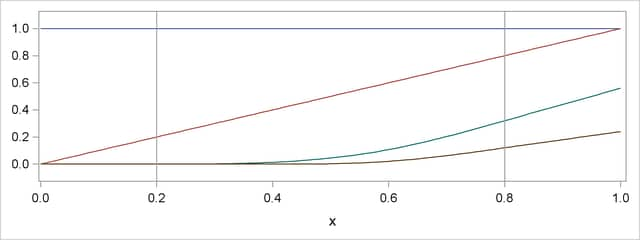
Natural Cubic Spline Basis
Natural cubic splines are cubic splines with the additional restriction that the splines are required to be linear beyond the extreme knots. Some authors use the terminology "restricted cubic splines" in preference to the terminology "natural cubic splines." The space of unrestricted cubic splines on  knots has dimension
knots has dimension 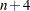 . Imposing the restrictions that the cubic polynomials beyond the first and last knot reduce to linear polynomials reduces the number of degrees of freedom by 4, and so a basis for the natural cubic splines consists of
. Imposing the restrictions that the cubic polynomials beyond the first and last knot reduce to linear polynomials reduces the number of degrees of freedom by 4, and so a basis for the natural cubic splines consists of  functions. Starting from the truncated power function basis for the unrestricted cubic splines, you can obtain a reduced basis by imposing linearity constraints. You can find details about this construction in Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman (2001). Figure 19.5 shows this natural cubic spline basis defined on
functions. Starting from the truncated power function basis for the unrestricted cubic splines, you can obtain a reduced basis by imposing linearity constraints. You can find details about this construction in Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman (2001). Figure 19.5 shows this natural cubic spline basis defined on 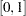 with four equally spaced internal knots at 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8. Note that this basis consists of four basis functions that are all linear beyond the extreme knots at 0.2 and 0.8.
with four equally spaced internal knots at 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, and 0.8. Note that this basis consists of four basis functions that are all linear beyond the extreme knots at 0.2 and 0.8.