correctly typed columns created for the
sample study provided by SAS. The source_study, source_tables, and
source_columns data sets are the minimally required SAS data sets
to create a Define-XML 2.0 file.
Location of Define-XML 2.0 Driver Programs
The Define-XML driver
programs are located in the
sample study library directory/cdisc-definexml-2.0-1.7/programs directory.
Step 1: Extract Available ADaM Source Metadata into the SAS Representation of Define-XML 2.0 Metadata
The initial task is
to extract the available ADaM metadata into Define-XML 2.0 metadata
files. The complete SAS representation of Define-XML 2.0 involves
54 data sets, but only 31 of these are typically used to create of
a Define-XML 2.0 file. The other 23 data sets contain Operational
Data Model (ODM) metadata or Analysis Results metadata, which are
extensions of the Define-XML 2.0 model.
The sample driver program
create_definexml_from_source_adam.sas, modified to point to your specific
ADaM study metadata, must be submitted to create the SAS representation
of Define-XML 2.0 metadata. This process builds 39 data sets in the
SAS WORK library, but it might not populate all of the data sets (depending
on the completeness of the metadata of your study). The 39 data sets
consist of the 31 core Define-XML 2.0 data sets and eight data sets
related to Analysis Results metadata.
The sample driver program
runs the following macro:
%define_sourcetodefine( _cstOutLib=srcdata, _cstSourceStudy=sampdata.source_study, _cstSourceTables=sampdata.source_tables, _cstSourceColumns=sampdata.source_columns, _cstSourceCodeLists=sampdata.source_codelists, _cstSourceValues=sampdata.source_values, _cstSourceDocuments=sampdata.source_documents, _cstSourceAnalysisResults=sampdata.source_analysisresults, _cstFullModel=N, _cstCheckLengths=Y, _cstLang=en );
The macro is located
in the
global standards library directory/standards/cdisc-definexml-2.0-1.7/macros directory.
Note: The key input files (source
files) are the ADaM metadata files (source_study, source_tables, source_columns,
source_codelists, source_values, source_documents, and source_analysisresults),
not the ADaM domain data sets. The metadata files (source files) to
create a Define-XML 2.0 file have a different structure than the metadata
files (source files) that are used to create a CRT-DDS 1.0 file.
In the sample study,
the source metadata files for the ADaM 2.1 study are located in the
sample study library directory/cdisc-definexml-2.0-1.7/
sascstdemodata/cdisc-adam-2.1/metadata directory.
Step 2: Create the define.xml File
At this point, all available
