| The REG Procedure |
| Simple Linear Regression |
Suppose that a response variable  can be predicted by a linear function of a regressor variable
can be predicted by a linear function of a regressor variable 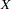 . You can estimate
. You can estimate 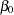 , the intercept, and
, the intercept, and  , the slope, in
, the slope, in
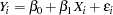 |
for the observations  . Fitting this model with the REG procedure requires only the following MODEL statement, where y is the outcome variable and x is the regressor variable.
. Fitting this model with the REG procedure requires only the following MODEL statement, where y is the outcome variable and x is the regressor variable.
proc reg;
model y=x;
run;
For example, you might use regression analysis to find out how well you can predict a child’s weight if you know that child’s height. The following data are from a study of nineteen children. Height and weight are measured for each child.
title 'Simple Linear Regression';
data Class;
input Name $ Height Weight Age @@;
datalines;
Alfred 69.0 112.5 14 Alice 56.5 84.0 13 Barbara 65.3 98.0 13
Carol 62.8 102.5 14 Henry 63.5 102.5 14 James 57.3 83.0 12
Jane 59.8 84.5 12 Janet 62.5 112.5 15 Jeffrey 62.5 84.0 13
John 59.0 99.5 12 Joyce 51.3 50.5 11 Judy 64.3 90.0 14
Louise 56.3 77.0 12 Mary 66.5 112.0 15 Philip 72.0 150.0 16
Robert 64.8 128.0 12 Ronald 67.0 133.0 15 Thomas 57.5 85.0 11
William 66.5 112.0 15
;
The equation of interest is
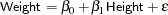 |
The variable Weight is the response or dependent variable in this equation, and 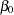 and
and  are the unknown parameters to be estimated. The variable Height is the regressor or independent variable, and
are the unknown parameters to be estimated. The variable Height is the regressor or independent variable, and  is the unknown error. The following commands invoke the REG procedure and fit this model to the data.
is the unknown error. The following commands invoke the REG procedure and fit this model to the data.
ods graphics on;
proc reg;
model Weight = Height;
run;
ods graphics off;
Figure 73.1 includes some information concerning model fit.
The 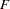 statistic for the overall model is highly significant (
statistic for the overall model is highly significant (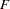 =57.076,
=57.076,  <0.0001), indicating that the model explains a significant portion of the variation in the data.
<0.0001), indicating that the model explains a significant portion of the variation in the data.
The degrees of freedom can be used in checking accuracy of the data and model. The model degrees of freedom are one less than the number of parameters to be estimated. This model estimates two parameters, 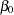 and
and  ; thus, the degrees of freedom should be
; thus, the degrees of freedom should be 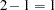 . The corrected total degrees of freedom are always one less than the total number of observations in the data set, in this case
. The corrected total degrees of freedom are always one less than the total number of observations in the data set, in this case 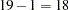 .
.
Several simple statistics follow the ANOVA table. The Root MSE is an estimate of the standard deviation of the error term. The coefficient of variation, or Coeff Var, is a unitless expression of the variation in the data. The R-square and Adj R-square are two statistics used in assessing the fit of the model; values close to 1 indicate a better fit. The R-square of 0.77 indicates that Height accounts for 77% of the variation in Weight.
| Analysis of Variance | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares |
Mean Square |
F Value | Pr > F |
| Model | 1 | 7193.24912 | 7193.24912 | 57.08 | <.0001 |
| Error | 17 | 2142.48772 | 126.02869 | ||
| Corrected Total | 18 | 9335.73684 | |||
| Root MSE | 11.22625 | R-Square | 0.7705 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Mean | 100.02632 | Adj R-Sq | 0.7570 |
| Coeff Var | 11.22330 |
The "Parameter Estimates" table in Figure 73.2 contains the estimates of 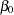 and
and  . The table also contains the
. The table also contains the  statistics and the corresponding
statistics and the corresponding  -values for testing whether each parameter is significantly different from zero. The
-values for testing whether each parameter is significantly different from zero. The  -values (
-values ( ,
,  and
and 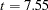 ,
, 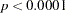 ) indicate that the intercept and Height parameter estimates, respectively, are highly significant.
) indicate that the intercept and Height parameter estimates, respectively, are highly significant.
From the parameter estimates, the fitted model is
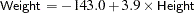 |
If you enable ODS Graphics with an ODS GRAPHICS statement, then PROC REG produces a variety of useful plots. Figure 73.3 shows a plot of the residuals versus the regressor and Figure 73.4 shows a panel of diagnostic plots.
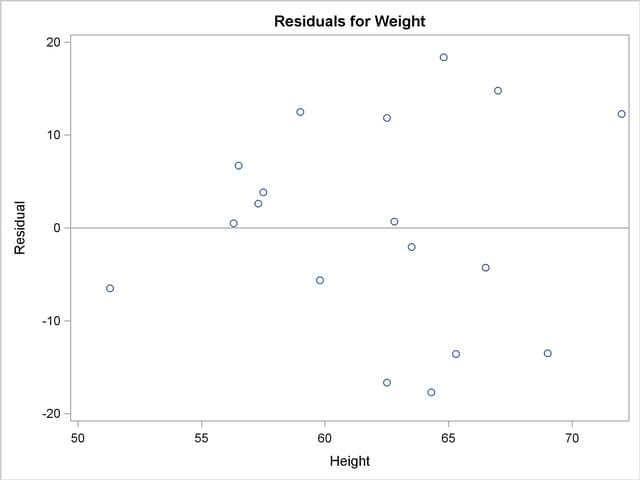
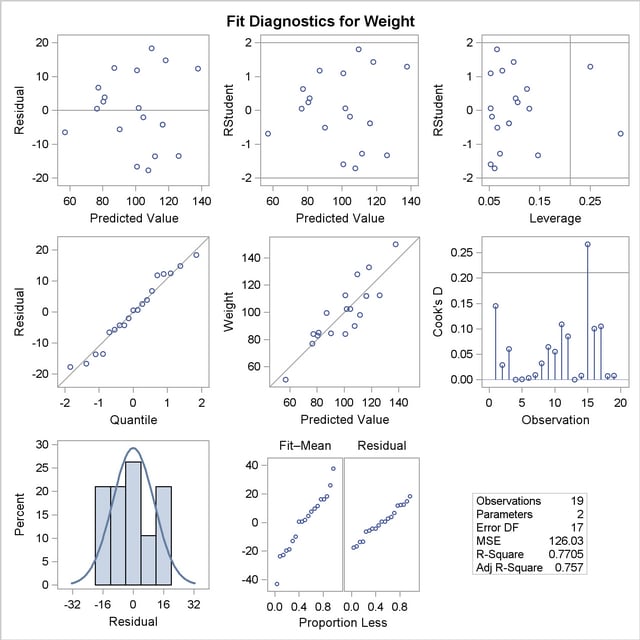
A trend in the residuals would indicate nonconstant variance in the data. The plot of residuals by predicted values in the upper-left corner of the diagnostics panel in Figure 73.4 might indicate a slight trend in the residuals; they appear to increase slightly as the predicted values increase. A fan-shaped trend might indicate the need for a variance-stabilizing transformation. A curved trend (such as a semicircle) might indicate the need for a quadratic term in the model. Since these residuals have no apparent trend, the analysis is considered to be acceptable.
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.