| The POWER Procedure |
| PAIREDMEANS Statement |
The PAIREDMEANS statement performs power and sample size analyses for  tests, equivalence tests, and confidence interval precision involving paired samples.
tests, equivalence tests, and confidence interval precision involving paired samples.
Summary of Options
Table 68.16 summarizes categories of options available in the PAIREDMEANS statement.
Task |
Options |
|---|---|
Define analysis |
|
Specify analysis information |
|
Specify effects |
|
Specify variability |
|
Specify sample size |
|
Specify power and related |
|
probabilities |
|
Control sample size rounding |
|
Control ordering in output |
Table 68.17 summarizes the valid result parameters for different analyses in the PAIREDMEANS statement.
Analyses |
Solve For |
Syntax |
|---|---|---|
TEST=DIFF |
Power |
|
Sample size |
||
TEST=RATIO |
Power |
|
Sample size |
||
TEST=EQUIV_DIFF |
Power |
|
Sample size |
||
TEST=EQUIV_RATIO |
Power |
|
Sample size |
||
CI=DIFF |
Prob(width) |
|
Sample size |
Dictionary of Options
- ALPHA=number-list
specifies the level of significance of the statistical test. The default is 0.05, corresponding to the usual 0.05
 100% = 5% level of significance. If the CI= and SIDES=1 options are used, then the value must be less than 0.5. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
100% = 5% level of significance. If the CI= and SIDES=1 options are used, then the value must be less than 0.5. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list. - CI
- CI=DIFF
specifies an analysis of precision of the confidence interval for the mean difference. Instead of power, the relevant probability for this analysis is the probability of achieving a desired precision. Specifically, it is the probability that the half-width of the observed confidence interval will be at most the value specified by the HALFWIDTH= option. If neither the CI= option nor the TEST= option is used, the default is TEST=DIFF.
- CORR=number-list
specifies the correlation between members of a pair. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- CV=number-list
specifies the coefficient of variation assumed to be common to both members of a pair. The coefficient of variation is defined as the ratio of the standard deviation to the mean. You can use this option only with DIST=LOGNORMAL. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- DIST=LOGNORMAL
- DIST=NORMAL
specifies the underlying distribution assumed for the test statistic. NORMAL corresponds the normal distribution, and LOGNORMAL corresponds to the lognormal distribution. The default value (also the only acceptable value in each case) is NORMAL for TEST=DIFF, TEST=EQUIV_DIFF, and CI=DIFF; and LOGNORMAL for TEST=RATIO and TEST=EQUIV_RATIO.
- HALFWIDTH=number-list
specifies the desired confidence interval half-width. The half-width is defined as the distance between the point estimate and a finite endpoint. This option can be used only with the CI=DIFF analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- LOWER=number-list
specifies the lower equivalence bound for the mean difference or mean ratio, in the original scale (whether DIST=NORMAL or DIST=LOGNORMAL). This option can be used only with the TEST=EQUIV_DIFF and TEST=EQUIV_RATIO analyses. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- MEANDIFF=number-list
specifies the mean difference, defined as the mean of the difference between the second and first members of a pair,
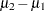 . This option can be used only with the TEST=DIFF and TEST=EQUIV_DIFF analyses. When TEST=EQUIV_DIFF, the mean difference is interpreted as the treatment mean minus the reference mean. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
. This option can be used only with the TEST=DIFF and TEST=EQUIV_DIFF analyses. When TEST=EQUIV_DIFF, the mean difference is interpreted as the treatment mean minus the reference mean. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list. - MEANRATIO=number-list
specifies the geometric mean ratio, defined as
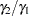 . This option can be used only with the TEST=RATIO and TEST=EQUIV_RATIO analyses. When TEST=EQUIV_RATIO, the mean ratio is interpreted as the treatment mean divided by the reference mean. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
. This option can be used only with the TEST=RATIO and TEST=EQUIV_RATIO analyses. When TEST=EQUIV_RATIO, the mean ratio is interpreted as the treatment mean divided by the reference mean. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list. - NFRACTIONAL
- NFRAC
enables fractional input and output for sample sizes. See the section Sample Size Adjustment Options for information about the ramifications of the presence (and absence) of the NFRACTIONAL option.
