| The GAM Procedure |
| Distribution Family and Canonical Link |
In general, there is not just one reasonable link function for a given response variable distribution. For parametric models, the choice of link function can lead to substantively different estimates and tests. However, the inherent flexibility of nonparametric models makes them less likely to be sensitive to the precise choice of link function. Thus, for simplicity and computational efficiency, the GAM procedure uses only the canonical link for each distribution, as discussed in the following sections.
The Gaussian Model
With this model, the link function is the identity function, and the generalized additive model is the additive model.
The Binomial Model
A binomial response model assumes that the proportion of successes  is such that
is such that  has a
has a 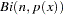 distribution.
distribution. 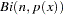 refers to the binomial distribution with the parameters
refers to the binomial distribution with the parameters  and
and 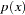 . Often the data are binary, in which case
. Often the data are binary, in which case 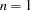 . The canonical link is
. The canonical link is
 |
By default, PROC GAM models the probability of response level with lower ordered value. Ordered values are assigned to response levels in ascending sorted order and are displayed in the “Response Profiles” table. For binary data, if your event category has a higher Ordered Value, then by default the nonevent is modeled. The effect of modeling the nonevent is to change the signs of the estimated coefficients for linear terms in the model for the event. You can change which probability is modeled by specifying the EVENT=, DESCENDING, or ORDER= response variable options in the MODEL statement.
The Poisson Model
The link function for the Poisson model is the log function. Assuming that the mean of the Poisson distribution is 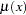 , the dependence of
, the dependence of 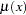 and independent variables
and independent variables 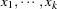 is
is
 |
The Gamma Model
Let the mean of the gamma distribution be 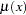 . The canonical link function for the gamma distribution is
. The canonical link function for the gamma distribution is 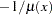 . Therefore, the relationship between
. Therefore, the relationship between 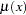 and the independent variables
and the independent variables 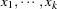 is
is
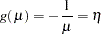 |
The Inverse Gaussian Model
Let the mean of the inverse gaussian distribution be 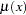 . The canonical link function for inverse gaussian distribution is
. The canonical link function for inverse gaussian distribution is  . Therefore, the relationship between
. Therefore, the relationship between 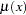 and the independent variables
and the independent variables 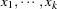 is
is
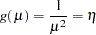 |
Copyright © 2009 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA. All rights reserved.