Usage Note 65600: SAS support for Microsoft Security Update ADV190023
 |  |  |
Microsoft published the 2020 LDAP channel binding and LDAP signing requirements for Windows article that states:
"LDAP channel binding and LDAP signing provide ways to increase the security for communications between LDAP clients and Active Directory domain controllers. A set of unsafe default configurations for LDAP channel binding and LDAP signing exist on Active Directory domain controllers that let LDAP clients communicate with them without enforcing LDAP channel binding and LDAP signing. This can open Active Directory domain controllers to an elevation of privilege vulnerability.
Microsoft recommends administrators make the hardening changes described in ADV190023."
In summary, after you complete the recommended steps, a simple bind to Active Directory without Transport Layer Security (TLS) fails whether the bind is anonymous or by a user name and password.
Contents:
- What Does This Mean for Your SAS Applications?
- How Do I Know Whether My Applications are Configured to Use LDAPS or startTLS?
- Quick Loggers
What Does This Mean for Your SAS Applications?
SAS®9 and SAS® Viya® support using encryption on the connection to your LDAP provider using either secure LDAP (LDAPS) or the Start TLS Operation (startTLS). SAS applications and jobs that are clients to Active Directory fail to connect to your Active Directory server if they are using a non-secure connection. These applications include the following:
- SAS®9 Metadata Server Direct LDAP Authentication (also referred to as Direct Use of LDAP)
- SAS®9 programs that use the LDAP CALL Routine Interface
- SAS®9 Sample Code for Active Directory (importad.sas), and your customized programs that use the User Import Macros to add or synchronize metadata identities to LDAP. This sample program uses the LDAP CALL Routine Interface.
- SAS Viya
How Do I Know Whether My Applications are Configured to Use LDAPS or startTLS?
The default TLS-configured ports for Microsoft Active Directory are 636 and 3269. Using either of these ports in SAS®9 connection properties, SAS®9 programs, and SAS Viya is a good indication that LDAPS is in use, though it still depends on how the ports on your Active Directory server are configured. The default ports for non-secured LDAP are 389 and 3268.
The following sections describe:
- the configuration options for integration with Microsoft Active Directory
- the location of these options
- expected errors when an unsecure bind is attempted against a Microsoft Active Directory server with the security update
SAS®9 SAS Metadata Server
The SAS Metadata Server supports LDAPS in its configuration for the Direct LDAP Authentication mechanism. Evaluate the configuration files on the metadata server to determine whether Direct LDAP Authentication is configured. The best practice is to provide the configuration options in the SAS-configuration-directory/SASMeta/MetadataServer/sasv9_usermods.cfg file. Here is an example:
-set AD_PORT 636
-set AD_TLSMODE 1
-AUTHPD (ADIR:company.com)
To comply with the Microsoft security update, make certain that the following are true:
- AD_PORT is a TLS-configured port on Active Directory.
- AD_TLSMODE is set to 1.
Here is an example message from SAS Management Console showing a failed authentication to a Microsoft Active Directory server that has the security update.
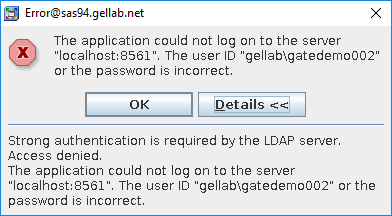
You can further confirm the protocol that is being used by enabling enhanced logging on the SAS Metadata Server, which writes messages to the metadata server log tracing the authentication process. Notice this connection is using a non-secured port (389):
2020-03-11T11:59:41,477 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - Attempting tcpSockConnect(10.96.7.202)
2020-03-11T11:59:41,478 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - 0x803fd003=tcpSockConnect(115): 'The specified operation is now in progress.'
2020-03-11T11:59:41,478 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - 0x0=tcpRegisterEvent()
2020-03-11T11:59:41,478 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - 0x0=tcpSockConnect(0): 'An unexpected error has occurred. Error number is 0.'
2020-03-11T11:59:41,480 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - tkldOpen encountered a failure in ldap_simple_bind_s.
2020-03-11T11:59:41,481 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - LDAP error number: 8.
2020-03-11T11:59:41,481 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - ld_error: LDAP server reports additionally: 00002028: LdapErr: DSID-0C090256, comment: The server requires binds to turn on integrity checking if SSL\TLS are not already active on the connection, data 0, v3839
2020-03-11T11:59:41,481 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - Strong authentication is required by the LDAP server.