- NPAIRS=number-list
specifies the number of pairs or requests a solution for the number of pairs with a missing value (NPAIRS=.). See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- NULLDIFF=number-list
- NULLD=number-list
specifies the null mean difference. The default value is 0. This option can be used only with the TEST=DIFF analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- NULLRATIO=number-list
- NULLR=number-list
specifies the null mean ratio. The default value is 1. This option can be used only with the TEST=RATIO analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- OUTPUTORDER=INTERNAL
- OUTPUTORDER=REVERSE
- OUTPUTORDER=SYNTAX
controls how the input and default analysis parameters are ordered in the output. OUTPUTORDER=INTERNAL (the default) arranges the parameters in the output according to the following order of their corresponding options:
The OUTPUTORDER=SYNTAX option arranges the parameters in the output in the same order in which their corresponding options are specified in the PAIREDMEANS statement. The OUTPUTORDER=REVERSE option arranges the parameters in the output in the reverse of the order in which their corresponding options are specified in the PAIREDMEANS statement.
- PAIREDCVS=grouped-number-list
specifies the coefficient of variation for each member of a pair. Unlike the CV= option, the PAIREDCVS= option supports different values for each member of a pair. Values must be nonnegative (unless both are equal to zero, which is permitted). This option can be used only with DIST=LOGNORMAL. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the grouped-number-list.
- PAIREDMEANS=grouped-number-list
- PMEANS=grouped-number-list
specifies the two paired means, in the original scale. The means are arithmetic if DIST=NORMAL and geometric if DIST=LOGNORMAL. This option cannot be used with the CI=DIFF analysis. When TEST=EQUIV_DIFF, the means are interpreted as the reference mean (first) and the treatment mean (second). See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the grouped-number-list.
- PAIREDSTDDEVS=grouped-number-list
- PAIREDSTDS=grouped-number-list
- PSTDDEVS=grouped-number-list
- PSTDS=grouped-number-list
specifies the standard deviation of each member of a pair. Unlike the STDDEV= option, the PAIREDSTDDEVS= option supports different values for each member of a pair. This option can be used only with DIST=NORMAL. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the grouped-number-list.
- POWER=number-list
specifies the desired power of the test or requests a solution for the power with a missing value (POWER=.). The power is expressed as a probability, a number between 0 and 1, rather than as a percentage. This option cannot be used with the CI=DIFF analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- PROBTYPE=keyword-list
specifies the type of probability for the PROBWIDTH= option. A value of CONDITIONAL (the default) indicates the conditional probability that the confidence interval half-width is at most the value specified by the HALFWIDTH= option, given that the true mean difference is captured by the confidence interval. A value of UNCONDITIONAL indicates the unconditional probability that the confidence interval half-width is at most the value specified by the HALFWIDTH= option. you can use the alias GIVENVALIDITY for CONDITIONAL. The PROBTYPE= option can be used only with the CI=DIFF analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the keyword-list.
- CONDITIONAL
width probability conditional on interval containing the mean
- UNCONDITIONAL
unconditional width probability
- PROBWIDTH=number-list
specifies the desired probability of obtaining a confidence interval half-width less than or equal to the value specified by the HALFWIDTH= option. A missing value (PROBWIDTH=.) requests a solution for this probability. The type of probability is controlled with the PROBTYPE= option. Values are expressed as probabilities (for example, 0.9) rather than percentages. This option can be used only with the CI=DIFF analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- SIDES=keyword-list
specifies the number of sides (or tails) and the direction of the statistical test or confidence interval. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the keyword-list. Valid keywords and their interpretation for the TEST= analyses are as follows:
- 1
one-sided with alternative hypothesis in same direction as effect
- 2
two-sided
- U
upper one-sided with alternative greater than null value
- L
lower one-sided with alternative less than null value
For confidence intervals, SIDES=U refers to an interval between the lower confidence limit and infinity, and SIDES=L refers to an interval between minus infinity and the upper confidence limit. For both of these cases and SIDES=1, the confidence interval computations are equivalent. The SIDES= option cannot be used with the TEST=EQUIV_DIFF and TEST=EQUIV_RATIO analyses. The default value is 2.
