The SIM2D Procedure
Computational Details
In the computation of 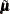 and
and  described in the previous section, the inverse
described in the previous section, the inverse 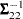 is never actually computed; an equation of the form
is never actually computed; an equation of the form
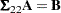 |
is solved for 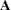 by using a modified Gaussian elimination algorithm that takes advantage of the fact that
by using a modified Gaussian elimination algorithm that takes advantage of the fact that 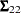 is symmetric with constant diagonal
is symmetric with constant diagonal 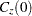 that is larger than all off-diagonal elements. The SINGULAR= option pertains to this algorithm. The value specified for the SINGULAR= option is scaled by
that is larger than all off-diagonal elements. The SINGULAR= option pertains to this algorithm. The value specified for the SINGULAR= option is scaled by 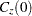 before comparison with the pivot element.
before comparison with the pivot element.
Memory Usage
For conditional simulations, the largest matrix held in core memory at any one time depends on the number of grid points and data points. Using the previous notation, the data-data covariance matrix  is
is  , where
, where  is the number of nonmissing observations for the VAR= variable in the DATA= data set. The grid-data cross covariance
is the number of nonmissing observations for the VAR= variable in the DATA= data set. The grid-data cross covariance  is
is 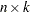 , where
, where 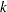 is the number of grid points. The grid-grid covariance
is the number of grid points. The grid-grid covariance 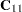 is
is 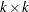 . The maximum memory required at any one time for storing these matrices is
. The maximum memory required at any one time for storing these matrices is
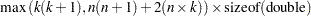 |
There are additional memory requirements that add to the total memory usage, but usually these matrix calculations dominate, especially when the number of grid points is large.