2020-03-11T11:59:41,481 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - Provider failed: 80bfd100
2020-03-11T11:59:41,481 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - SecurityRefDestroy: Token id [3857da00] Reference count decreased to: 0
2020-03-11T11:59:41,483 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - SecurityRefDestroy: calling SecurityTokenDestroy(3857da00)
2020-03-11T11:59:41,483 DEBUG [00000064] :sas - SecurityTokenDestroy: calling bkTokenDestroy(3857da00)
2020-03-11T11:59:41,482 WARN [00000064] :sas - New client connection (10) rejected from server port 8561 for user gellab\gatedemo002. Peer IP address and port are [::ffff:10.96.17.222]:37836 for APPNAME=SASManagementConsole 904601.
Refer to the following documentation for more information:
- How to Configure Direct LDAP Authentication in SAS® 9.4 Intelligence Platform: Security Administration Guide.
- How to Configure TLS between the Metadata Server and an LDAP Server in SAS® 9.4 Intelligence Platform: Security Administration Guide.
- SAS Note 51911, "Troubleshooting SAS® Metadata Server authentication issues in SAS® 9.3 and later"
- The Quick Loggers section at the bottom of this note.
SAS®9 Programs That Use the LDAP CALL Routine Interface, Including Sample Code for Active Directory (importad.sas)
The LDAP CALL Routine Interface in SAS®9 supports LDAPS. The call routines allow a SAS program to make a connection to an LDAP server and to perform various actions on LDAP directory entries. Here are typical program uses of the LDAP CALL Routine Interface, which are all indicated by their use of the CALL LDAPS_OPEN routine:
- the Sample Code for Active Directory, importad.sas, which is used to add identities to metadata from an Active Directory source
- programs that query Active Directory to find person information, such as an email address, to distribute reports or other information
- any SAS program that uses the CALL LDAPS_OPEN routine
To comply with the Microsoft security update, make certain that all instances of the CALL LDAPS_OPEN routine in the SAS program specify a TLS-configured port and either of the following:
- The CALL LDAPS_OPEN routine specifies the session option: TLS_MODE_ON.
- The environment variable LDAP_TLSMODE has a value of 1.
Here is an example of the CALL LDAPS_OPEN routine:
Here is an example of setting the LDAP_TLSMODE environment variable on the SAS invocation command:
Here is an example message in the SAS Log showing a failed connection to a Microsoft Active Directory server that has the security update:
ERROR: Strong authentication is required by LDAP server. ERROR: LDAP server reports additionally: 00002028: LdapErr: DSID-0C090256,
comment: The server requires binds to turn on integrity checking if SSL\TLS are not already active on the connection, data 0, v3839
Additionally, if you enable TRACE or DEBUG level logging for the App.tk.LDAP logger for the SAS session, the program log also contains an error similar to the following:
2020-03-11T12:06:54,988 DEBUG App.tk.LDAP - LDAP error number: 8.
2020-03-11T12:06:54,988 DEBUG App.tk.LDAP - ld_error: LDAP server reports additionally: 00002028: LdapErr: DSID-0C090256, comment: The server requires binds to turn on integrity checking if SSL\TLS are not already active on the connection, data 0, v3839
2020-03-11T12:06:54,988 DEBUG App.tk.LDAP - Strong authentication is required by the LDAP server.
Refer to the following documentation links for more information:
- CALL LDAPS_OPEN Routine in SAS® 9.4 Integration Technologies: Directory Services Reference
- About the Sample Code for Active Directory in SAS® 9.4 Intelligence Platform: Security Administration Guide, Third Edition
- The Logging Facility for SAS Programs in SAS® 9.4 Logging: Configuration and Programming Reference, Second Edition
- The Quick Loggers section at the bottom of this note
SAS Viya
The identities and SASLogon services in SAS Viya 3.3 and earlier support LDAPS. In SAS Viya 3.4 and later, identities and SASLogon services support LDAPS and startTLS. The services use LDAP to determine which users can access SAS Viya web applications. The connection from the identities and SASLogon services to LDAP is determined by the properties under the sas.identities.providers.ldap.connection configuration instance for each service. Here is an example:
host: ad-server.company.com
password: Password123
port: 636
startTLS.mode: none
url: ldaps://${sas.identities.providers.ldap.connection.host}:${sas.identities.providers.ldap.connection.port}
To comply with the Microsoft security update, make certain that either of the following are true:
- The port is a TLS-configured port and the URL specifies the ldaps protocol.