- STDDEV=number-list
- STD=number-list
specifies the standard deviation assumed to be common to both members of a pair. This option can be used only with DIST=NORMAL. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- TEST
- TEST=DIFF
- TEST=EQUIV_DIFF
- TEST=EQUIV_RATIO
- TEST=RATIO
specifies the statistical analysis. TEST or TEST=DIFF (the default) specifies a paired
 test on the mean difference. TEST=EQUIV_DIFF specifies an additive equivalence test of the mean difference by using a two one-sided tests (TOST) analysis (Schuirmann 1987). TEST=EQUIV_RATIO specifies a multiplicative equivalence test of the mean ratio by using a TOST analysis. TEST=RATIO specifies a paired
test on the mean difference. TEST=EQUIV_DIFF specifies an additive equivalence test of the mean difference by using a two one-sided tests (TOST) analysis (Schuirmann 1987). TEST=EQUIV_RATIO specifies a multiplicative equivalence test of the mean ratio by using a TOST analysis. TEST=RATIO specifies a paired  test on the geometric mean ratio. If neither the TEST= option nor the CI= option is used, the default is TEST=DIFF.
test on the geometric mean ratio. If neither the TEST= option nor the CI= option is used, the default is TEST=DIFF. specifies the upper equivalence bound for the mean difference or mean ratio, in the original scale (whether DIST=NORMAL or DIST=LOGNORMAL). This option can be used only with the TEST=EQUIV_DIFF and TEST=EQUIV_RATIO analyses. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
Restrictions on Option Combinations
To define the analysis, choose one of the following parameterizations:
a statistical test (by using the TEST= option)
confidence interval precision (by using the CI= option)
To specify the means, choose one of the following parameterizations:
individual means (by using the PAIREDMEANS= option)
mean difference (by using the MEANDIFF= option)
mean ratio (by using the MEANRATIO= option)
To specify the coefficient of variation, choose one of the following parameterizations:
common coefficient of variation (by using the CV= option)
individual coefficients of variation (by using the PAIREDCVS= option)
To specify the standard deviation, choose one of the following parameterizations:
common standard deviation (by using the STDDEV= option)
individual standard deviations (by using the PAIREDSTDDEVS= option)
Option Groups for Common Analyses
This section summarizes the syntax for the common analyses supported in the PAIREDMEANS statement.
Paired t Test
You can express effects in terms of the mean difference and variability in terms of a correlation and common standard deviation, as in the following statements. Default values for the DIST=, SIDES=, NULLDIFF=, and ALPHA= options specify a two-sided test for no difference with a normal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=diff
meandiff = 7
corr = 0.4
stddev = 12
npairs = 50
power = .;
run;
You can also express effects in terms of individual means and variability in terms of correlation and individual standard deviations:
proc power;
pairedmeans test=diff
pairedmeans = 8 | 15
corr = 0.4
pairedstddevs = (7 12)
npairs = .
power = 0.9;
run;
Paired t Test of Mean Ratio with Lognormal Data
You can express variability in terms of correlation and a common coefficient of variation, as in the following statements. Defaults for the DIST=, SIDES=, NULLRATIO= and ALPHA= options specify a two-sided test of mean ratio = 1 assuming a lognormal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=ratio
meanratio = 7
corr = 0.3
cv = 1.2
npairs = 30
power = .;
run;
You can also express variability in terms of correlation and individual coefficients of variation:
proc power;
pairedmeans test=ratio
meanratio = 7
corr = 0.3
pairedcvs = 0.8 | 0.9
npairs = 30
power = .;
run;
Additive Equivalence Test for Mean Difference with Normal Data
The following statements demonstrate a sample size computation for a TOST equivalence test for a normal mean difference. Default values for the DIST= and ALPHA= options specify a normal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=equiv_diff
lower = 2
upper = 5
meandiff = 4
corr = 0.2
stddev = 8
npairs = .
power = 0.9;
run;
Multiplicative Equivalence Test for Mean Ratio with Lognormal Data
The following statements demonstrate a power computation for a TOST equivalence test for a lognormal mean ratio. Default values for the DIST= and ALPHA= options specify a lognormal distribution and a significance level of 0.05.
proc power;
pairedmeans test=equiv_ratio
lower = 3
upper = 7
meanratio = 5
corr = 0.2
cv = 1.1
npairs = 50
power = .;
run;
Confidence Interval for Mean Difference
By default CI=DIFF analyzes the conditional probability of obtaining the desired precision, given that the interval contains the true mean difference, as in the following statements. The defaults of SIDES=2 and ALPHA=0.05 specify a two-sided interval with a confidence level of 0.95.
proc power;
pairedmeans ci = diff
halfwidth = 4
corr = 0.35
stddev = 8
npairs = 30
probwidth = .;
run;
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.