The MDS Procedure
The following notation is used:
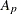
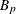
-
slope for partition p
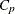
-
power for partition p
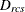
-
distance computed from the model between objects r and c for subject s
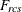
-
data weight for objects r and c for subject s obtained from the cth WEIGHT variable, or 1 if there is no WEIGHT statement
- f
-
value of the FIT= option
- N
-
number of objects
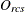
-
observed dissimilarity between objects r and c for subject s
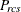
-
partition index for objects r and c for subject s
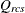
-
dissimilarity after applying any applicable estimated transformation for objects r and c for subject s
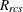
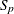
-
standardization factor for partition p
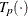
-
estimated transformation for partition p
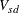
-
coefficient for subject s on dimension d
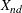
-
coordinate for object n on dimension d
Summations are taken over nonmissing values.
Distances are computed from the model as
![\[ \begin{tabular}{p{.25in}p{.1in}p{1.5in}p{3in}} $D_{rcs}$ & = & $\sqrt {\displaystyle {\sum _ d(X_{rd}-X_{cd})^2}}$ & {\mbox{for COEF=IDENTITY:} \linebreak Euclidean distance} \\ & = & $\sqrt {\displaystyle {\sum _ d V_{sd}^2(X_{rd}-X_{cd})^2}}$ & {\mbox{for COEF=DIAGONAL:} \linebreak weighted Euclidean distance} \\ \end{tabular} \]](images/statug_mds0025.png)
![\[ \begin{tabular}{p{.3in}p{.1in}p{1.1in}p{1.8in}} $P_{rcs}$ & = & 1 & \mbox{for CONDITION=UN} \\ & = & \Mathtext{s} & \mbox{for CONDITION=MATRIX} \\ & = & $(s-1)N+r$ & \mbox{for CONDITION=ROW} \end{tabular} \]](images/statug_mds0026.png)
The estimated transformation for each partition is
![\[ \begin{tabular}{p{.3in}p{.1in}p{1.1in}p{1.8in}} $T_ p(d)$ & = & \Mathtext{d} & \mbox{for LEVEL=ABSOLUTE} \\ & = & $B_ pd$ & \mbox{for LEVEL=RATIO} \\ & = & $A_ p+B_ pd$ & \mbox{for LEVEL=INTERVAL} \\ & = & $B_ pd^{C_ p}$ & \mbox{for LEVEL=LOGINTERVAL} \end{tabular} \]](images/statug_mds0027.png)
For LEVEL=ORDINAL, ![]() is computed as a least-squares monotone transformation.
is computed as a least-squares monotone transformation.
For LEVEL=ABSOLUTE, RATIO, or INTERVAL, the residuals are computed as
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
For LEVEL=ORDINAL, the residuals are computed as
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If f is 0, then natural logarithms are used in place of the fth powers.
For each partition, let
![\[ U_ p = \frac{\displaystyle {\sum _{r,c,s}F_{rcs}}}{\displaystyle {\sum _{r,c,s | P_{rcs}=p}F_{rcs}}} \]](images/statug_mds0037.png)
and
![\[ \overline{Q}_ p = \frac{\displaystyle {\sum _{r,c,s | P_{rcs}=p}Q_{rcs}F_{rcs}}}{\displaystyle {\sum _{r,c,s | P_{rcs}=p}F_{rcs}}} \]](images/statug_mds0038.png)
Then the standardization factor for each partition is
![\[ \begin{array}{llll} S_ p & =& 1 & \mbox{for FORMULA=0} \\ & =& U_ p \displaystyle {\sum _{r,c,s | P_{rcs}=p} Q_{rcs}^2F_{rcs} } & \mbox{for FORMULA=1} \\ & =& U_ p \displaystyle {\sum _{r,c,s | P_{rcs}=p} (Q_{rcs}-\overline{Q}_ p)^2F_{rcs} } & \mbox{for FORMULA=2} \end{array} \]](images/statug_mds0039.png)
The badness-of-fit criterion that the MDS procedure tries to minimize is