- The port is unsecured, the startTLS is simple, and the URL specifies the ldap protocol.
When the connection to Microsoft Active Directory is not secure, the identities service fails to connect to Active Directory. The Users page in SAS Environment Manager reports "No users were found" and "No groups were found" when you select the Users and Groups views, respectively.
Additionally, the identities service log contains the message:
Note: The identities service log is located in /opt/sas/viya/config/var/log/identities/default/.
In a full or visual-only deployment, the default authentication mechanism is LDAP. In this scenario, and when the the connection to Active Directory is not secure, the SASLogon service fails to connect to Active Directory. End users see the following message in their browser:
Additionally, the SASLogon log contains the following message:
Note: The SASLogon service log is located in /opt/sas/viya/config/var/log/saslogon/default/.
Refer to the following documentation links for more information:
- Encrypt LDAP Connections in Encryption in SAS® Viya® 3.5: Data in Motion.
- SAS KB0036450, "Troubleshooting identities and the identities service in SAS® Viya®"
- SAS Viya The Importance of LDAP Encryption
- The Quick Loggers section at the bottom of this note
Quick Loggers
Use this section to quickly enable enhanced logging. Logging can be important to capture bind failures to an LDAP directory server, including Microsoft Active Directory. Note that it is important to return loggers to their previous levels after you have collected the needed data. Otherwise, log files will grow rapidly in size, potentially consuming all available disk space.
SAS Metadata Server
-
Edit the following code by providing valid values for the HOST=, PORT=, USER=, and PASS= options in order to connect to the SAS Metadata Server:
proc iomoperate;
connect host='host-name'
port=port-number
user='user-ID'
pass='password';
list attributes category="Loggers" name="Audit.Authentication";
list attributes category="Loggers" name="App.tk.LDAP";
list attributes category="Loggers" name="App.tk.eam.ssl";
set attribute category="Loggers" name="Audit.Authentication" value="Debug";
set attribute category="Loggers" name="App.tk.LDAP" value="Debug";
set attribute category="Loggers" name="App.tk.eam.ssl" value="Trace";
quit;
- Submit the step from within a Base SAS® session. It is generally best to use a SAS session that is launched from the SAS Metadata Server, but it is not mandatory as long as the SAS session can connect to the SAS Metadata Server.
Note: The LIST statement within the IOMOPERATE procedure generates a listing of logger levels before changing their value. This is a useful reference when returning logging levels to their previous level.
- Return logger levels to their previous value by editing the above code. Change the value Trace to be the value that was written to the SAS log before setting the new value. Note that the value might be NULL. Submit the step.
Note: Restarting the SAS Metadata Server reverts logging to the original levels. These levels are determined by the log configuration file.
SAS Program That Uses CALL LDAPS_OPEN
- Insert the following lines at the top of your program. Edit the FILENAME to specify a valid path and name for the log file.
%log4sas();
%LOG4SAS_APPENDER(ldapappend, "FileRefAppender", 'FILEREF=ldapopen PATTERN="%d %-5p %c - %m"');
%LOG4SAS_LOGGER(App,'ADDITIVITY=FALSE level=info appender-ref=(ldapappend)');
%LOG4SAS_LOGGER(App.LDAP,'ADDITIVITY=FALSE level=info appender-ref=(ldapappend)');
%LOG4SAS_LOGGER(App.tk.LDAP,'ADDITIVITY=FALSE level=trace appender-ref=(ldapappend)');
%LOG4SAS_LOGGER(App.tk.eam.ssl,'level=trace appender-ref=(ldapappend)');
- Submit your program in batch or in a standard SAS session. Because of conflicts with default logging for compute servers in an Intelligence Platform deployment, these statements do not enable logging in IOM compute server sessions.
In addition to the standard job log, you will have a separate file containing the trace data for the LDAP bind. The name and location of this second file is specified in the FILENAME statement in the example.
SAS Viya
For SAS Viya 3.4 and later, use the following commands to set loggers for the identities and SASLogon services. Each of these commands should be run as a single line from a shell prompt on the machine running the SAS® Configuration Server, and should be run as the sas user (or a user with sudo privileges).
- Determine whether loggers are already set, and if so, at which level:
source /opt/sas/viya/config/consul.confexport CONSUL_HTTP_TOKEN=$(sudo cat /opt/sas/viya/config/etc/SASSecurityCertificateFramework/tokens/consul/default/client.token)/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv read --recurse config/identities/logging.level/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv read --recurse config/SASLogon/logging.level
Note: These two read commands return logging levels for the identities and SASLogon services. This is a useful reference when returning logging levels to their previous level. If nothing is returned by the read command, then no logging level is explicitly set.
