| The MIXED Procedure |
Syntax: MIXED Procedure
The following statements are available in PROC MIXED.
- PROC MIXED <options> ;
- BY variables ;
- CLASS variables ;
- ID variables ;
- MODEL dependent = <fixed-effects> </ options> ;
- RANDOM random-effects </ options> ;
- REPEATED <repeated-effect></ options> ;
- PARMS (value-list) ...</ options> ;
- PRIOR <distribution >< / options> ;
-
CONTRAST
’label’ <fixed-effect values ...>
<| random-effect values ...>, ...</ options> ; -
ESTIMATE
’label’ <fixed-effect values ...>
<| random-effect values ...></ options> ; - LSMEANS fixed-effects </ options> ;
- LSMESTIMATE model-effect lsmestimate-specification < / options> ;
- SLICE model-effect </ options> ;
- STORE <OUT=>item-store-name </ LABEL='label'> ;
- WEIGHT variable ;
Items within angle brackets ( < > ) are optional. The CONTRAST, ESTIMATE, LSMEANS, and RANDOM statements can appear multiple times; all other statements can appear only once.
The PROC MIXED and MODEL statements are required, and the MODEL statement must appear after the CLASS statement if a CLASS statement is included. The CONTRAST, ESTIMATE, LSMEANS, RANDOM, and REPEATED statements must follow the MODEL statement. The CONTRAST and ESTIMATE statements must also follow any RANDOM statements. The LSMESTIMATE, SLICE, and STORE statements are shared with many procedures. Summary descriptions of functionality and syntax for these statements are also given after the PROC MIXED statement in alphabetical order, but you can find full documentation on them in Chapter 19, Shared Concepts and Topics.
Table 56.1 summarizes the basic functions and important options of each PROC MIXED statement. The syntax of each statement in Table 56.1 is described in the following sections in alphabetical order after the description of the PROC MIXED statement.
Statement |
Description |
Important Options |
|---|---|---|
Invokes the procedure |
DATA= specifies input data set, METHOD= specifies estimation method |
|
Performs multiple PROC MIXED analyses in one invocation |
None |
|
Declares qualitative variables that create indicator variables in design matrices |
None |
|
Lists additional variables to be included in predicted values tables |
None |
|
Specifies dependent variable and fixed effects, setting up |
S requests solution for fixed-effects parameters, DDFM= specifies denominator degrees of freedom method, OUTP= outputs predicted values to a data set, INFLUENCE computes influence diagnostics |
|
Specifies random effects, setting up |
SUBJECT= creates block-diagonality, TYPE= specifies covariance structure, S requests solution for random-effects parameters, G displays estimated |
|
Sets up |
SUBJECT= creates block-diagonality, TYPE= specifies covariance structure, R displays estimated blocks of |
|
Specifies a grid of initial values for the covariance parameters |
HOLD= and NOITER hold the covariance parameters or their ratios constant, PARMSDATA= reads the initial values from a SAS data set |
|
Performs a sampling-based Bayesian analysis for variance component models |
NSAMPLE= specifies the sample size, SEED= specifies the starting seed |
|
Constructs custom hypothesis tests |
E displays the |
|
Constructs custom scalar estimates |
CL produces confidence limits |
|
Computes least squares means for classification fixed effects |
DIFF computes differences of the least squares means, ADJUST= performs multiple comparisons adjustments, AT changes covariates, OM changes weighting, CL produces confidence limits, SLICE= tests simple effects |
|
Provides custom hypothesis tests among the least squares means |
ADJUST= determines the method for multiple comparison adjustment of LS-mean differences, JOINT requests a joint F or chi-square test for the rows of the estimate |
|
Performs a partitioned analysis of LS–means for an interaction |
ADJUST= determines the method for multiple comparison adjustment of LS-mean differences, DIFF requests differences of LS-means |
|
Saves the context and results of the analysis |
LABEL= adds a custom label |
|
Specifies a variable by which to weight |
None |
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
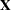
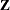 and
and 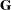
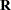
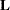 matrix coefficients
matrix coefficients