Transpose Data Task
About the Transpose Data Task
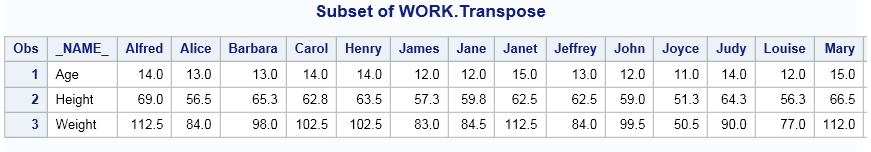
The Transpose Data task turns selected columns of an input table into the rows of an output table. If you do not use grouping variables, then each selected column is turned into a single row. If you use grouping variables,
then the selected columns are divided into subcolumns based on the values of the grouping
variables. Each subcolumn is turned into a row of the output table.
Assigning Data to Roles
To run the Transpose
Data task, you must assign a column to the Variables to
transpose role.
|
Roles
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Roles
|
|
|
Variables
to transpose
|
Each variable that you assign to this role becomes one or more rows of the output
table. If you do not select any grouping variables, then an entire column is turned
into a single row. If you select one or more grouping
variables, then the grouping variables are used to segment each column into subcolumns,
each of which is turned into a row. In this case, a column is transposed to the number
of rows that is equal to the number of groups that are defined by the grouping variables.
You must assign at least
one column to the Transpose variables role. To select a grouping variable, assign a column to the Group
analysis by role.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Group analysis
by
|
Each variable that you assign to this role is used to segment the about-to-be-transposed
columns into subcolumns that will be transposed separately. Each subcolumn, defined
by a set of values of the grouping variables, becomes a row of the output table.
|
|
Output Data Set
|
|
|
Copy to
output data set
|
Each variable that you assign to this role is copied directly from the input table
to the output table without being transposed. Because these columns are copied directly
to the output
table, the number of rows in the output table equals the number of rows in the input
table. The output table is padded with missing values if the number of rows in the input table does not equal the number of variables that
it transposes.
|
|
Show output
data
|
specifies whether to include the output data in the results that appear on the Results tab. You can include all or a subset of the output data. The task always creates the output data set that appears on the Output Data tab. This data set is also saved to the specified location.
|
Setting Options
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Names and Labels of
Transposed Variables
|
|
|
Construct New Variable
Names
|
|
|
Use prefix
|
You can specify a prefix to use in constructing the names for the transposed variables
in the output data set. When you use a prefix, the variable name begins with the prefix
value and is followed
by the number 1, 2, and so on.
|
|
Select a
variable that contains the names of the new variables
|
The variable that you
assign to the New column names role is used to name the transposed variables in the output data set.
If you specified to
use a prefix in the name, the name for the new variable begins with
the prefix and is followed by the value of the New column
names variable.
If you select the Allow
duplicate of ID values check box, the transposed output data set contains only the last observation for each BY group.
|
|
Construct New Variable
Labels
|
|
|
Select a
variable that contains the labels of the new variables
|
The values of the variable
that you assign to the New column labels role are used to label the variables in the output data set.
|
|
Names and Labels of
Original Variables
|
|
|
Put original
variable names in a new variable
|
Each row of the output table includes the name of the variable in the input table
to which the values in that output row belong. To specify a heading for the output column that contains these variable names, enter the heading in the Name box. The name can include special characters, leading numbers, and white space, but it cannot exceed 32 characters. The default
name is _Name_.
|
|
Put original
variable labels in a new variable
|
Each row of the output table includes the label of the variable in the input table
to which the values in that output row belong. To specify a heading for the output
column that contains these variable labels, enter the heading in the Label box. The label can include special characters, leading numbers, and white space,
but it cannot exceed 32 characters. The default
label is _Label_.
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.