- Set loggers for enhanced logging:
/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv write --force config/identities/logging.level/com.sas.identities.provider.ldap "TRACE"/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv write --force config/identities/logging.level/org.springframework.security.ldap "TRACE"/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv write --force config/SASLogon/logging.level/org.springframework.ldap "DEBUG"
- Return loggers to their previous value. If no data was returned by the read command in step 1, then you should delete the logger keys you created by the write command. Here is an example that shows how to delete each key that was created:
/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv delete config/identities/logging.level/com.sas.identities.provider.ldap/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv delete config/identities/logging.level/org.springframework.security.ldap/opt/sas/viya/home/bin/sas-bootstrap-config kv delete config/SASLogon/logging.level/org.springframework.ldap
Operating System and Release Information
| Product Family | Product | System | SAS Release | |
| Reported | Fixed* | |||
| SAS System | Base SAS | Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Std | ||
| 64-bit Enabled AIX | ||||
| Windows Vista | ||||
| Windows Vista for x64 | ||||
| Windows Millennium Edition (Me) | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise 32 bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP Professional | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2019 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Std | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2016 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows NT Workstation | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled HP-UX | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled Solaris | ||||
| ABI+ for Intel Architecture | ||||
| AIX | ||||
| HP-UX | ||||
| HP-UX IPF | ||||
| IRIX | ||||
| Linux | ||||
| Linux for x64 | ||||
| Linux on Itanium | ||||
| OpenVMS Alpha | ||||
| OpenVMS on HP Integrity | ||||
| Solaris | ||||
| Solaris for x64 | ||||
| Tru64 UNIX | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 95/98 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 10 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Pro x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Pro 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| OS/2 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft® Windows® for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft® Windows® for 64-Bit Itanium-based Systems | ||||
| OpenVMS VAX | ||||
| Macintosh | ||||
| z/OS | ||||
| z/OS 64-bit | ||||
| SAS System | SAS Integration Technologies | z/OS | ||
| z/OS 64-bit | ||||
| Microsoft® Windows® for 64-Bit Itanium-based Systems | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft® Windows® for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Pro 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Pro x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 10 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 95/98 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional | ||||
| Microsoft Windows NT Workstation | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Std | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Std | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2016 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2019 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP Professional | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate x64 | ||||
| Windows Millennium Edition (Me) | ||||
| Windows Vista | ||||
| Windows Vista for x64 | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled AIX | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled HP-UX | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled Solaris | ||||
| AIX | ||||
| HP-UX | ||||
| HP-UX IPF | ||||
| Linux | ||||
| Linux for x64 | ||||
| Linux on Itanium | ||||
| OpenVMS Alpha | ||||
| OpenVMS on HP Integrity | ||||
| Solaris | ||||
| Solaris for x64 | ||||
| Tru64 UNIX | ||||
| SAS System | SAS Metadata Server | z/OS | ||
| Microsoft® Windows® for 64-Bit Itanium-based Systems | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP 64-bit Edition | ||||
| Microsoft® Windows® for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Pro 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8 Pro x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro 32-bit | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 8.1 Pro x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 10 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 95/98 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Advanced Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Datacenter Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Server | ||||
| Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional | ||||
| Microsoft Windows NT Workstation | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Datacenter Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2003 for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2008 for x64 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Std | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2012 Std | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2016 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows Server 2019 | ||||
| Microsoft Windows XP Professional | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Enterprise x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Home Premium x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Professional x64 | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate 32 bit | ||||
| Windows 7 Ultimate x64 | ||||
| Windows Millennium Edition (Me) | ||||
| Windows Vista | ||||
| Windows Vista for x64 | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled AIX | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled HP-UX | ||||
| 64-bit Enabled Solaris | ||||
| HP-UX IPF | ||||
| Linux | ||||
| Linux for x64 | ||||
| Linux on Itanium | ||||
| Solaris for x64 | ||||
| SAS System | SAS Viya | Microsoft® Windows® for x64 | Viya | |
| Linux for x64 | Viya | |||
| Type: | Usage Note |
| Priority: |
| Date Modified: | 2020-03-16 10:39:37 |
| Date Created: | 2020-02-24 09:43:08 |