| The POWER Procedure |
| ONESAMPLEFREQ Statement |
The ONESAMPLEFREQ statement performs power and sample size analyses for exact and approximate tests (including equivalence, noninferiority, and superiority) and confidence interval precision for a single binomial proportion.
Summary of Options
Table 68.8 summarizes categories of options available in the ONESAMPLEFREQ statement.
Task |
Options |
|---|---|
Define analysis |
|
Specify analysis information |
|
Specify effect |
|
Specify variance estimation |
|
Specify sample size |
|
Specify power and related |
|
probabilities |
|
Control sample size rounding |
|
Choose computational method |
|
Control ordering in output |
Table 68.9 summarizes the valid result parameters for different analyses in the ONESAMPLEFREQ statement.
Analyses |
Solve For |
Syntax |
|---|---|---|
CI=WILSON |
Prob(width) |
|
CI=AGRESTICOULL |
Prob(width) |
|
CI=JEFFREYS |
Prob(width) |
|
CI=EXACT |
Prob(width) |
|
CI=WALD |
Prob(width) |
|
CI=WALD_CORRECT |
Prob(width) |
|
Power |
||
Power |
||
Sample size |
||
Power |
||
Power |
||
Sample size |
||
TEST=EQUIV_EXACT |
Power |
|
Power |
||
Power |
||
Sample size |
||
TEST=EXACT |
Power |
|
Power |
||
Power |
||
Sample size |
Dictionary of Options
- ALPHA=number-list
specifies the level of significance of the statistical test. The default is 0.05, corresponding to the usual 0.05
 100% = 5% level of significance. If the CI= and SIDES=1 options are used, then the value must be less than 0.5. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
100% = 5% level of significance. If the CI= and SIDES=1 options are used, then the value must be less than 0.5. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list. - CI
- CI=AGRESTICOULL | AC
- CI=JEFFREYS
- CI=EXACT | CLOPPERPEARSON | CP
- CI=WALD
- CI=WALD_CORRECT
- CI=WILSON | SCORE
specifies an analysis of precision of a confidence interval for the sample binomial proportion.
The value of the CI= option specifies the type of confidence interval. The CI=AGRESTICOULL option is a generalization of the "Adjusted Wald / add 2 successes and 2 failures" interval of Agresti and Coull (1998) and is presented in Brown, Cai, and DasGupta (2001). It corresponds to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (AGRESTICOULL) option in PROC FREQ. The CI=JEFFREYS option specifies the equal-tailed Jeffreys prior Bayesian interval, corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (JEFFREYS) option in PROC FREQ. The CI=EXACT option specifies the exact Clopper-Pearson confidence interval based on enumeration, corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (EXACT) option in PROC FREQ. The CI=WALD option specifies the confidence interval based on the Wald test (also commonly called the
 test or normal-approximation test), corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (WALD) option in PROC FREQ. The CI=WALD_CORRECT option specifies the confidence interval based on the Wald test with continuity correction, corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (CORRECT WALD) option in PROC FREQ. The CI=WILSON option (the default) specifies the confidence interval based on the score statistic, corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (WILSON) option in PROC FREQ.
test or normal-approximation test), corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (WALD) option in PROC FREQ. The CI=WALD_CORRECT option specifies the confidence interval based on the Wald test with continuity correction, corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (CORRECT WALD) option in PROC FREQ. The CI=WILSON option (the default) specifies the confidence interval based on the score statistic, corresponding to the TABLES / BINOMIAL (WILSON) option in PROC FREQ. Instead of power, the relevant probability for this analysis is the probability of achieving a desired precision. Specifically, it is the probability that the half-width of the confidence interval will be at most the value specified by the HALFWIDTH= option.
- EQUIVBOUNDS=grouped-number-list
specifies the lower and upper equivalence bounds, representing the same information as the combination of the LOWER= and UPPER= options but grouping them together. The EQUIVBOUNDS= option can be used only with equivalence analyses (TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ | EQUIV_EXACT | EQUIV_Z). Values must be strictly between 0 and 1. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the grouped-number-list.
- HALFWIDTH=number-list
specifies the desired confidence interval half-width. The half-width for a two-sided interval is the length of the confidence interval divided by two. This option can be used only with the CI= analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- LOWER=number-list
specifies the lower equivalence bound for the binomial proportion. The LOWER= option can be used only with equivalence analyses (TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ | EQUIV_EXACT | EQUIV_Z). Values must be strictly between 0 and 1. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- MARGIN=number-list
specifies the equivalence or noninferiority or superiority margin, depending on the analysis.
