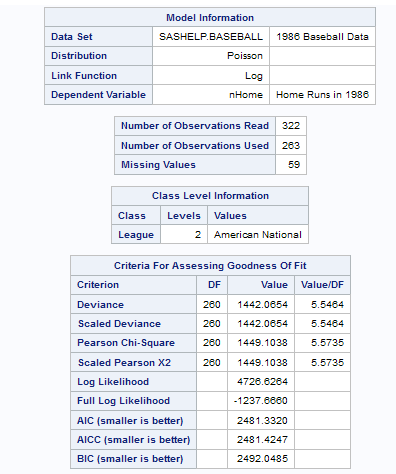
Generalized Linear Models
About the Generalized Linear Models Task
Generalized linear models
are an extension of traditional linear models. In a generalized linear
model, the mean of a population depends on a linear predictor through
a nonlinear link function. The response probability distribution can
be any member of the exponential family of distributions. Examples
of generalized linear models include classical linear models with
normal errors, logistic and probit models for binary data, and log-linear
models for multinomial data. Other statistical models can be formulated
as generalized linear models by the selection of an appropriate link
function and response probability distribution.
The Generalized Linear
Models task provides model fitting and model building for generalized
linear models. It fits models for standard distributions such as Normal,
Poisson, and Tweedie in the exponential family. This task also fits
multinomial models for ordinal and nominal responses. The task provides
forward, backward, and stepwise selection methods.
Assigning Data to Roles
To run the Generalized
Linear Models task, you must assign a column to the Response
variable role for all distribution types except binomial.
If you select a binomial distribution, you must assign either a single
response variable or a pair of variables to the Number
of events and Number of trials roles.
|
Option Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Roles
|
|
|
Response
|
|
|
Distribution
|
specifies the distribution
for your model. You can choose from these distributions:
|
|
Options for Binomial
Distribution
|
|
|
Response
data consists of numbers of events and trials
|
specifies that a pair
of variables consists of response data for events and trials.
|
|
Number of
events
|
specifies the column
that contains the number of events.
|
|
Number of
trials
|
specifies the column
that contains the number of trials.
|
|
Response
|
specifies the single
variable that contains response values.
Use the Event
of interest option to select a value of the response
variable that represents the event that you want to model.
Note: The Response role
and the Event of interest option are available
only if you do not select the Response data consists of
numbers of events and trials check box.
|
|
Options for All Distribution
Types
|
|
|
Response
|
specifies the variable
that contains the response data. For most distribution types, you
specify a single numeric variable.
|
|
Link function
|
specifies the link function
for your model. The functions that are available depend on the selected
distribution.
|
|
Explanatory Variables
|
|
|
Classification
variables
|
specifies the variables
to use to group (classify) data in the analysis. Classification variables
can be either character or numeric. A classification variable is
a variable that enters the statistical analysis or model through its
levels, not through its values. The process of associating values
of a variable with levels is termed levelization.
|
|
Parameterization of
Effects
|
|
|
Coding
|
specifies the parameterization
method for the classification variable. Design matrix columns are
created from the classification variables according to the selected
coding scheme.
You can select from
these coding schemes:
|
|
Treatment of Missing
Values
|
|
|
An observation is excluded
from the analysis when either of these conditions is met:
|
|
|
Continuous
variables
|
specifies the independent
covariates (regressors) for the regression model. If you do not specify
a continuous variable, the task fits a model that contains only an
intercept.
|
|
Offset variable
|
specifies a variable
to be used as an offset to the linear predictor. An offset plays the
role of an effect whose coefficient is known to be 1. Observations
that have missing values for the offset variable are excluded from
the analysis.
|
|
Additional Roles
|
|
|
Frequency
count
|
specifies the numeric
column that contains the frequency of occurrence for each observation.
|
|
Weight variable
|
specifies the numeric
column to use as a weight to perform a weighted analysis of the data.
|
|
Group analysis
by
|
specifies the column
to use as the BY variable.
|
Building a Model
Requirements for Building a Model
By default, no effects
are specified, which results in the task fitting an intercept-only
model. To specify an effect, you must assign at least one variable
to the Classification variables role or the Continuous
variables role. You can select combinations of variables
to create crossed, nested, factorial, or polynomial effects.
To create a model, use
the model builder on the Models tab. After
you create the model, you can specify whether to include the intercept
in the model.
Create a Nested Effect
Nested effects are specified
by following a main effect or crossed effect with a classification
variable or list of classification variables enclosed in parentheses.
The main effect or crossed effect is nested within the effects listed
in parentheses. Here are examples of nested effects: B(A), C(B*A),
D*E(C*B*A). In this example, B(A) is read "A nested within B."
Create N-Way Factorial
For example, if you
select the Height, Weight, and Age variables and then specify the
value of N as 2, when you click N-way Factorial,
these model effects are created: Age, Height, Weight, Age*Height,
Age*Weight, and Height*Weight. If N is set to a value greater than
the number of variables in the model, N is effectively set to the
number of variables.
Create Polynomial Effects of the Nth Order
Specifying Model Effects for Zero-Inflated Models
These options are available
if you selected Zero-inflated negative binomial or Zero-inflated
Poisson as the distribution on the Data tab.
You must choose the
type of model that you want to create:
If you choose to include effects in the zero-inflated
models, specify the link function for those effects.
-
an intercept-only model.
-
a model that includes effects from the main model. You define these model effects by using the model builder.
-
a custom model. You specify these effects in the Enter a custom model text box. If you specify multiple effects, use a space between each effect.
Setting Options
|
Option
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Methods
|
|
|
Dispersion
|
|
|
Adjust for
overdispersion
|
adjusts the parameter
covariance matrix and the likelihood function by a scale parameter.
For the dispersion parameter, you can select a Pearson estimate or
a deviance estimate. To define the subpopulations for calculating
the Pearson and deviance chi-square goodness-of-fit tests, assign
one or more variables to the role.
Note: This option is available
only for binomial and multinomial distributions.
|
|
Estimate
dispersion parameter
|
enables you to specify
a fixed dispersion parameter for those distributions that have a dispersion
parameter. By default, this parameter is estimated.
Note: This option is not available
for binomial and multinomial distributions, but it is available for
the other distribution types.
|
|
Optimization
|
|
|
Maximum
number of iterations
|
specifies the maximum
number of iterations to perform for the selected optimization technique.
|
|
Statistics
|
|
|
You can select the statistics
to include in the output.
Here are the additional
statistics that you can include:
|
|
|
Plots
|
|
|
Here are some plots
that you can include in your results:
|
|
Copyright © SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.