| The MIANALYZE Procedure |
Getting Started: MIANALYZE Procedure
Consider the following Fitness data set that has been altered to contain an arbitrary pattern of missingness:
*----------------- Data on Physical Fitness -----------------*
| These measurements were made on men involved in a physical |
| fitness course at N.C. State University. |
| Only selected variables of |
| Oxygen (oxygen intake, ml per kg body weight per minute), |
| Runtime (time to run 1.5 miles in minutes), and |
| RunPulse (heart rate while running) are used. |
| Certain values were changed to missing for the analysis. |
*------------------------------------------------------------*;
data FitMiss;
input Oxygen RunTime RunPulse @@;
datalines;
44.609 11.37 178 45.313 10.07 185
54.297 8.65 156 59.571 . .
49.874 9.22 . 44.811 11.63 176
. 11.95 176 . 10.85 .
39.442 13.08 174 60.055 8.63 170
50.541 . . 37.388 14.03 186
44.754 11.12 176 47.273 . .
51.855 10.33 166 49.156 8.95 180
40.836 10.95 168 46.672 10.00 .
46.774 10.25 . 50.388 10.08 168
39.407 12.63 174 46.080 11.17 156
45.441 9.63 164 . 8.92 .
45.118 11.08 . 39.203 12.88 168
45.790 10.47 186 50.545 9.93 148
48.673 9.40 186 47.920 11.50 170
47.467 10.50 170
;
Suppose that the data are multivariate normally distributed and that the missing data are missing at random (see the "Statistical Assumptions for Multiple Imputation" section in the chapter "The MI Procedure" for a description of these assumptions). The following statements use the MI procedure to impute missing values for the FitMiss data set:
proc mi data=FitMiss seed=3237851 noprint out=outmi; var Oxygen RunTime RunPulse; run;
The MI procedure creates imputed data sets, which are stored in the outmi data set. A variable named _Imputation_ indicates the imputation numbers. Based on  imputations,
imputations,  different sets of the point and variance estimates for a parameter can be computed. In this example,
different sets of the point and variance estimates for a parameter can be computed. In this example, 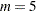 is the default.
is the default.
The following statements generate regression coefficients for each of the five imputed data sets:
proc reg data=outmi outest=outreg covout noprint; model Oxygen= RunTime RunPulse; by _Imputation_; run;
The following statements display (in Figure 55.1) output parameter estimates and covariance matrices from PROC REG for the first two imputed data sets:
proc print data=outreg(obs=8);
var _Imputation_ _Type_ _Name_
Intercept RunTime RunPulse;
title 'Parameter Estimates from Imputed Data Sets';
run;
| Parameter Estimates from Imputed Data Sets |
| Obs | _Imputation_ | _TYPE_ | _NAME_ | Intercept | RunTime | RunPulse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | PARMS | 86.544 | -2.82231 | -0.05873 | |
| 2 | 1 | COV | Intercept | 100.145 | -0.53519 | -0.55077 |
| 3 | 1 | COV | RunTime | -0.535 | 0.10774 | -0.00345 |
| 4 | 1 | COV | RunPulse | -0.551 | -0.00345 | 0.00343 |
| 5 | 2 | PARMS | 83.021 | -3.00023 | -0.02491 | |
| 6 | 2 | COV | Intercept | 79.032 | -0.66765 | -0.41918 |
| 7 | 2 | COV | RunTime | -0.668 | 0.11456 | -0.00313 |
| 8 | 2 | COV | RunPulse | -0.419 | -0.00313 | 0.00264 |
The following statements combine the five sets of regression coefficients:
proc mianalyze data=outreg; modeleffects Intercept RunTime RunPulse; run;
The "Model Information" table in Figure 55.2 lists the input data set(s) and the number of imputations.
The "Variance Information" table in Figure 55.3 displays the between-imputation, within-imputation, and total variances for combining complete-data inferences. It also displays the degrees of freedom for the total variance, the relative increase in variance due to missing values, the fraction of missing information, and the relative efficiency for each parameter estimate.
| Variance Information | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Variance | DF | Relative Increase in Variance |
Fraction Missing Information |
Relative Efficiency |
||
| Between | Within | Total | |||||
| Intercept | 45.529229 | 76.543614 | 131.178689 | 23.059 | 0.713777 | 0.461277 | 0.915537 |
| RunTime | 0.019390 | 0.106220 | 0.129487 | 123.88 | 0.219051 | 0.192620 | 0.962905 |
| RunPulse | 0.001007 | 0.002537 | 0.003746 | 38.419 | 0.476384 | 0.355376 | 0.933641 |
The "Parameter Estimates" table in Figure 55.4 displays a combined estimate and standard error for each regression coefficient (parameter). Inferences are based on t distributions. The table displays a 95% confidence interval and a t test with the associated p-value for the hypothesis that the parameter is equal to the value specified with the THETA0= option (in this case, zero by default). The minimum and maximum parameter estimates from the imputed data sets are also displayed.
| Parameter Estimates | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Estimate | Std Error | 95% Confidence Limits | DF | Minimum | Maximum | Theta0 | t for H0: Parameter=Theta0 |
Pr > |t| | |
| Intercept | 90.837440 | 11.453327 | 67.14779 | 114.5271 | 23.059 | 83.020730 | 100.839807 | 0 | 7.93 | <.0001 |
| RunTime | -3.032870 | 0.359844 | -3.74511 | -2.3206 | 123.88 | -3.204426 | -2.822311 | 0 | -8.43 | <.0001 |
| RunPulse | -0.068578 | 0.061204 | -0.19243 | 0.0553 | 38.419 | -0.112840 | -0.024910 | 0 | -1.12 | 0.2695 |
Copyright © SAS Institute, Inc. All Rights Reserved.