The MARGIN= option can be used with one-sided analyses (SIDES = 1 | U | L), in which case it specifies the margin added to the null proportion value in the hypothesis test, resulting in a noninferiority or superiority test (depending on the agreement between the effect and hypothesis directions and the sign of the margin). A test with a null proportion
 and a margin
and a margin  is the same as a test with null proportion
is the same as a test with null proportion 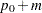 and no margin.
and no margin. The MARGIN= option can also be used with equivalence analyses (TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ | EQUIV_EXACT | EQUIV_Z) when the NULLPROPORTION= option is used, in which case it specifies the lower and upper equivalence bounds as
 and
and 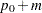 , where
, where  is the value of the NULLPROPORTION= option and
is the value of the NULLPROPORTION= option and  is the value of the MARGIN= option.
is the value of the MARGIN= option. The MARGIN= option cannot be used in conjunction with the SIDES=2 option. (Instead, specify an equivalence analysis by using TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ or TEST=EQUIV_EXACT or TEST=EQUIV_Z). Also, the MARGIN= option cannot be used with the CI= option.
Values must be strictly between –1 and 1. In addition, the sum of NULLPROPORTION and MARGIN must be strictly between 0 and 1 for one-sided analyses, and the derived lower equivalence bound (2 * NULLPROPORTION – MARGIN) must be strictly between 0 and 1 for equivalence analyses.
See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- METHOD=EXACT
- METHOD=NORMAL
specifies the computational method. METHOD=EXACT (the default) computes exact results by using the binomial distribution. METHOD=NORMAL computes approximate results by using the normal approximation to the binomial distribution.
- NFRACTIONAL
- NFRAC
enables fractional input and output for sample sizes. This option is invalid when the METHOD=EXACT option is specified. See the section Sample Size Adjustment Options for information about the ramifications of the presence (and absence) of the NFRACTIONAL option.
- NTOTAL=number-list
specifies the sample size or requests a solution for the sample size with a missing value (NTOTAL=.). See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- NULLPROPORTION=number-list
- NULLP=number-list
specifies the null proportion. A value of 0.5 corresponds to the sign test. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- OUTPUTORDER=INTERNAL
- OUTPUTORDER=REVERSE
- OUTPUTORDER=SYNTAX
controls how the input and default analysis parameters are ordered in the output. OUTPUTORDER=INTERNAL (the default) arranges the parameters in the output according to the following order of their corresponding options:
The OUTPUTORDER=SYNTAX option arranges the parameters in the output in the same order in which their corresponding options are specified in the ONESAMPLEFREQ statement. The OUTPUTORDER=REVERSE option arranges the parameters in the output in the reverse of the order in which their corresponding options are specified in the ONESAMPLEFREQ statement.
- POWER=number-list
specifies the desired power of the test or requests a solution for the power with a missing value (POWER=.). The power is expressed as a probability, a number between 0 and 1, rather than as a percentage. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- PROBWIDTH=number-list
specifies the desired probability of obtaining a confidence interval half-width less than or equal to the value specified by the HALFWIDTH= option. A missing value (PROBWIDTH=.) requests a solution for this probability. Values are expressed as probabilities (for example, 0.9) rather than percentages. This option can be used only with the CI= analysis. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- PROPORTION=number-list
- P=number-list
specifies the binomial proportion—that is, the expected proportion of successes in the hypothetical binomial trial. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- SIDES=keyword-list
specifies the number of sides (or tails) and the direction of the statistical test. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the keyword-list. Valid keywords are as follows:
- 1
one-sided with alternative hypothesis in same direction as effect
- 2
two-sided
- U
upper one-sided with alternative greater than null value
- L
lower one-sided with alternative less than null value
If the effect size is zero, then SIDES=1 is not permitted; instead, specify the direction of the test explicitly in this case with either SIDES=L or SIDES=U. The default value is 2.
- TEST
- TEST= ADJZ
- TEST= EQUIV_ADJZ
- TEST= EQUIV_EXACT
- TEST= EQUIV_Z
- TEST= EXACT
- TEST= Z
specifies the statistical analysis. TEST=ADJZ specifies a normal-approximate z test with continuity adjustment. TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ specifies a normal-approximate two-sided equivalence test based on the
 statistic with continuity adjustment and a TOST (two one-sided tests) procedure. TEST=EQUIV_EXACT specifies the exact binomial two-sided equivalence test based on a TOST (two one-sided tests) procedure. TEST=EQUIV_Z specifies a normal-approximate two-sided equivalence test based on the
statistic with continuity adjustment and a TOST (two one-sided tests) procedure. TEST=EQUIV_EXACT specifies the exact binomial two-sided equivalence test based on a TOST (two one-sided tests) procedure. TEST=EQUIV_Z specifies a normal-approximate two-sided equivalence test based on the  statistic without any continuity adjustment, which is the same as the chi-square statistic, and a TOST (two one-sided tests) procedure. TEST or TEST=EXACT (the default) specifies the exact binomial test. TEST=Z specifies a normal-approximate z test without any continuity adjustment, which is the same as the chi-square test when SIDES=2.
statistic without any continuity adjustment, which is the same as the chi-square statistic, and a TOST (two one-sided tests) procedure. TEST or TEST=EXACT (the default) specifies the exact binomial test. TEST=Z specifies a normal-approximate z test without any continuity adjustment, which is the same as the chi-square test when SIDES=2. - UPPER=number-list
specifies the upper equivalence bound for the binomial proportion. The UPPER= option can be used only with equivalence analyses (TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ | EQUIV_EXACT | EQUIV_Z). Values must be strictly between 0 and 1. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the number-list.