content for the define.xml file has been captured in the SAS representation
(39 data sets) of the CDISC Define-XML 2.0 standard. The next step
is to build and validate the define-adam-2.1.xml file.
In the driver program,
the call to the %DEFINE_WRITE macro requests that the default style
sheet provided by SAS (based on the CDISC style sheet) be copied to
the folder location that contains the generated define-adam-2.1.xml
file. The macro is located in the
global standards library directory/standards/cdisc-definexml-2.0-1.7/macros directory.
Here is the macro:
%define_write(_cstCreateDisplayStyleSheet=1,
_cstHeaderComment=%str(Produced from SAS data using the SAS
Clinical Standards Toolkit &_cstVersion));Here is a portion of
the define-adam-2.1.xml file, as rendered by the default style sheet
in a browser. Links among tables, columns, codelists, and other file
elements are provided.
Partial Sample define-adam-2.1.xml File (as Rendered by the
Default Style Sheet)
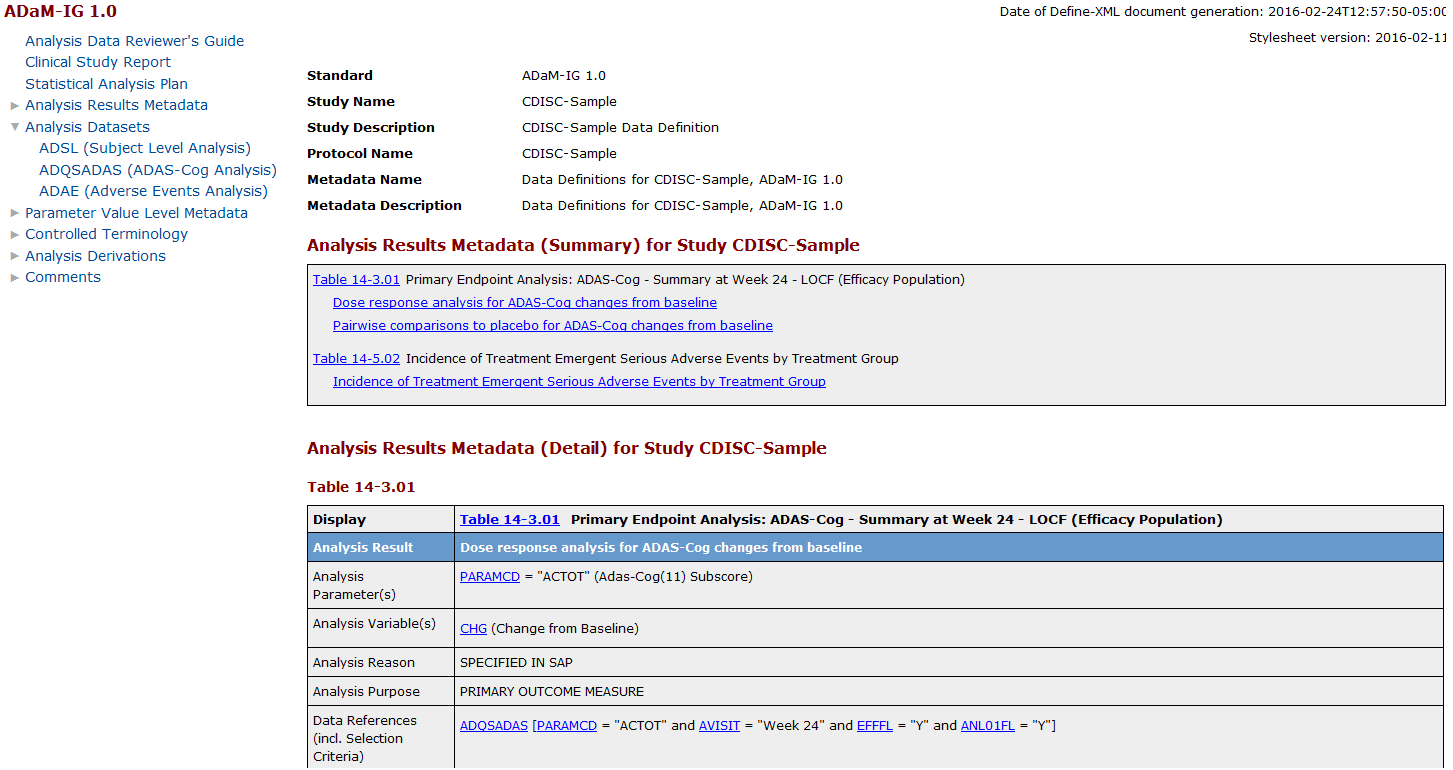
The next task in the
sample create_definexml_from_source_adam.sas driver program is to
call the %CSTUTILXMLVALIDATE macro to perform the schema validation.
This involves verifying that the Define-XML file is valid both structurally
and syntactically, according to the XML schema.
The sample create_definexml_from_source_adam.sas
driver program also contains SAS code to create the HTML rendition
define-adam-2.1.html of the define-adam-2.1.xml using the define2-0-0.xsl
style sheet:
proc xsl in=extxml xsl=xslt01 out="&studyOutputPath/sourcexml/%sysfunc(tranwrd(&_cstDefineFile, %str(.xml), %str(.html)))"; parameter 'nCodeListItemDisplay'=5 'displayMethodsTable'=1 'displayCommentsTable'=1; run;
If the style sheet parameters
displayMethodsTable and displayCommentsTable were set to 0, the resulting
HTML file would not have the separate tables for methods and comments.
Note: The SAS Clinical Standards
Toolkit 1.7
does not contain validation checks to validate the SAS representation
of the Define-XML 2.0 standard. The only methodology included in the
SAS Clinical Standards Toolkit 1.7
to validate a Define-XML 2.0 file is XML schema validation.
Here is a sample Results
data set produced by the validation process:
Partial Sample Results Data Set (CDISC Define-XML 2.0 Create
Process)
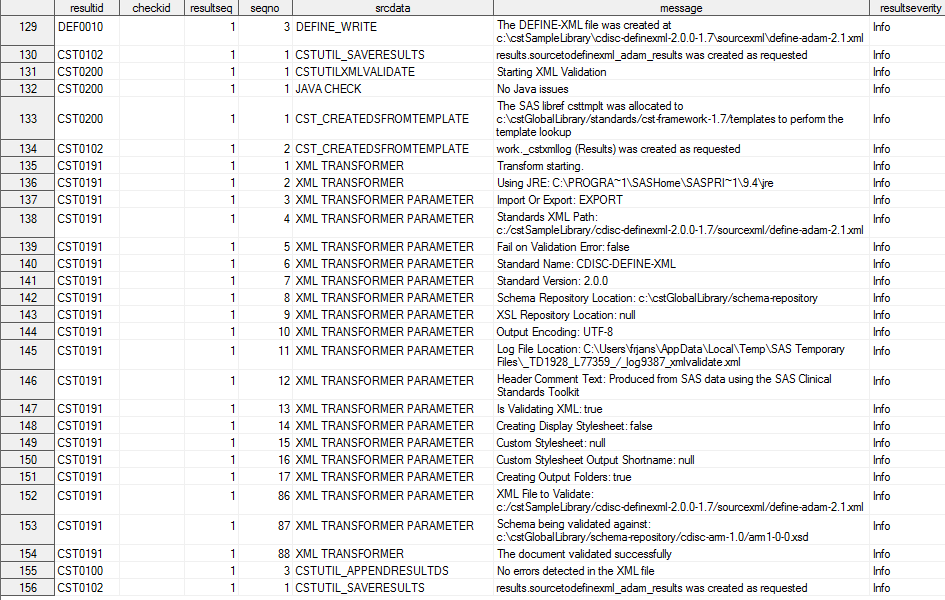
The Results data set
provides process information and the location of the generated define-adam-2.1.xml
file. The Results data set confirms that no problems were found with
the file following validation of the file.
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All Rights Reserved.