- VAREST=keyword-list
specifies how the variance is computed in the test statistic for the TEST=Z, TEST=ADJZ, TEST=EQUIV_Z, and TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ analyses. See the section Specifying Value Lists in Analysis Statements for information about specifying the keyword-list. Valid keywords are as follows:
- NULL
(the default) estimates the variance by using the null proportion(s) (specified by some combination of the NULLPROPORTION=, MARGIN=, LOWER=, and UPPER= options). For TEST=Z and TEST=ADJZ, the null proportion is the value of the NULLPROPORTION= option plus the value of the MARGIN= option (if it is used). For TEST=EQUIV_Z and TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ, there are two null proportions, corresponding to the lower and upper equivalence bounds, one for each test in the TOST (two one-sided tests) procedure.
- SAMPLE
estimates the variance by using the observed sample proportion.
This option is ignored if the analysis is one other than TEST=Z, TEST=ADJZ, TEST=EQUIV_Z, or TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ.
Option Groups for Common Analyses
This section summarizes the syntax for the common analyses supported in the ONESAMPLEFREQ statement.
Exact Test of a Binomial Proportion
The following statements demonstrate a power computation for the exact test of a binomial proportion. Defaults for the SIDES= and ALPHA= options specify a two-sided test with a 0.05 significance level.
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=exact
nullproportion = 0.2
proportion = 0.3
ntotal = 100
power = .;
run;
z Test
The following statements demonstrate a sample size computation for the z test of a binomial proportion. Defaults for the SIDES=, ALPHA=, and VAREST= options specify a two-sided test with a 0.05 significance level that uses the null variance estimate.
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=z method=normal
nullproportion = 0.8
proportion = 0.85
sides = u
ntotal = .
power = .9;
run;
z Test with Continuity Adjustment
The following statements demonstrate a sample size computation for the z test of a binomial proportion with a continuity adjustment. Defaults for the SIDES=, ALPHA=, and VAREST= options specify a two-sided test with a 0.05 significance level that uses the null variance estimate.
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=adjz method=normal
nullproportion = 0.15
proportion = 0.1
sides = l
ntotal = .
power = .9;
run;
Exact Equivalence Test for a Binomial Proportion
You can specify equivalence bounds by using the EQUIVBOUNDS= option, as in the following statements:
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=equiv_exact
proportion = 0.35
equivbounds = (0.2 0.4)
ntotal = 50
power = .;
run;
You can also specify the combination of NULLPROPORTION= and MARGIN= options:
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=equiv_exact
proportion = 0.35
nullproportion = 0.3
margin = 0.1
ntotal = 50
power = .;
run;
Finally, you can specify the combination of LOWER= and UPPER= options:
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=equiv_exact
proportion = 0.35
lower = 0.2
upper = 0.4
ntotal = 50
power = .;
run;
Note that the three preceding analyses are identical.
Exact Noninferiority Test for a Binomial Proportion
A noninferiority test corresponds to an upper one-sided test with a negative-valued margin, as demonstrated in the following statements:
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=exact
sides = U
proportion = 0.15
nullproportion = 0.1
margin = -0.02
ntotal = 130
power = .;
run;
Exact Superiority Test for a Binomial Proportion
A superiority test corresponds to an upper one-sided test with a positive-valued margin, as demonstrated in the following statements:
proc power;
onesamplefreq test=exact
sides = U
proportion = 0.15
nullproportion = 0.1
margin = 0.02
ntotal = 130
power = .;
run;
Confidence Interval Precision
The following statements performs a confidence interval precision analysis for the Wilson score-based confidence interval for a binomial proportion. The default value of the ALPHA= option specifies a confidence level of 0.95.
proc power;
onesamplefreq ci=wilson
halfwidth = 0.1
proportion = 0.3
ntotal = 70
probwidth = .;
run;
Restrictions on Option Combinations
To specify the equivalence bounds for TEST=EQUIV_ADJZ, TEST=EQUIV_EXACT, and TEST=EQUIV_Z, use any of these three option sets:
lower and upper equivalence bounds, using the EQUIVBOUNDS= option
lower and upper equivalence bounds, using the LOWER= and UPPER= options
null proportion (NULLPROPORTION=) and margin (MARGIN=)
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.